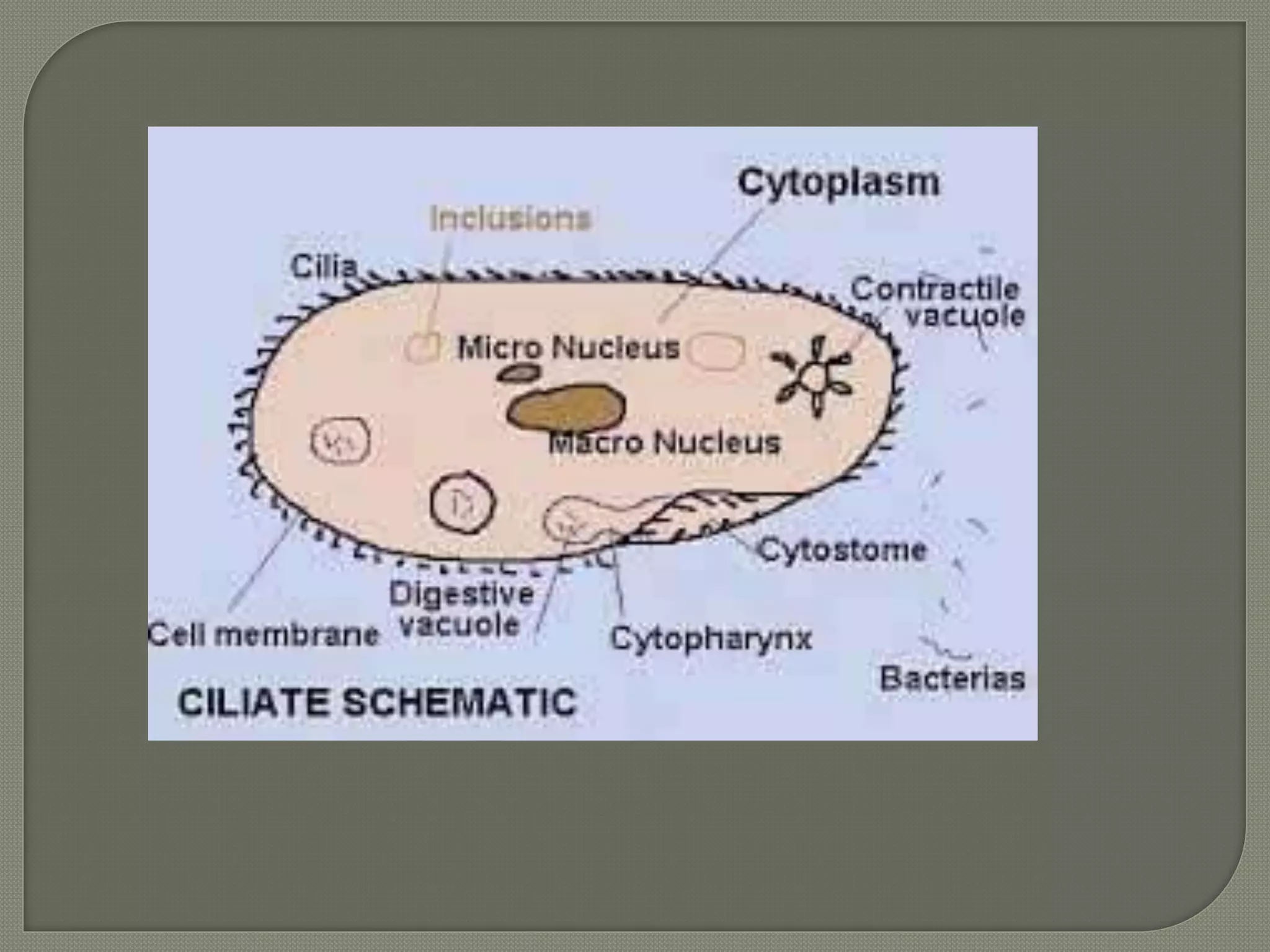
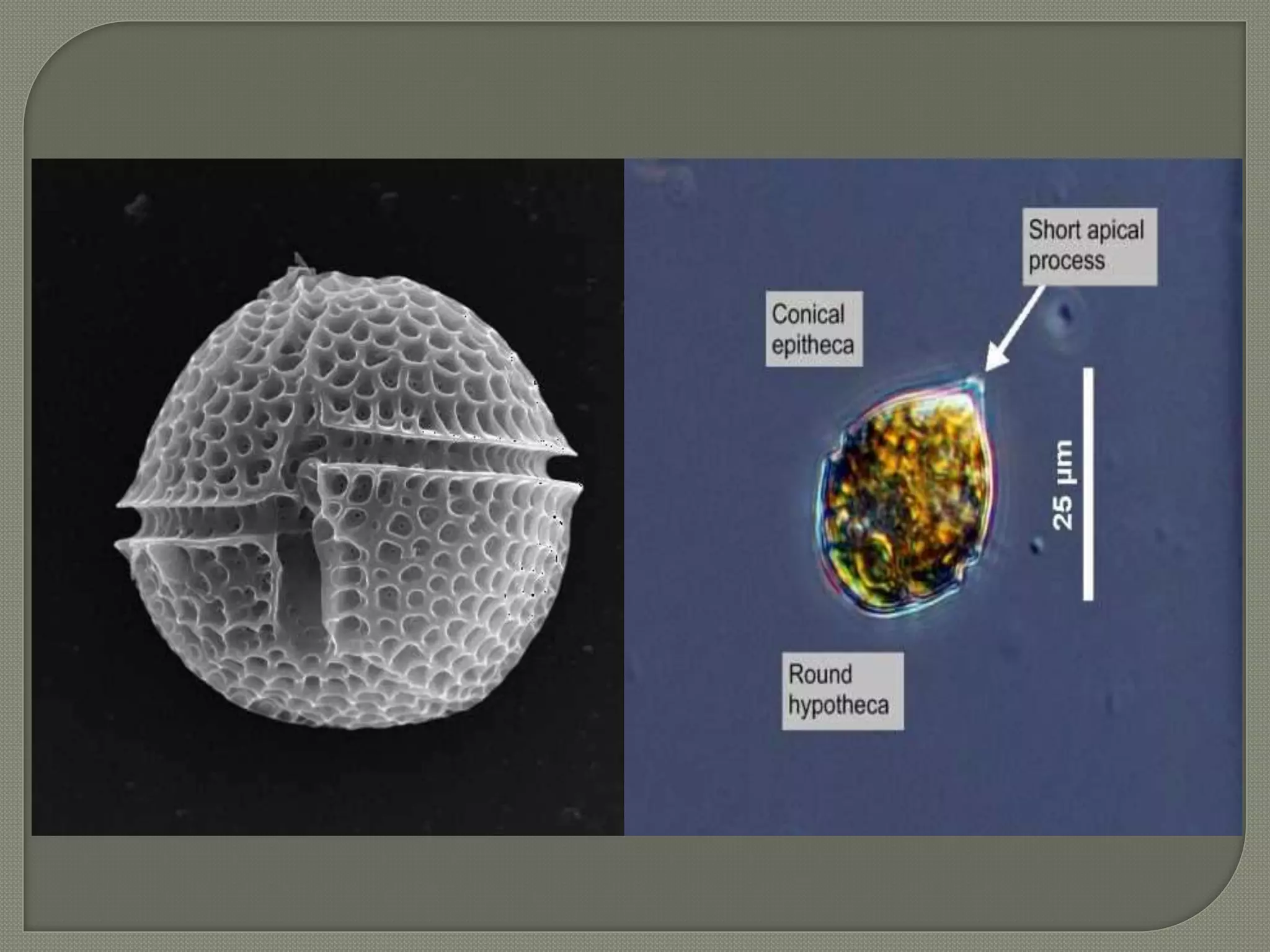
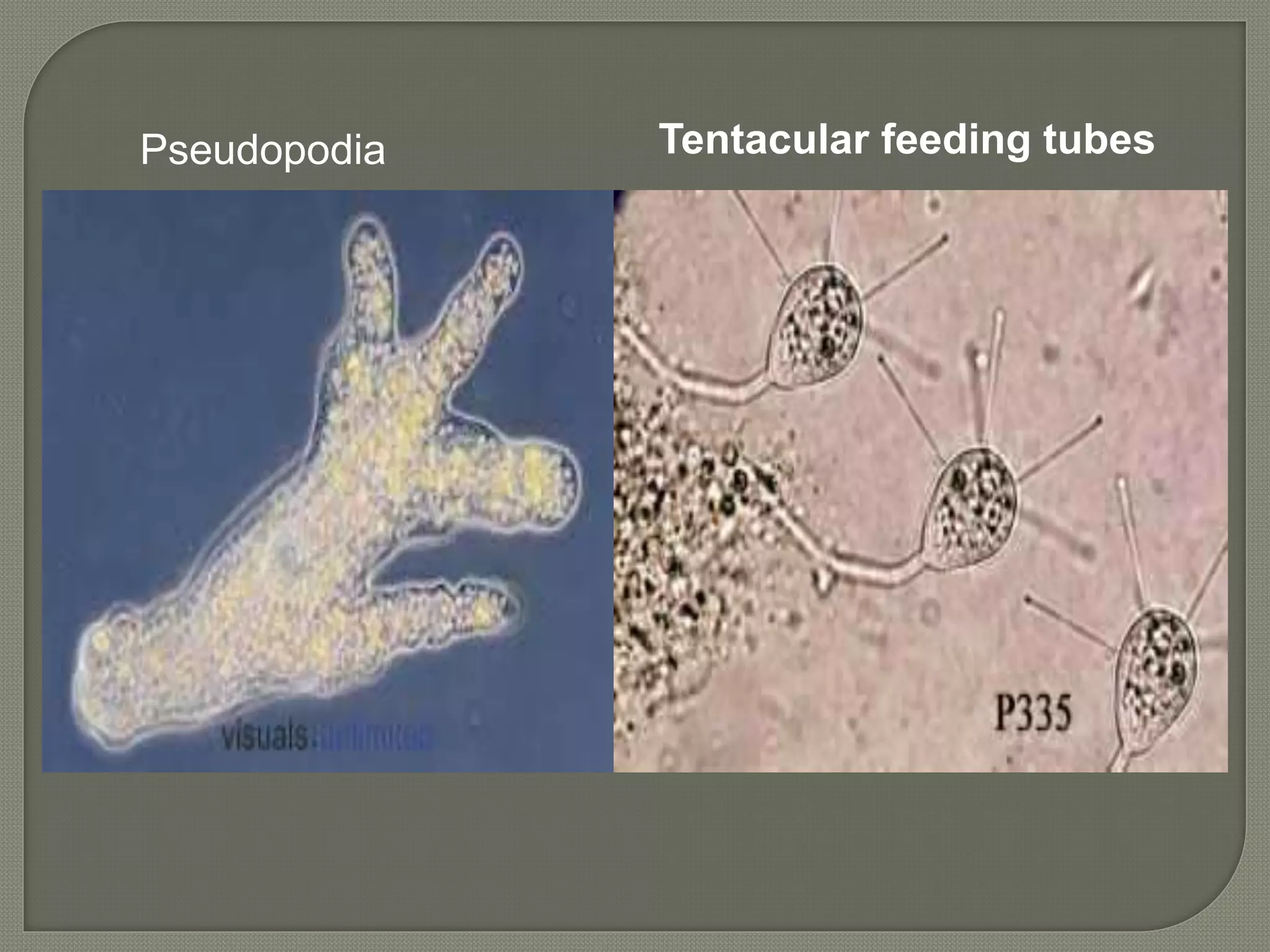
