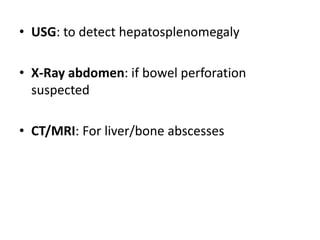
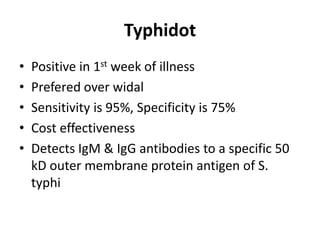
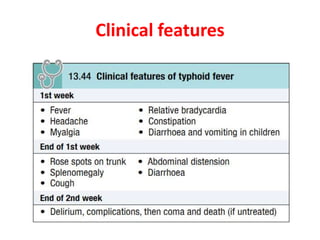
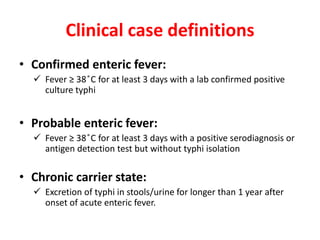
Enteric fever is caused by Salmonella enterica serovars Typhi and Paratyphi. It is transmitted through the fecal-oral route. The bacteria infects the lymphoid tissues of the small intestine and spreads to the liver, spleen and bone marrow. Common symptoms include sustained fever over 38°C, abdominal pain and hepatosplenomegaly. Blood cultures are the gold standard for diagnosis but other tests like the Widal test and Typhidot can also be used. Fluoroquinolones are usually the treatment of choice but azithromycin is an alternative. Treatment duration is typically 14 days to prevent relapse. Improving sanitation and hygiene as well as vaccination can







![Investigtions
• CBC:
– Mild anaemia,
– low to normal TLC,
– Neutrophilia, Eosinopenia, thrombocytopenia
– [Anaemia & thrombocytopenia in advanced cases]
• CRP/ESR may be elevated
• LFT:
– ALP, Transaminases, bilirubin may be increased](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/entericfever-200903033210/85/Enteric-fever-10-320.jpg)