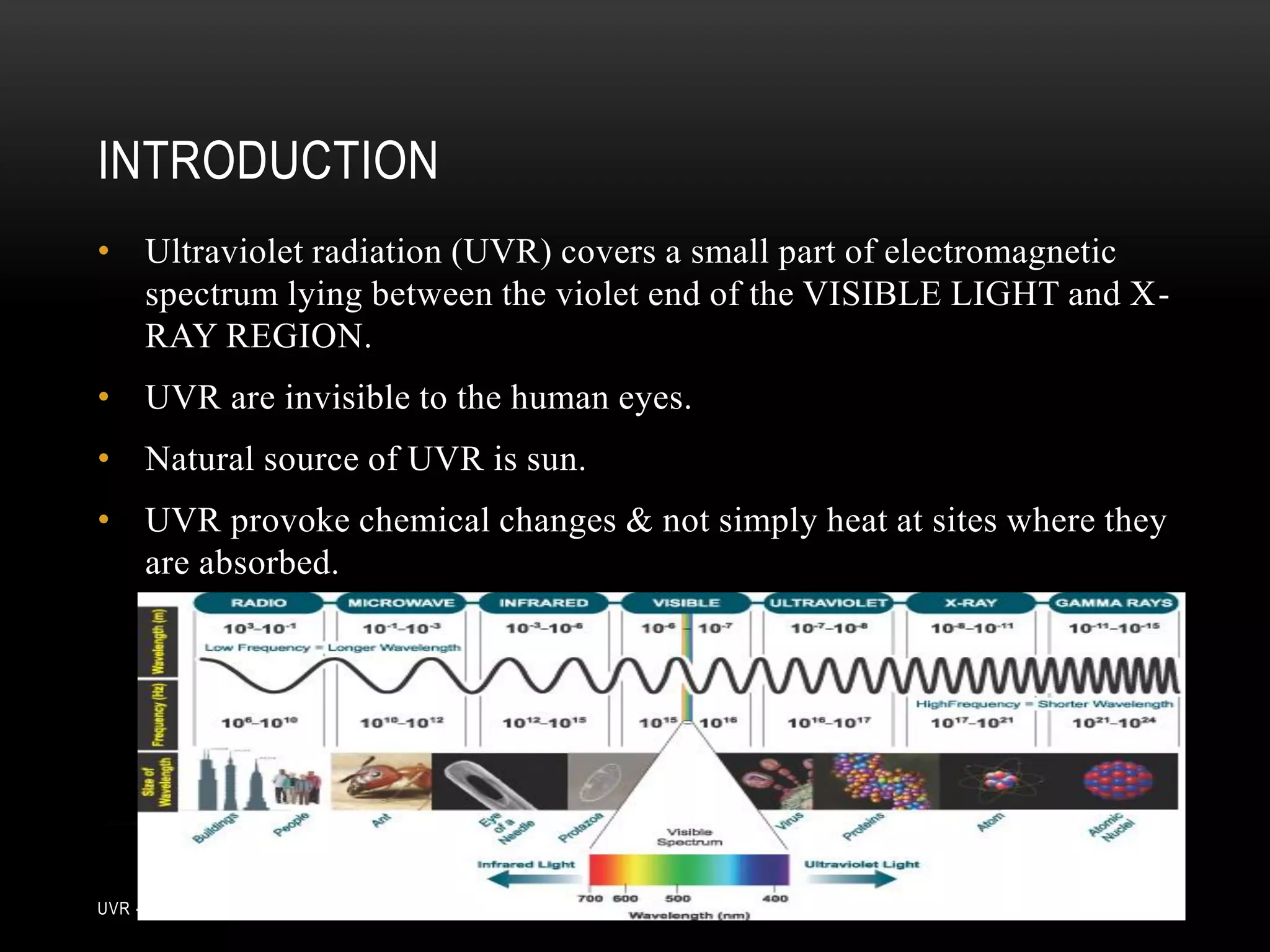
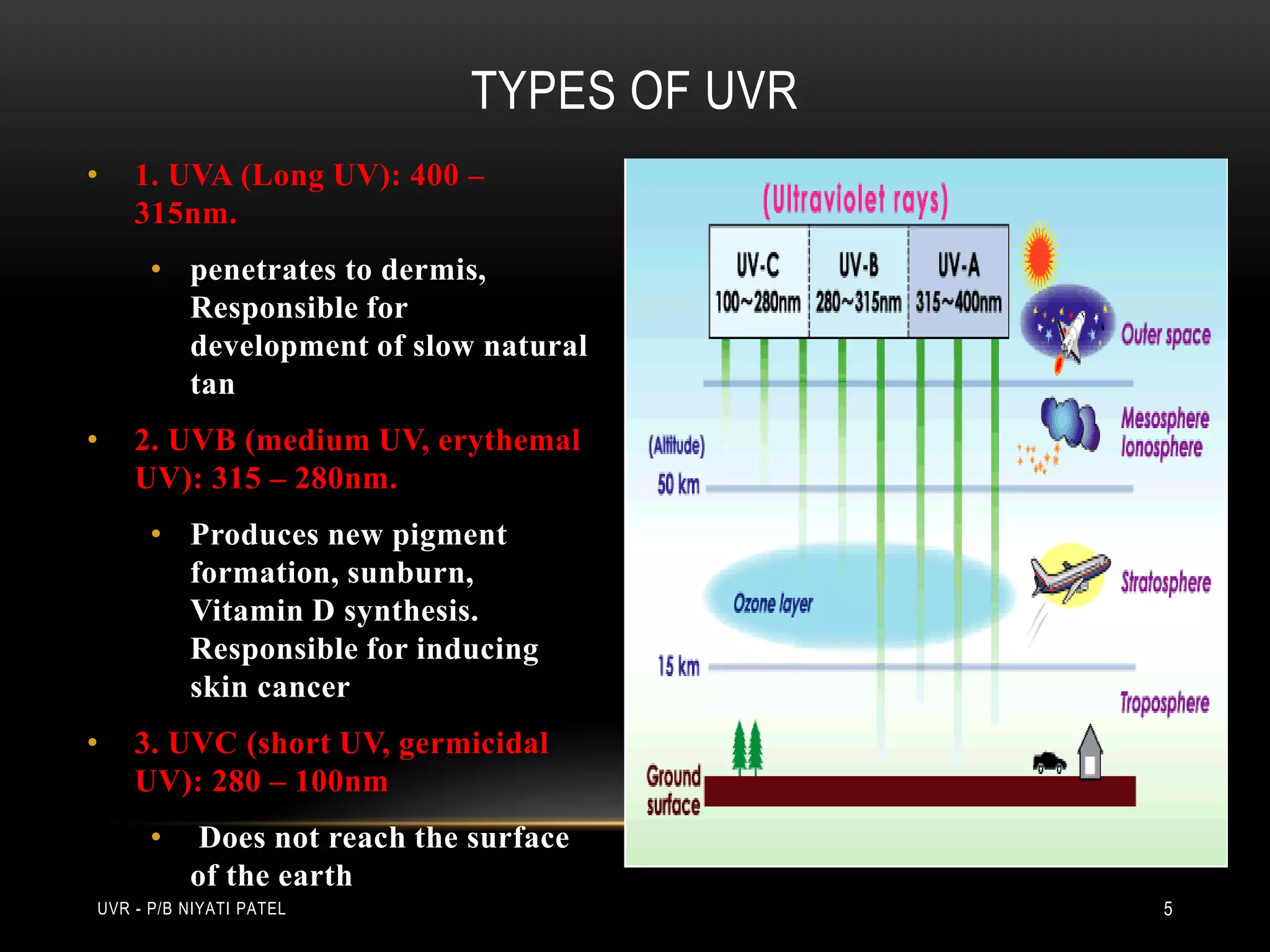
