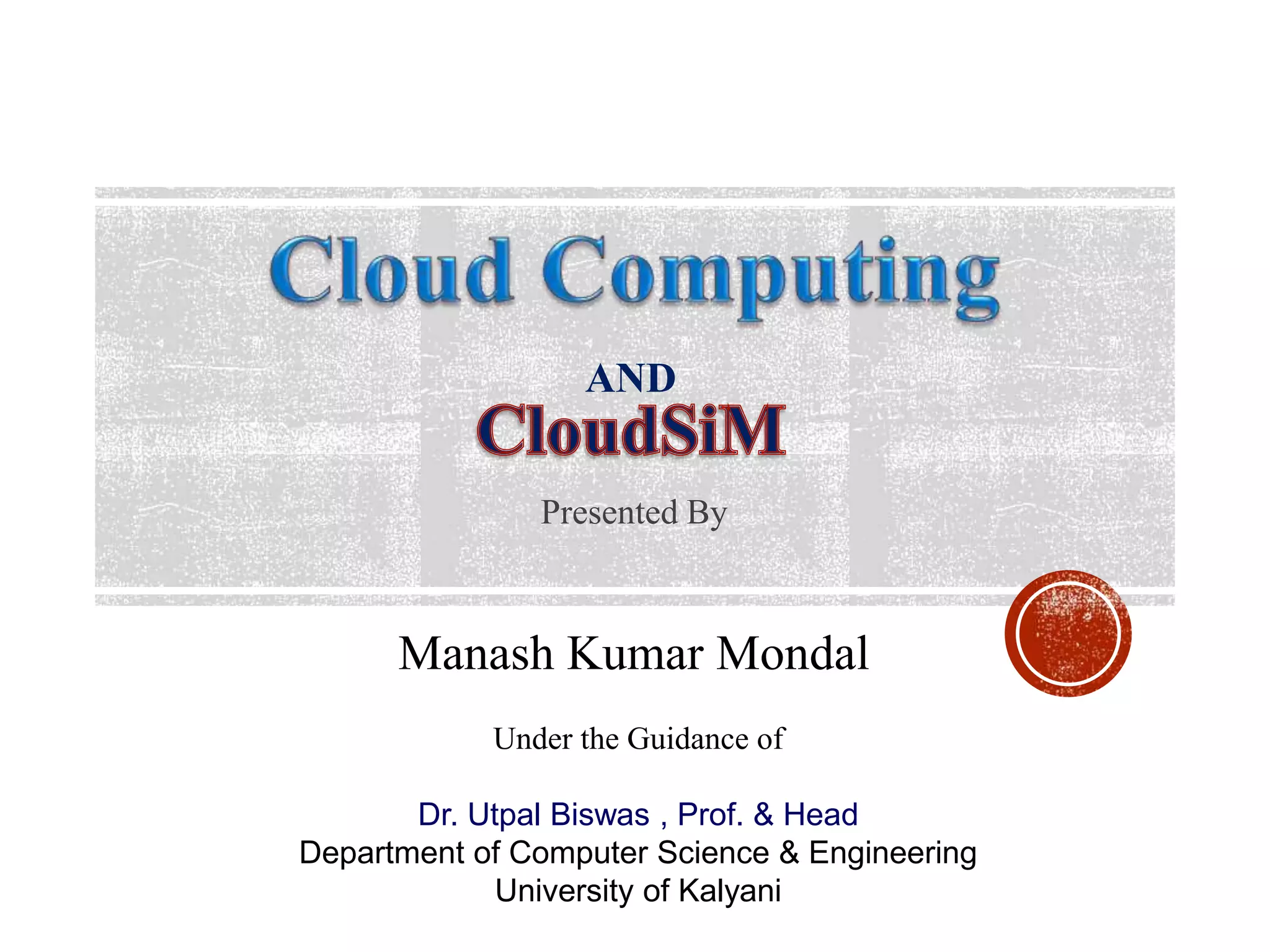
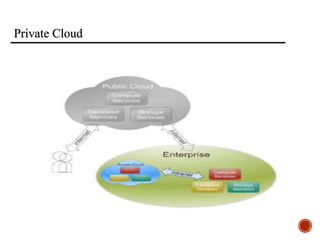
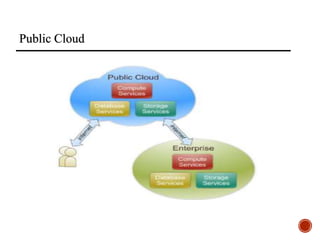
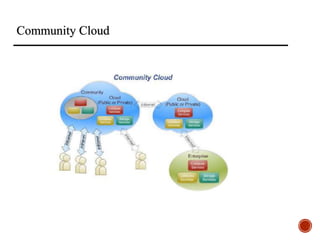
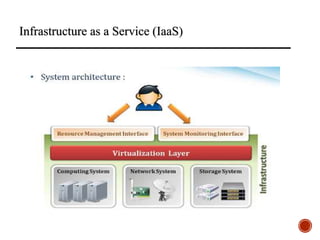
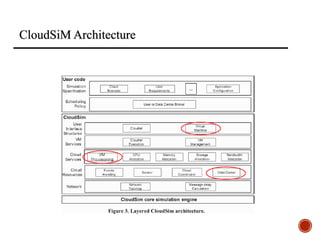
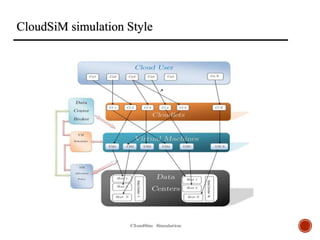
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its history, architecture, deployment models, and service models. It discusses benefits such as cost savings and scalability, as well as disadvantages like security issues and potential downtime. Additionally, it introduces the CloudSim toolkit for modeling and simulation of cloud infrastructures.