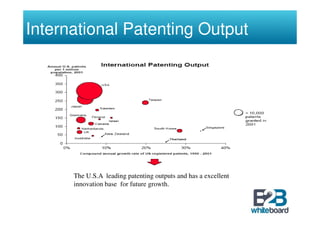
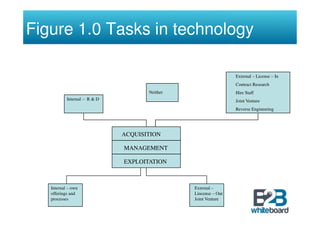
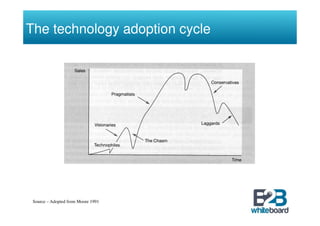
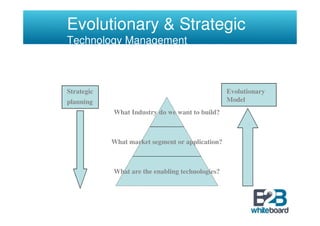
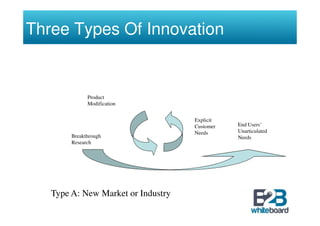
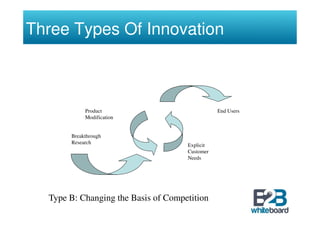
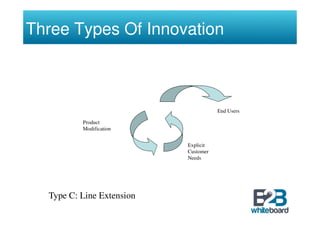
The document discusses technology in business networks and its management. It explains that companies need a wide range of skills and technologies to meet customer needs that are developing rapidly. To control costs and innovation, companies must collaborate and acquire technologies externally through partnerships or licensing. The text also outlines frameworks for analyzing a company's technological assets and adopting innovations through incremental or breakthrough approaches to adapt to changing business environments and networks.