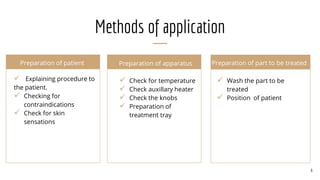
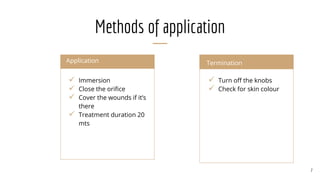
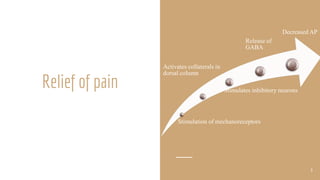
Fluidotherapy is a dry heat modality that uses suspended air streams with properties similar to liquid. It is used to treat distal extremities from 38-45°C. The fluidotherapy unit consists of a metal tank, power controls, thermostat, fan, and auxiliary heater. It is applied by immersing the treated area in the air stream for 20 minutes and checking skin color afterward. Therapeutic effects include relief of pain, reduction of muscle spasm, increased range of motion, decreased inflammation and edema, and enhanced healing. Indications for fluidotherapy are scar tissue, post-operative stiffness, pain, contractures, arthritis, and edema. Contraindications include fever, cancerous tissue, impaired sensation