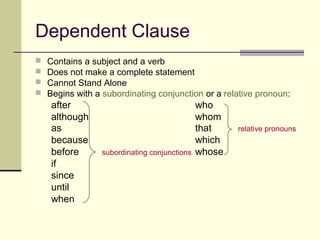
This document provides an overview of phrases and clauses. It defines the different types of phrases, including prepositional phrases, infinitive phrases, participial phrases, and gerund phrases. It also defines the two types of clauses - independent clauses and dependent clauses. Examples are given for each type of phrase and clause. The document concludes with exercises for the learner to identify phrases and clauses in sample sentences.