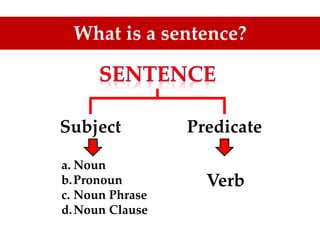
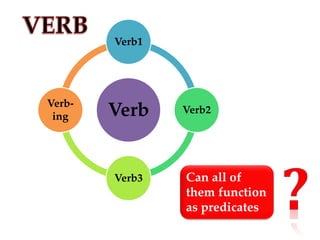
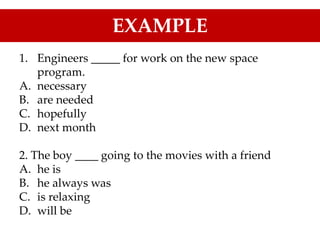
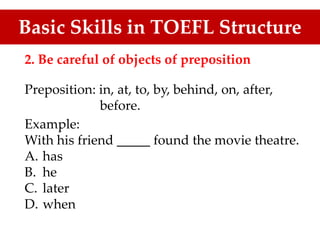
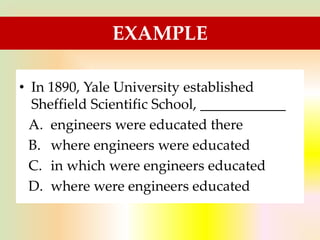
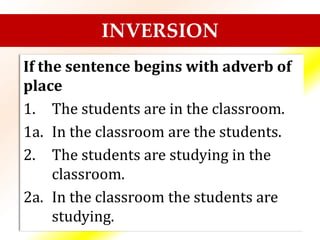
The document is a guide on sentence structure and written expression, particularly for the TOEFL exam. It covers subjects, predicates, verb forms, prepositions, appositives, participles, and conjunctions, providing examples and exercises for clarity. The material emphasizes the importance of sentence construction and grammatical accuracy in writing.