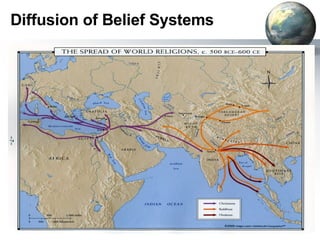
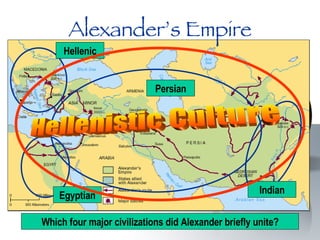
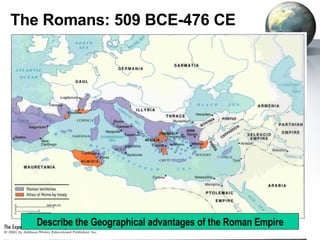
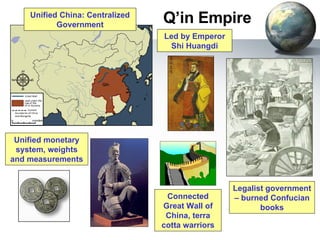
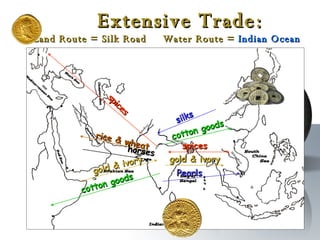
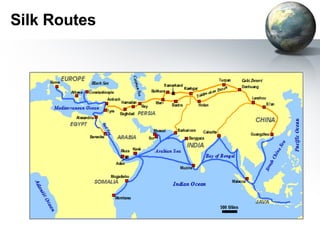
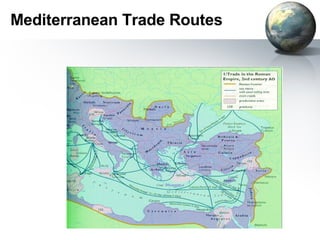
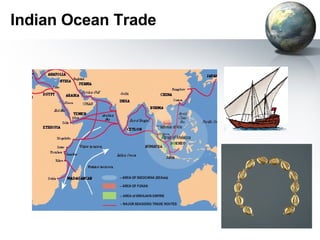
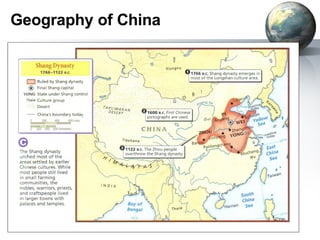
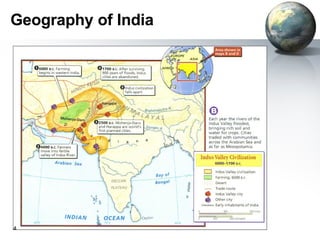
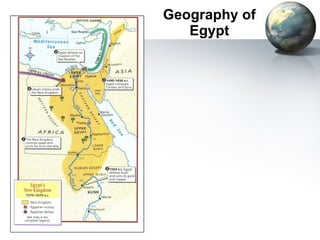
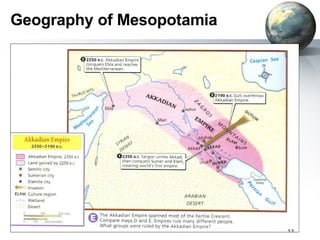
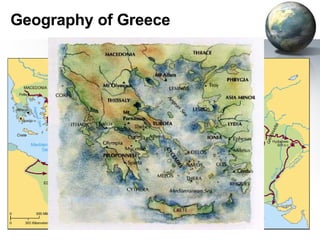
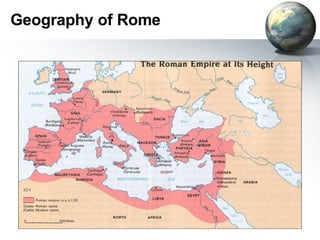
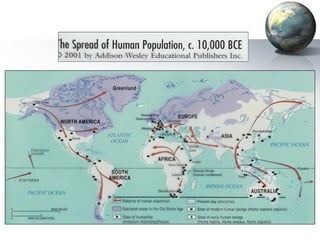
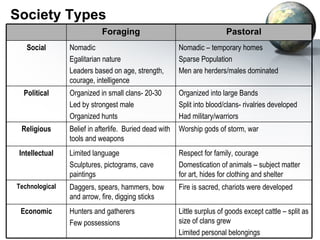
The document provides an overview of major foundations and developments in early civilizations from 10,000 BCE to 600 CE. It discusses key themes like man's interaction with nature, the rise and fall of empires, and sources of change. It then summarizes the major geographic features and developments of early civilizations in places like China, India, Egypt, Mesopotamia, Greece, and Rome. These civilizations established foundations for advanced societies, technologies, religions, and belief systems that spread widely through trade and cultural diffusion networks by 600 CE.










![From Caucasus Mtns. Black/Caspian Sea Nomads who settled Vedas, Upanashads basis for Hinduism Caste system warriors, priests, peasants later re-ordered: Brahmins (priests), warriors, landowners-merchants, peasants, untouchables (out castes) Aryans: The Vedic Age: 1500-500 B.C.E.. Shudras Vaishyas Kshatriyas Pariahs [ Harijan ] Untouchables Brahmins](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volumesnonameapworldreviewfoundationsreview-090420170031-phpapp02/85/Unit-I-Foundations-Review-25-320.jpg)