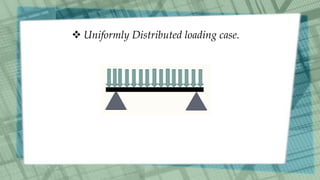
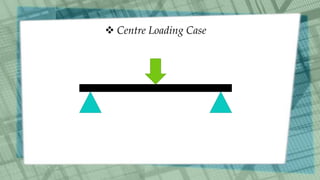
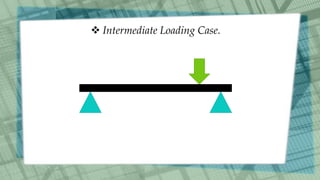
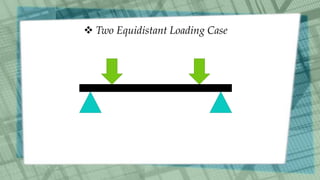
This document discusses simply supported beams, which are horizontal structural members used to transfer loads to supports. It covers their classification, loading conditions, advantages, and disadvantages, noting the importance of shear forces and bending moments in their analysis. Examples include bridge girders, and the document highlights that while they are easy to analyze and install, they have limitations in resisting bending loads compared to fixed beams.