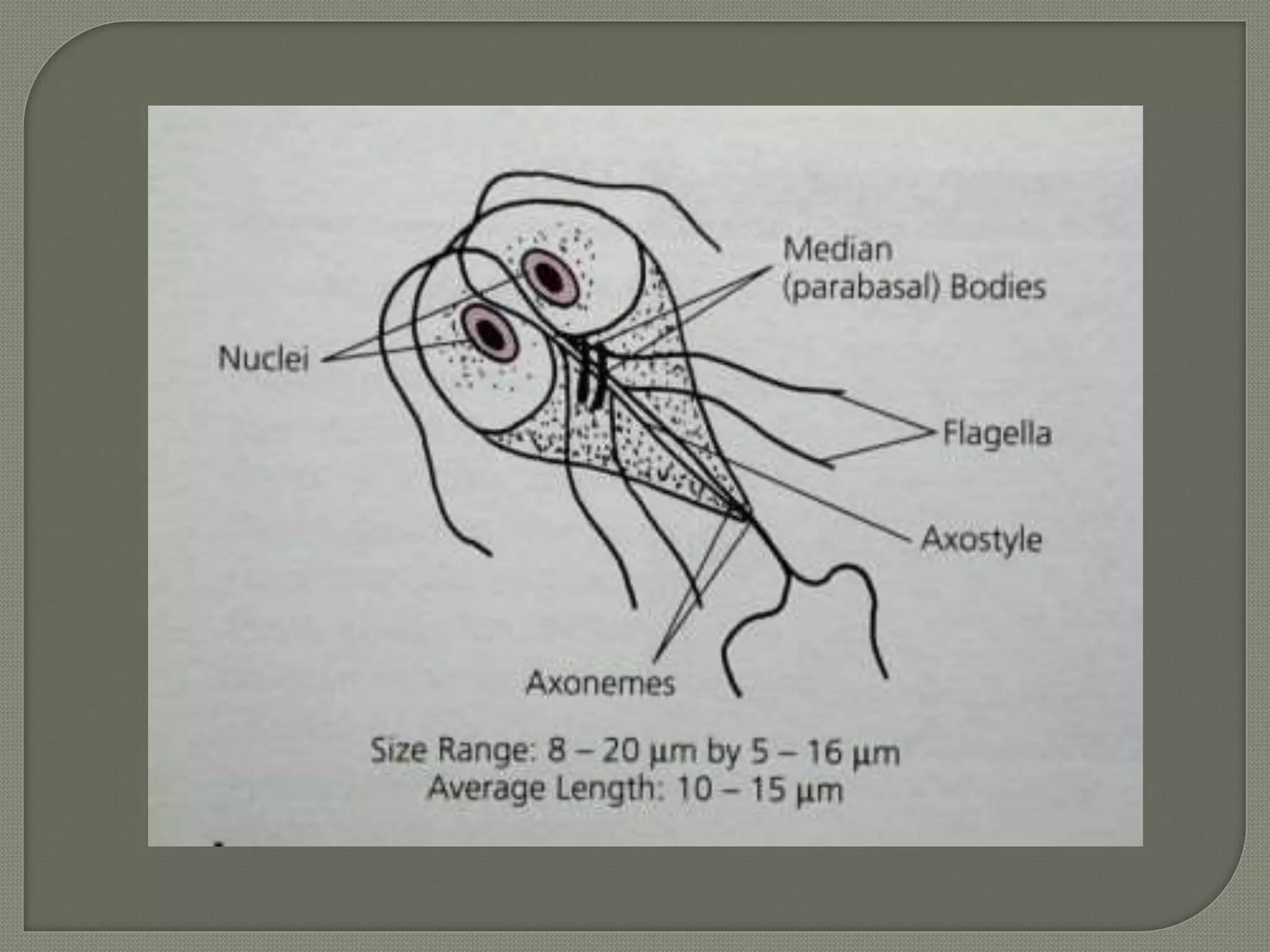
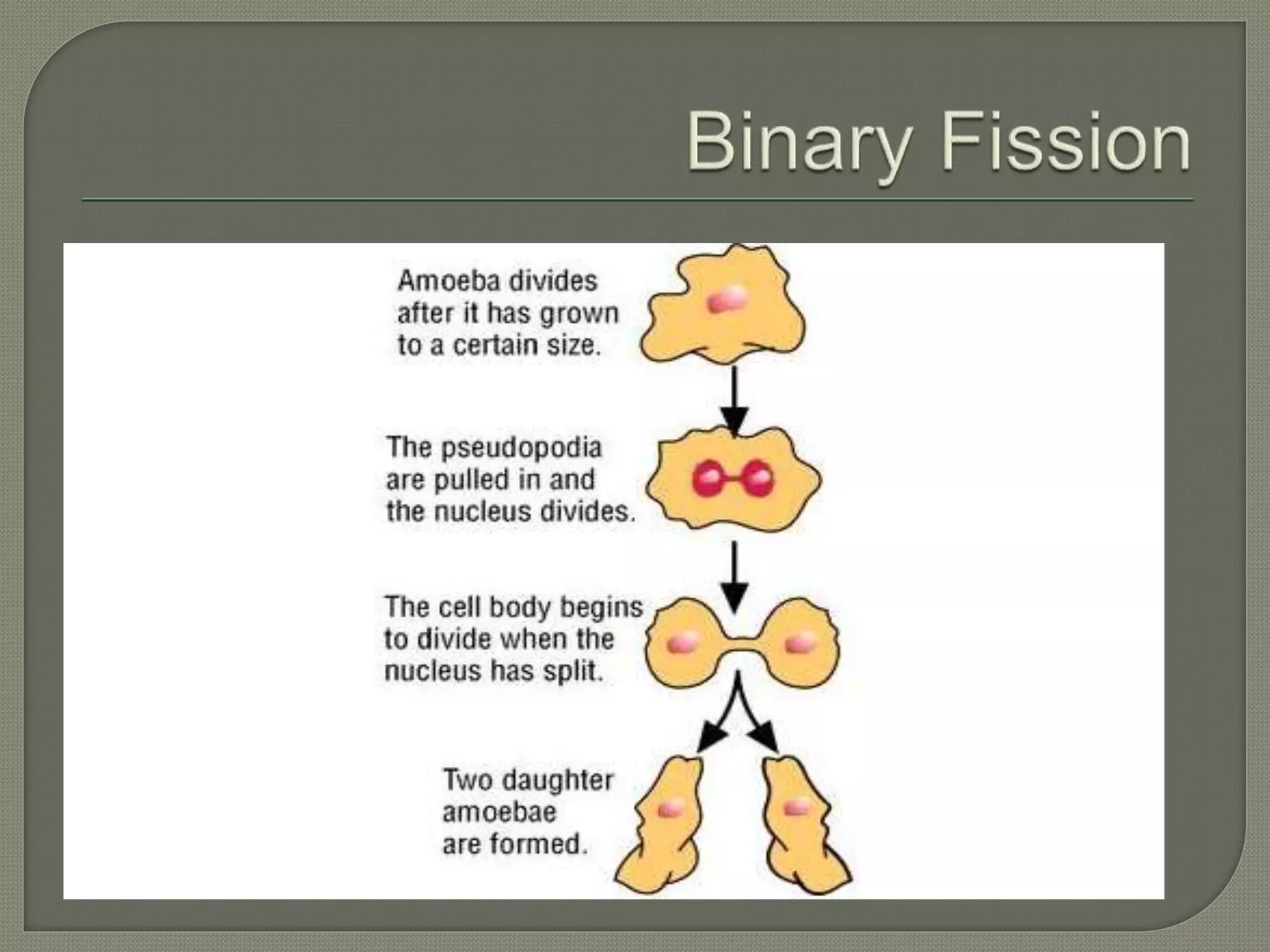
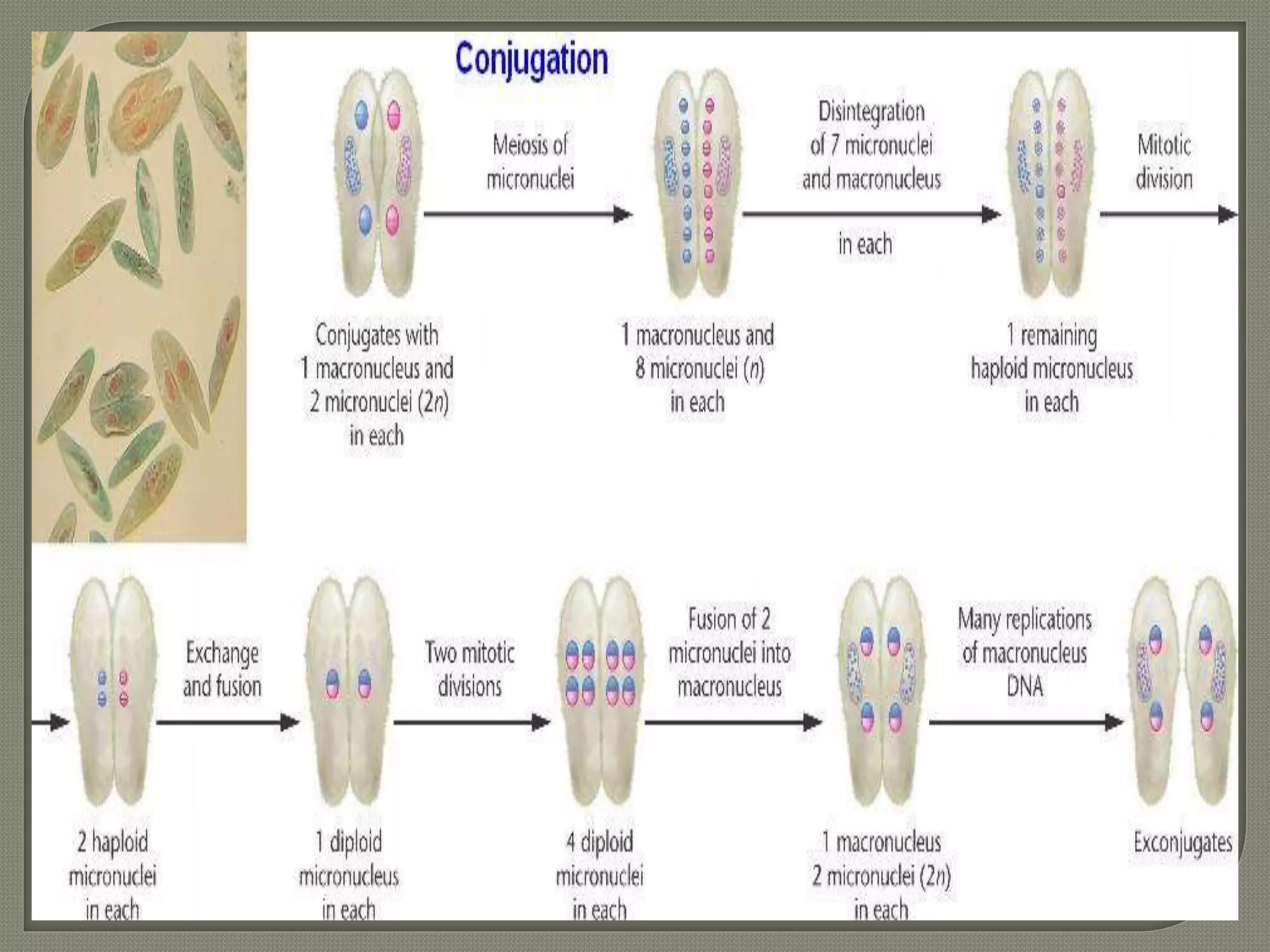
This document defines parasites and summarizes different types of parasites and their life cycles. It discusses ectoparasites that live on the outer surface of hosts, and endoparasites that live within hosts. Obligate parasites cannot exist without a host, while facultative parasites can live with or without a host. Accidental parasites may infect unusual hosts. The document also examines different types of hosts and relationships between parasites and hosts.