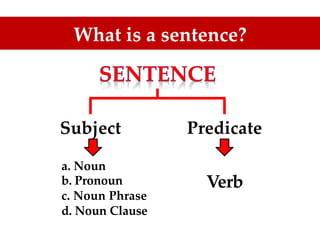
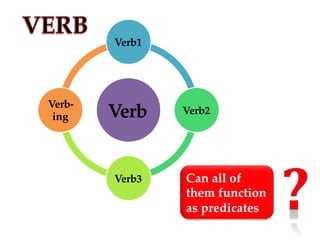
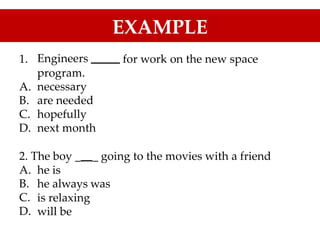
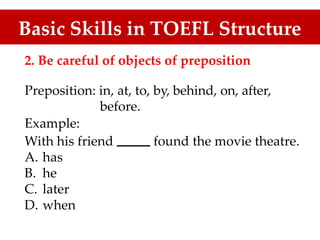
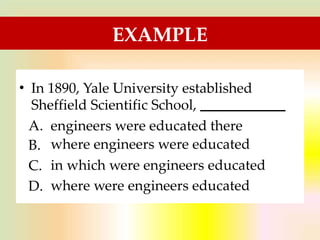
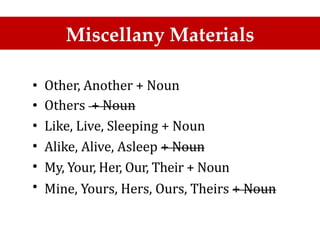
The document discusses the importance of TOEFL and related English proficiency tests such as TOEIC, emphasizing their relevance for academic, international communication, and general English purposes. It provides detailed insights into sentence structures and grammar rules necessary for TOEFL, including subjects, predicates, and the proper use of conjunctions and prepositions. Various examples and exercises are presented to illustrate these concepts effectively.