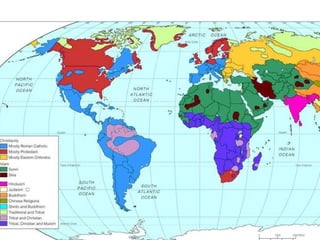
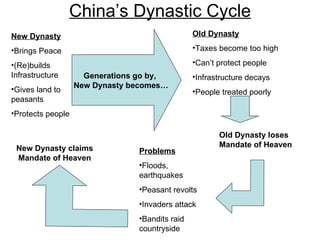
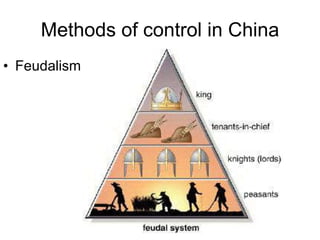
The document provides an overview of key concepts in social studies including:
1) Definitions of various social science fields like history, economics, geography, and their practitioners.
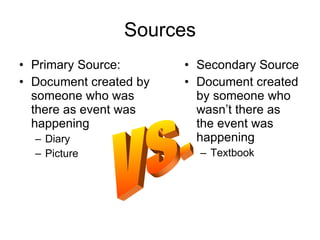
2) Distinctions between primary and secondary sources.
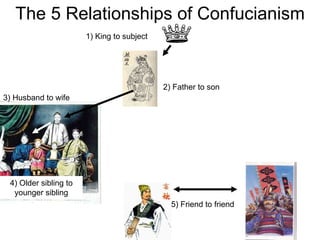
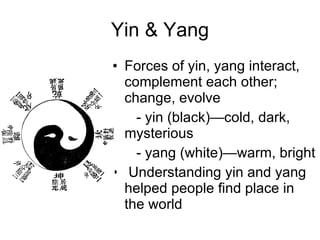
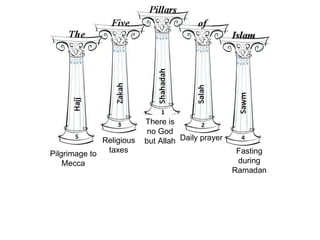
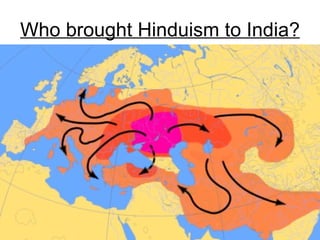
3) Concepts of cultural diffusion and ethnocentrism with examples.
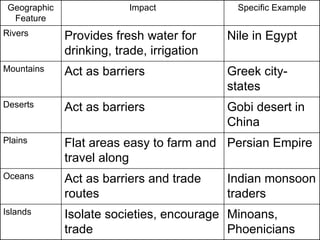
4) Influences of geographic features on river valley civilizations and trade.
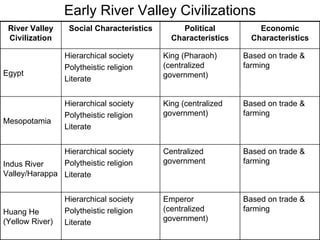
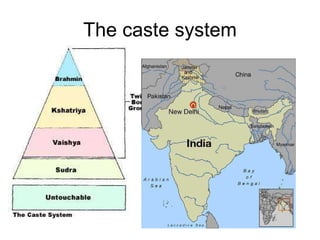
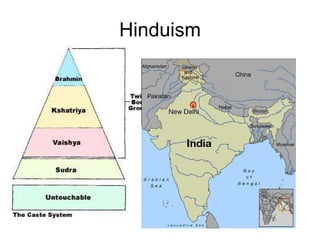
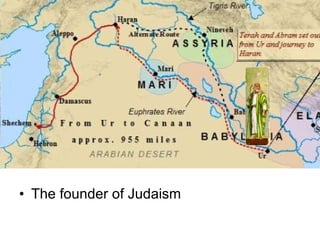
5) Characteristics of early civilizations in Mesopotamia, Egypt, Indus River Valley.