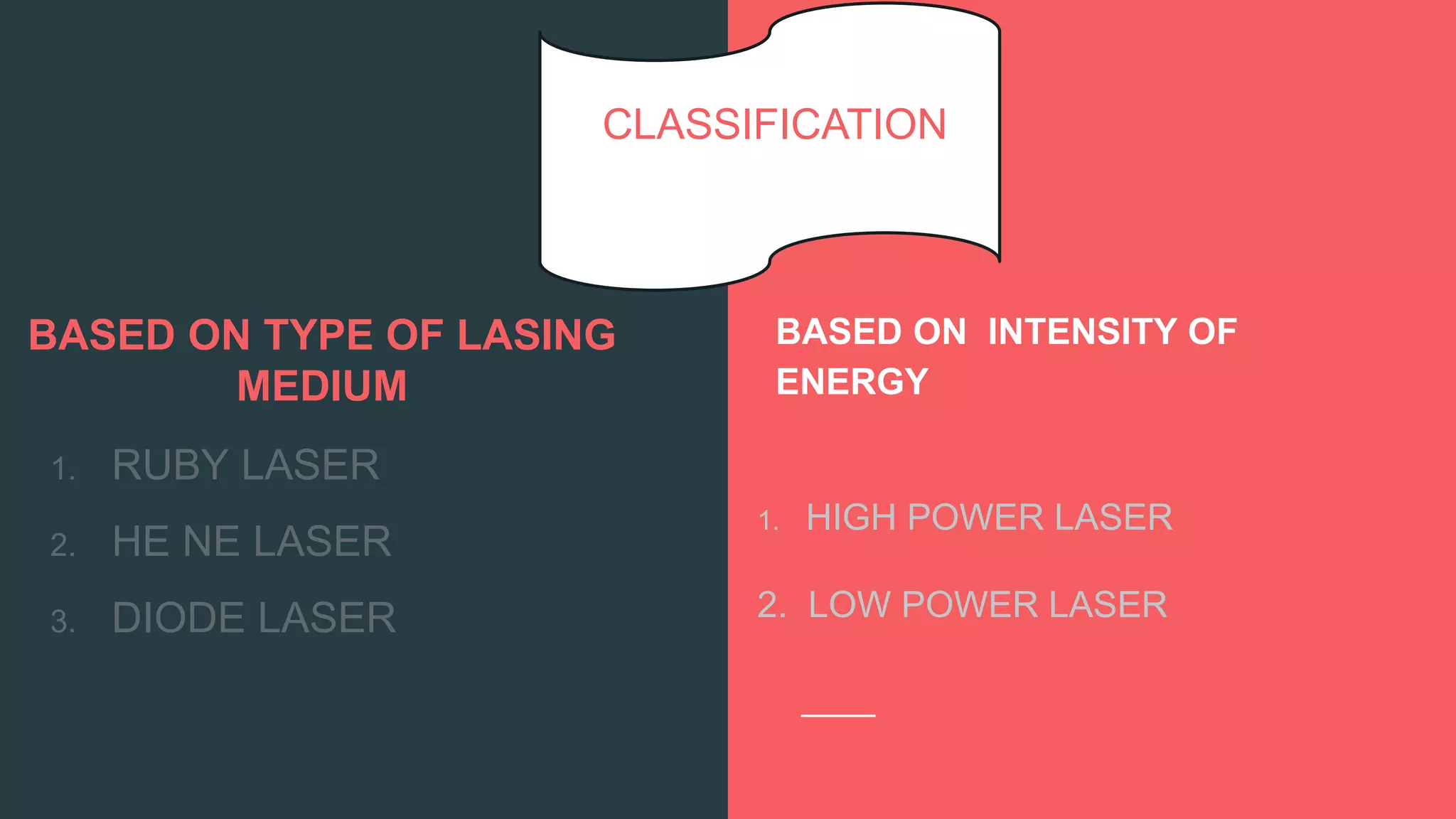
This document discusses laser therapy, including its production, types, effects, applications, and techniques. It begins by defining laser as light amplified by stimulated emission of radiation. It then describes the key properties of lasers as monochromaticity, coherence, and collimation. It discusses the different types of lasers based on lasing medium (ruby, HeNe, diode) and intensity (high power, low power). The physiological and therapeutic effects of lasers are outlined, including effects on wound healing, pain relief, and inflammation. Applications such as wound healing and reducing pain and inflammation are indicated. The document concludes by describing techniques for laser application and important parameters like wavelength, energy density, and dosage.