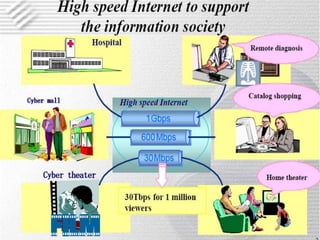
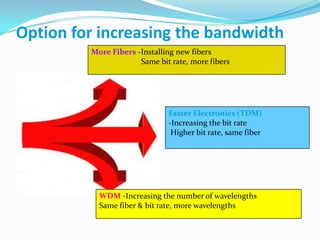
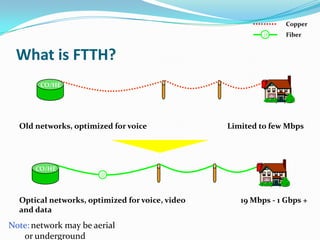
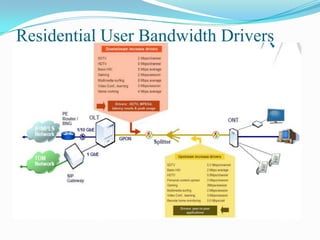
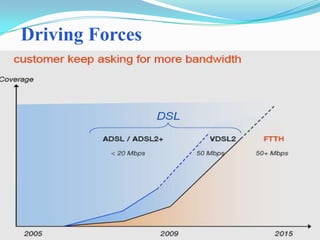
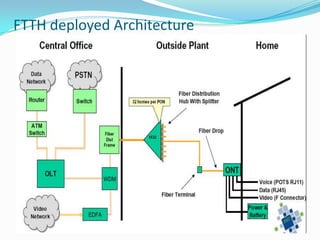
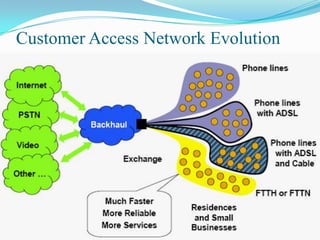
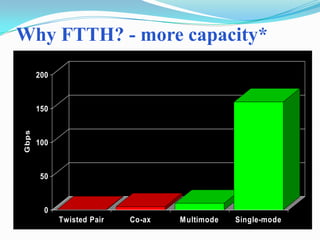
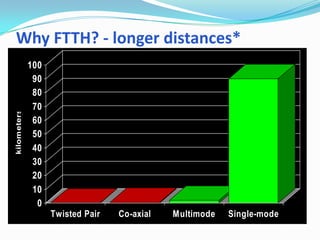
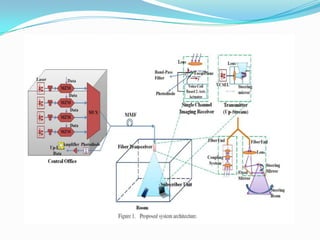
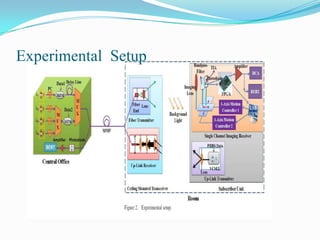
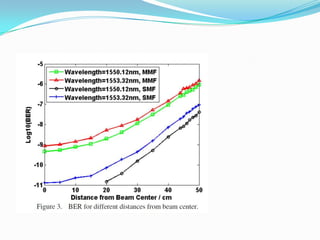
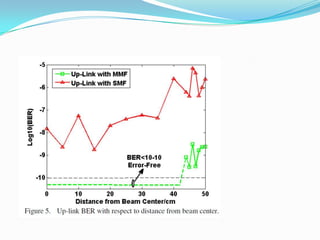
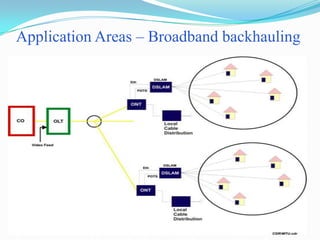
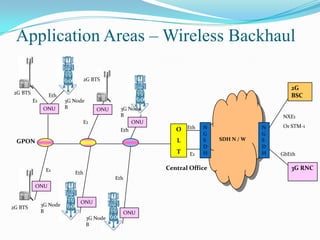
The document discusses options for increasing bandwidth, highlighting approaches such as installing more fibers, utilizing faster electronics, and employing wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). It explains the importance of fiber to the home (FTTH) technology for high-speed internet access and various application areas, including residential services and high-definition TV. Additionally, it outlines the capacity and distance advantages of FTTH over traditional copper and coaxial networks.