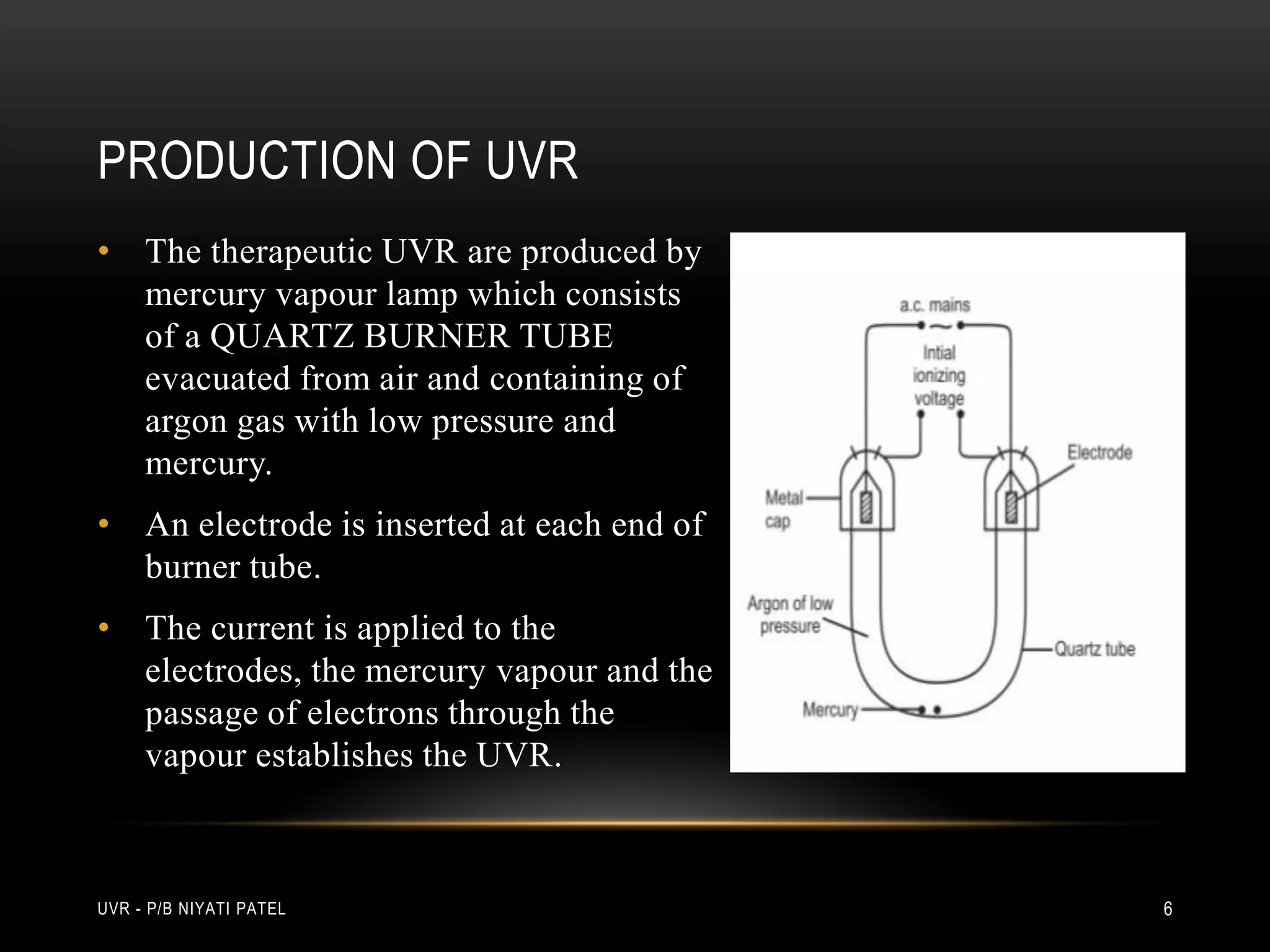
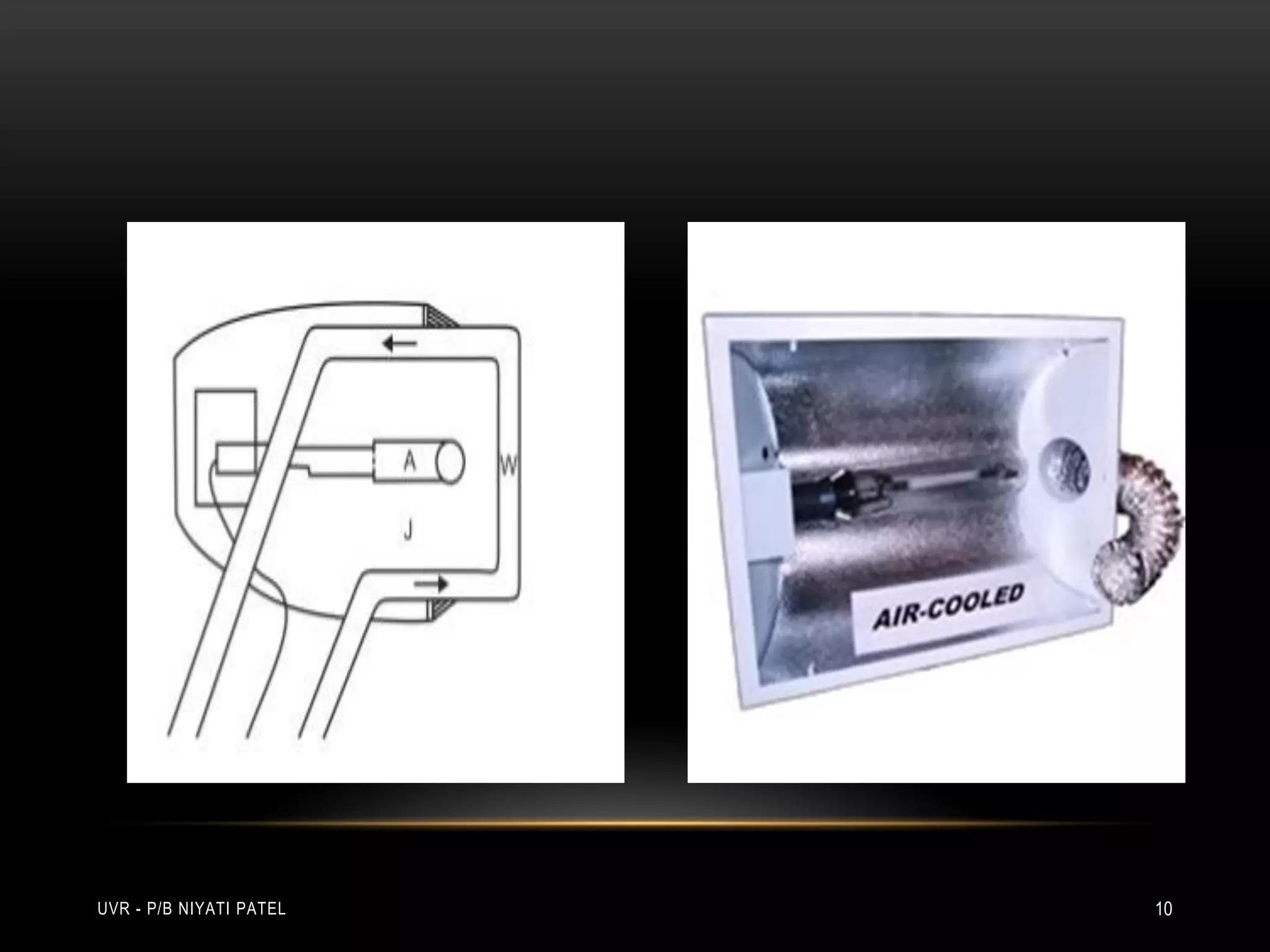
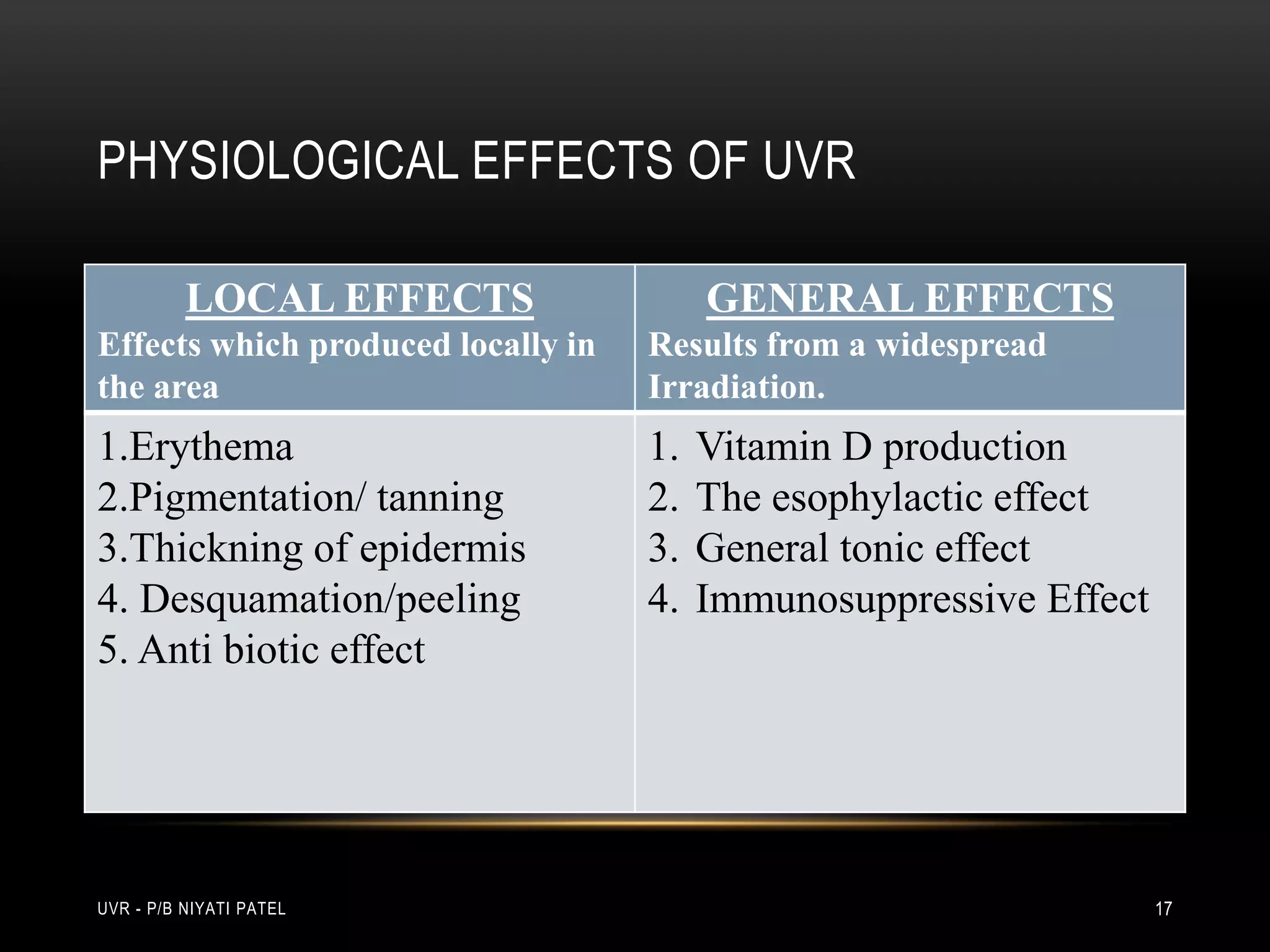
