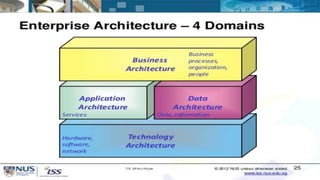
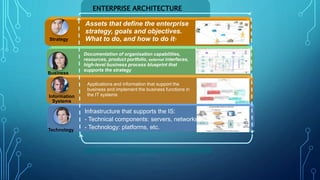
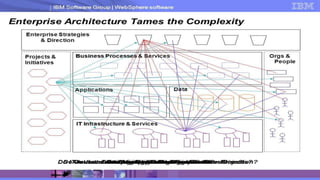
Enterprise architecture (EA) defines an organization's current and desired future state in terms of business processes, information systems, and technologies. EA aims to align IT with business goals and provide a roadmap for transitioning from the current to future state. Common EA frameworks include Zachman Framework and TOGAF, which provide categories and processes for documenting EA artifacts like business processes, applications, data, and infrastructure. Implementing EA allows organizations to better align IT with business strategy, reduce redundancies, reuse solutions, and make more informed decisions.