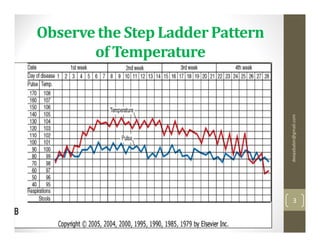
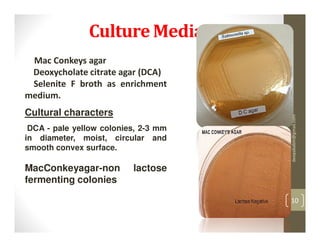
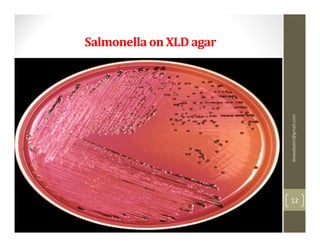
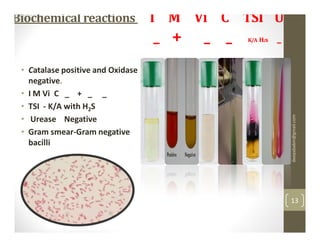
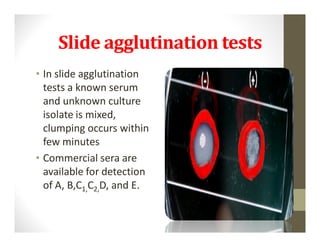
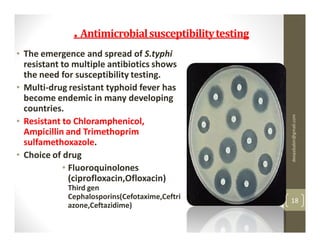
The 20-year-old male student presented with a week of fever showing a step-ladder pattern, along with mild hepatomegaly. This suggests a provisional diagnosis of enteric fever. Diagnosis can be confirmed through microbiological investigation of blood, bone marrow, blood clots, stool, or urine cultures, which ideally should be done in the first week of illness. Antibiotic susceptibility testing is important as multidrug-resistant strains of Salmonella Typhi have emerged. Prevention emphasizes good sanitation and vaccination.