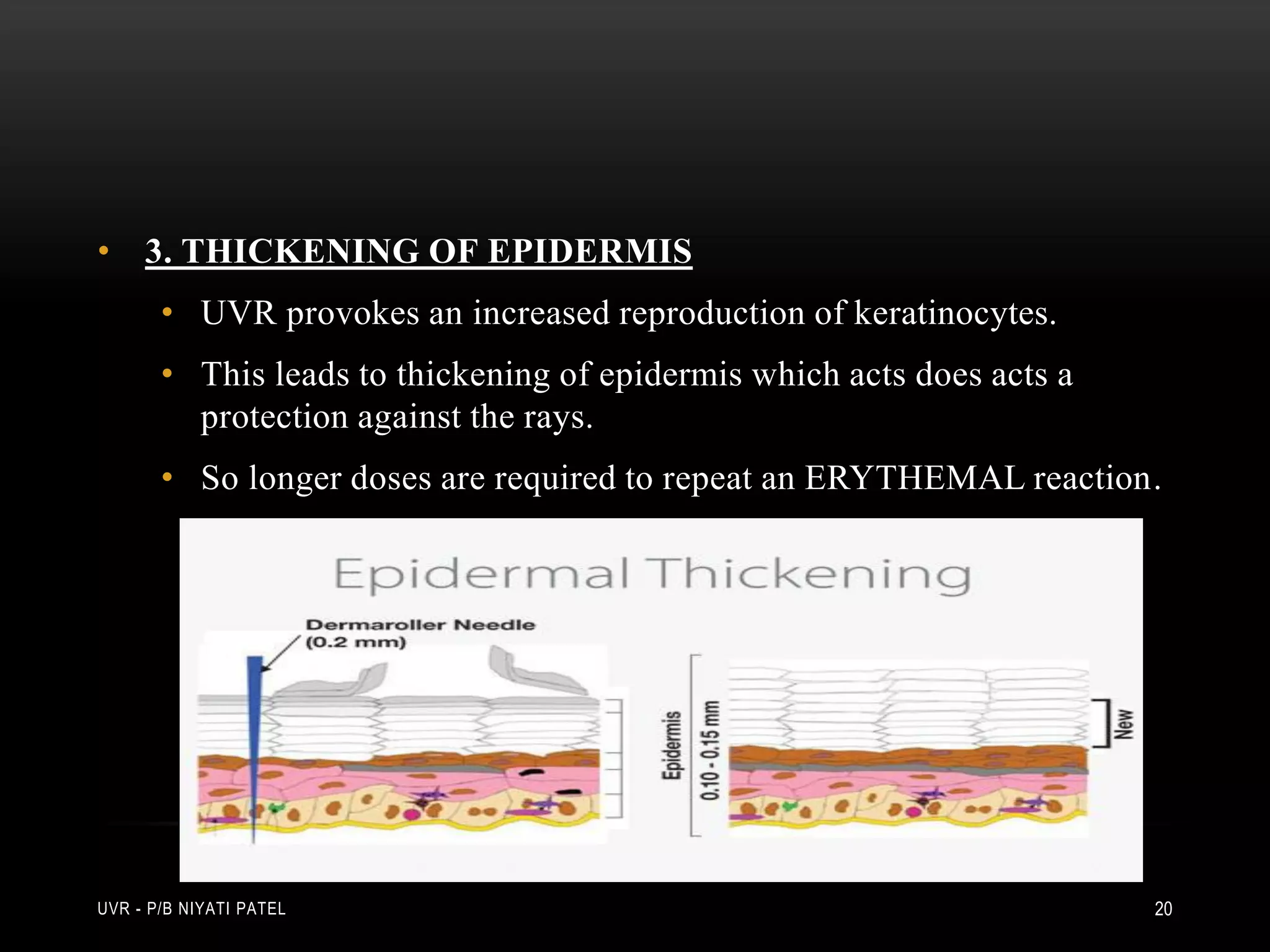
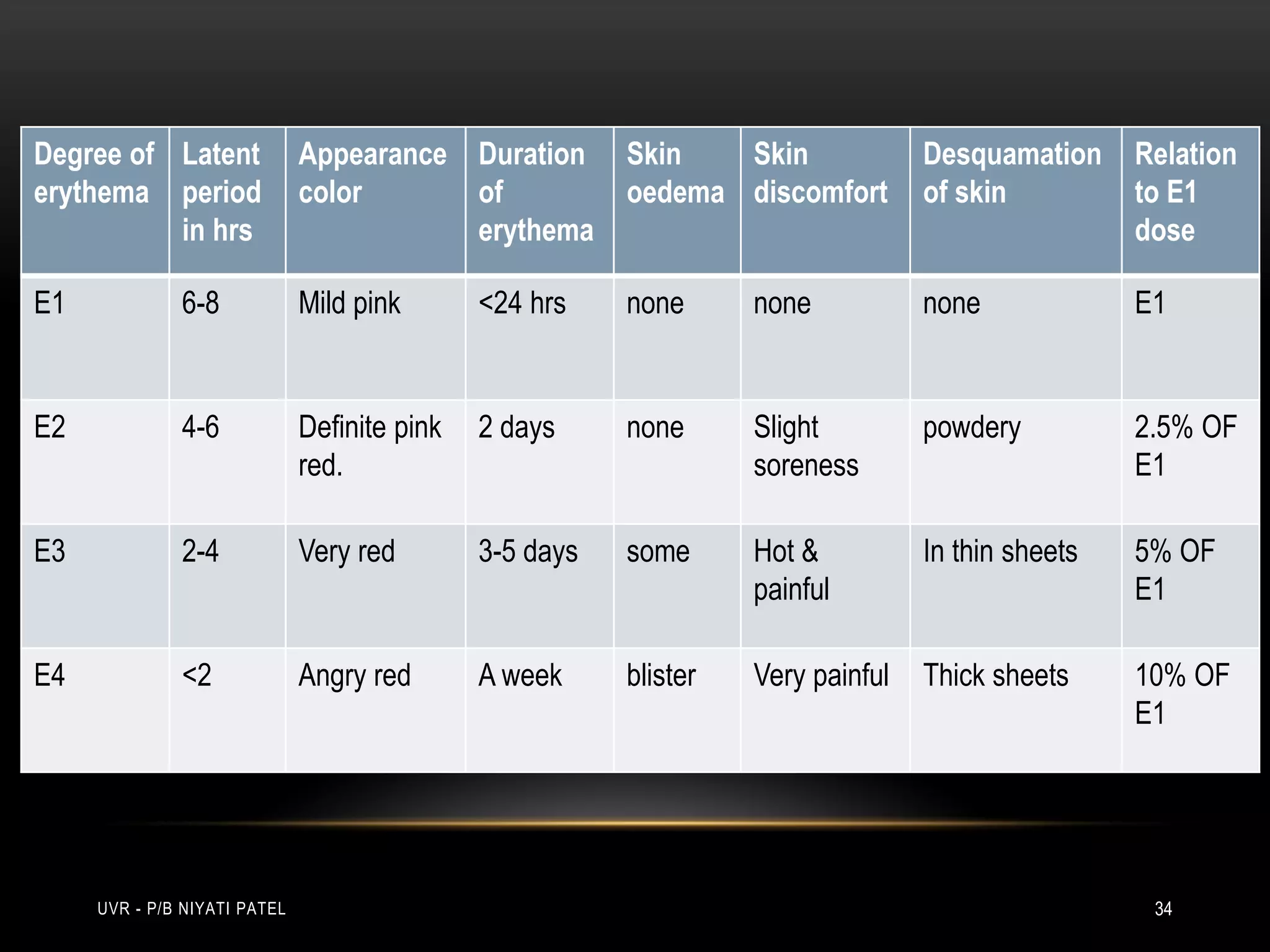
