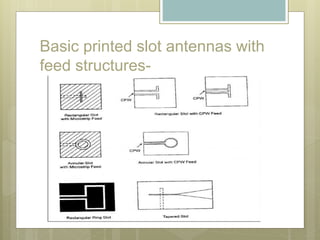
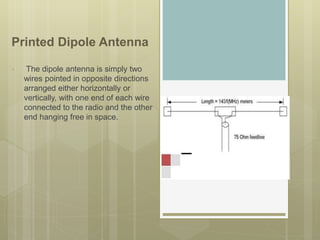
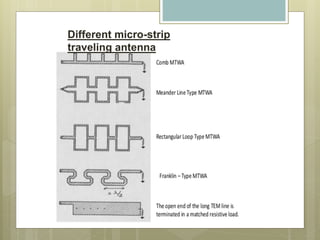
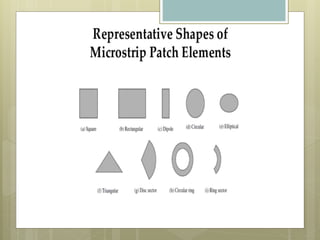
Microstrip antennas come in various types based on their feeding mechanism, patch shape, operating frequency, and bandwidth. The main types include microstrip patch antennas, microstrip dipole antennas, printed slot antennas, and microstrip traveling wave antennas. Printed slot antennas comprise a slot in the ground plane of a grounded substrate and can take any shape. They are typically bidirectional radiators but can be made unidirectional using a reflected plate. Microstrip dipole antennas simply consist of two lengths of metal arranged end to end with feed in the middle. Microstrip traveling wave antennas support transverse wave propagation along periodic microstrip lines or long segments.