This document discusses internet security and cybercrime. It begins with an introduction by Sam Lumpkin of 2AB, Inc and then covers the following topics: how different groups view security (management, users, hackers); examples of security breaches and headlines; how common unauthorized access is; what hackers can do; why companies should care about security; how to begin securing a network; implementing security through awareness, physical controls, electronic access controls, access authorization, policy, and logging; and enforcing security policies.



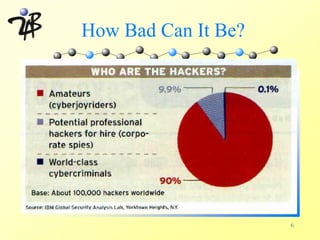

![Current Headlines
Microsoft Store Offline After Insecurity Exposed.
By Brian McWilliams, Newsbytes
Jan 11 2002 5:52PM PT
An online store operated by Microsoft Corp. [NASDAQ:
MSFT] for software developers was unavailable today
following reports that a security flaw gave visitors the
ability to take control of the site, including access of
customer data.
www.securityfocus.com
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/a6704d01-120309033545-phpapp02/85/A6704d01-8-320.jpg)