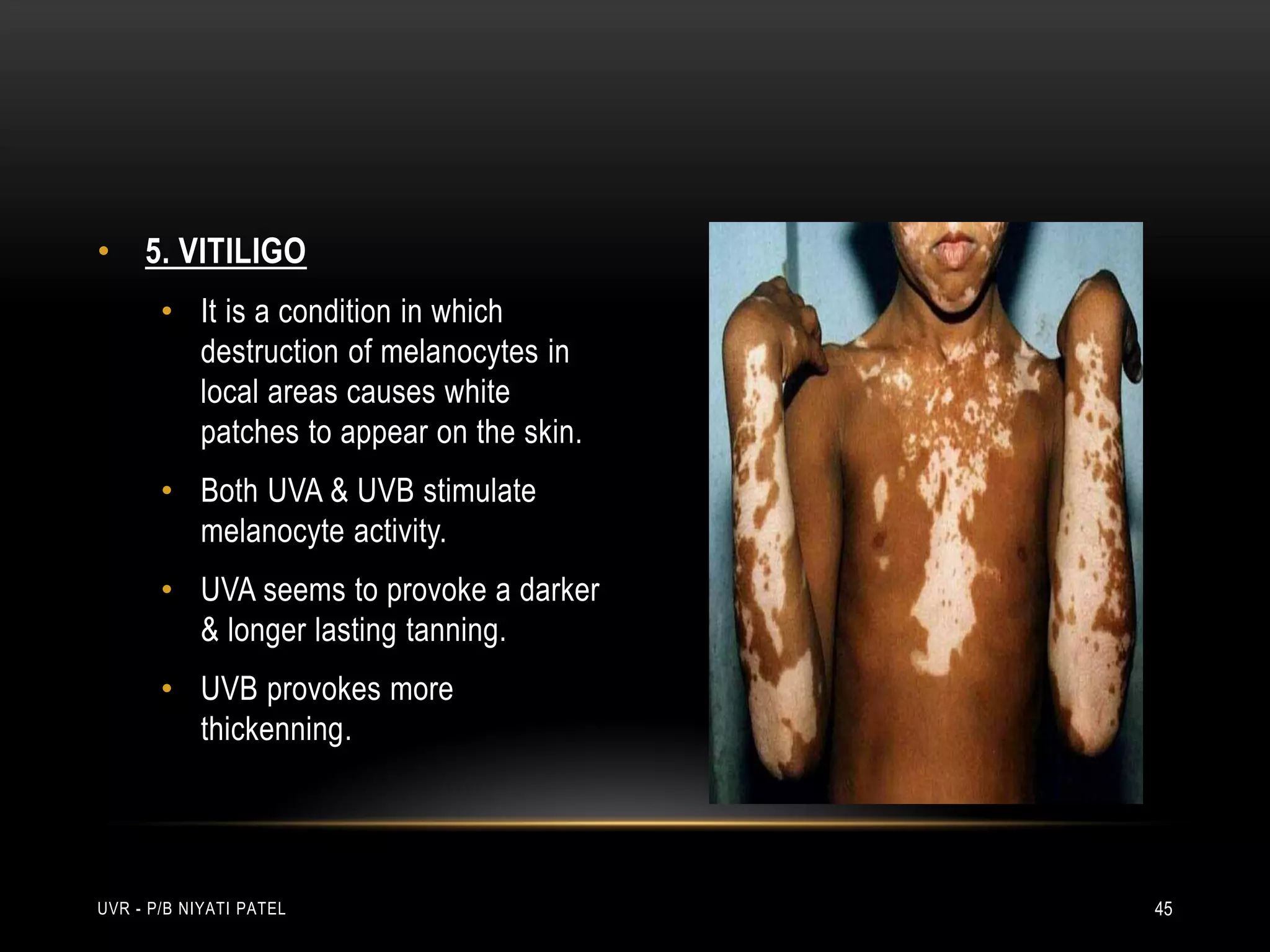
The document discusses ultraviolet radiation (UVR), its types, sources, and its therapeutic applications in treating various skin conditions. It details how UVR interacts with human skin, the physiological effects it induces including erythema and pigmentation, and guidelines for dosage and patient education regarding UVR exposure. Specific therapeutic uses for conditions like psoriasis, acne, and eczema are also highlighted, emphasizing the importance of monitoring skin responses.