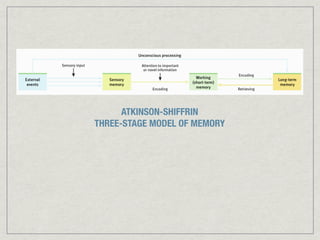
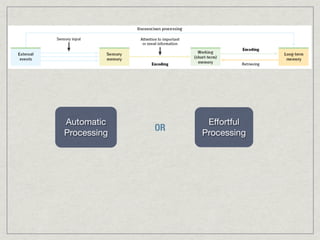
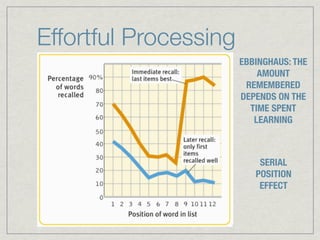
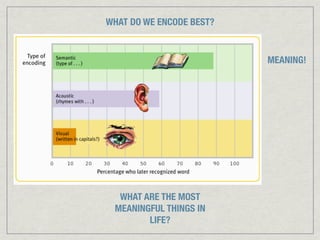
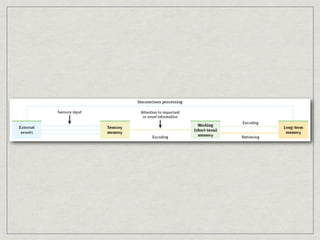
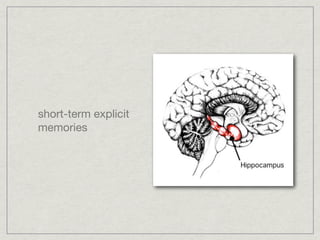
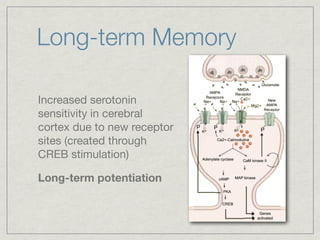
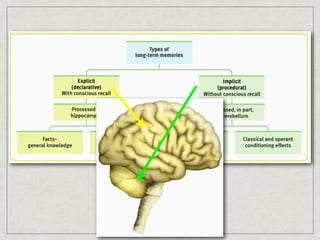
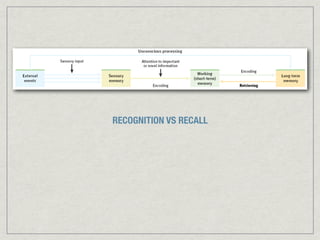
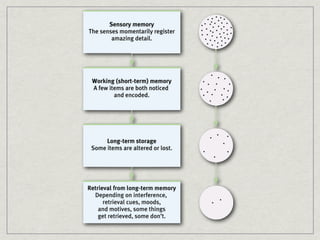
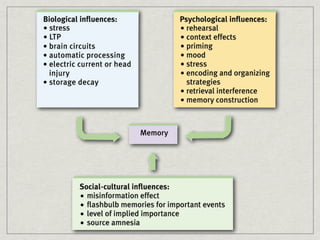
Memory is the persistence of learning over time through the storage and retrieval of information. There are several types of memory including sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Memories can be forgotten due to factors like decay over time, interference from new memories, being in a different state than when the memory was encoded, or not having the proper cues at retrieval that were present during encoding. The low accuracy of police sketches can be attributed to forgetting details over time as well as interference and lack of cues, since witnesses are asked to recall and describe a face they saw briefly in a high-stress situation.