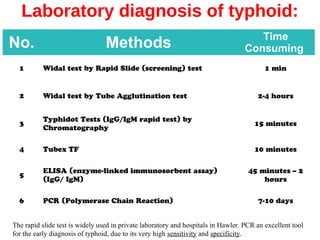
The Widal test is a serological method used to diagnose typhoid fever caused by Salmonella spp. It involves detecting agglutinating antibodies in patient serum against O and H antigens and has limitations due to low specificity and potential for false positives. Despite advancements in diagnostic techniques, the Widal test remains widely used in developing countries due to its cost-effectiveness and simplicity.