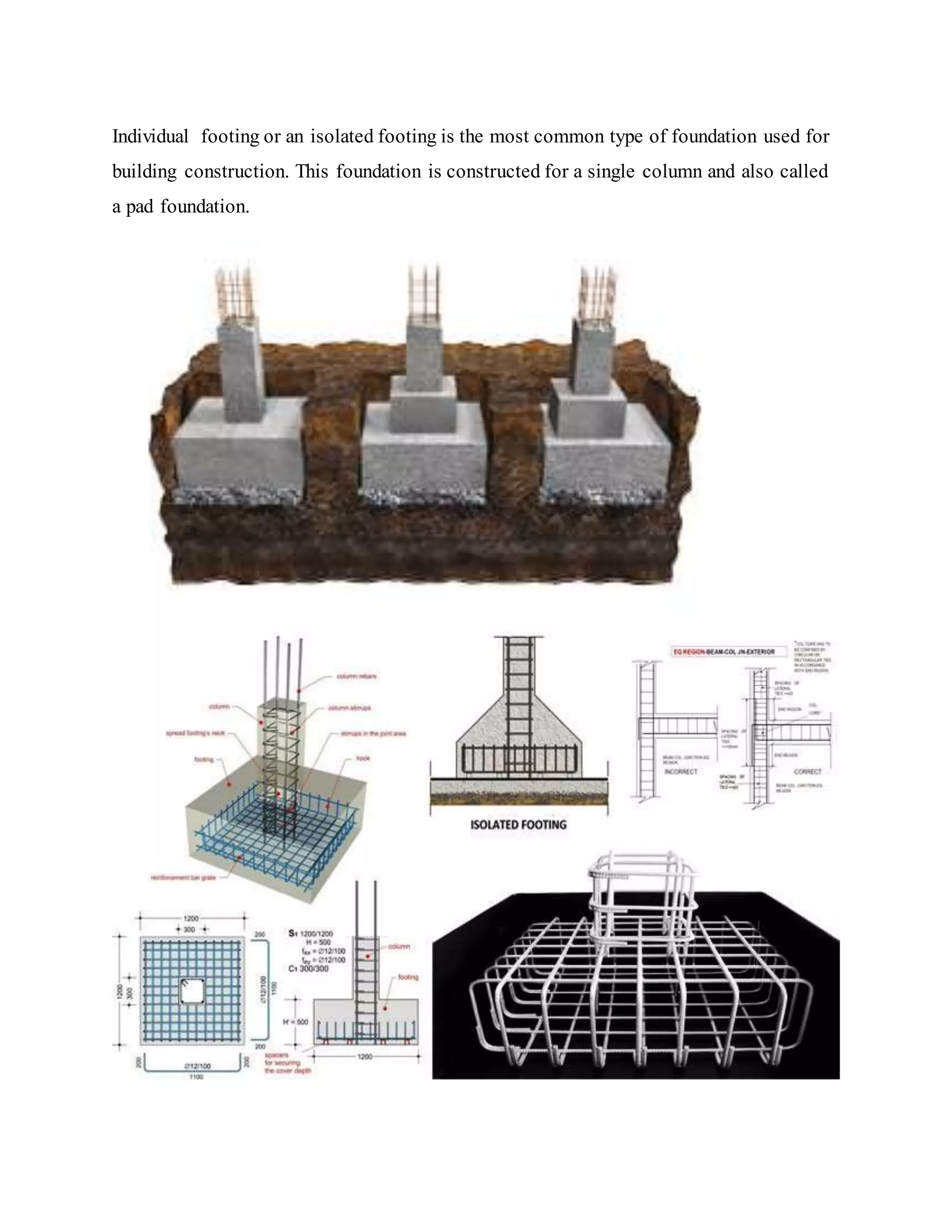
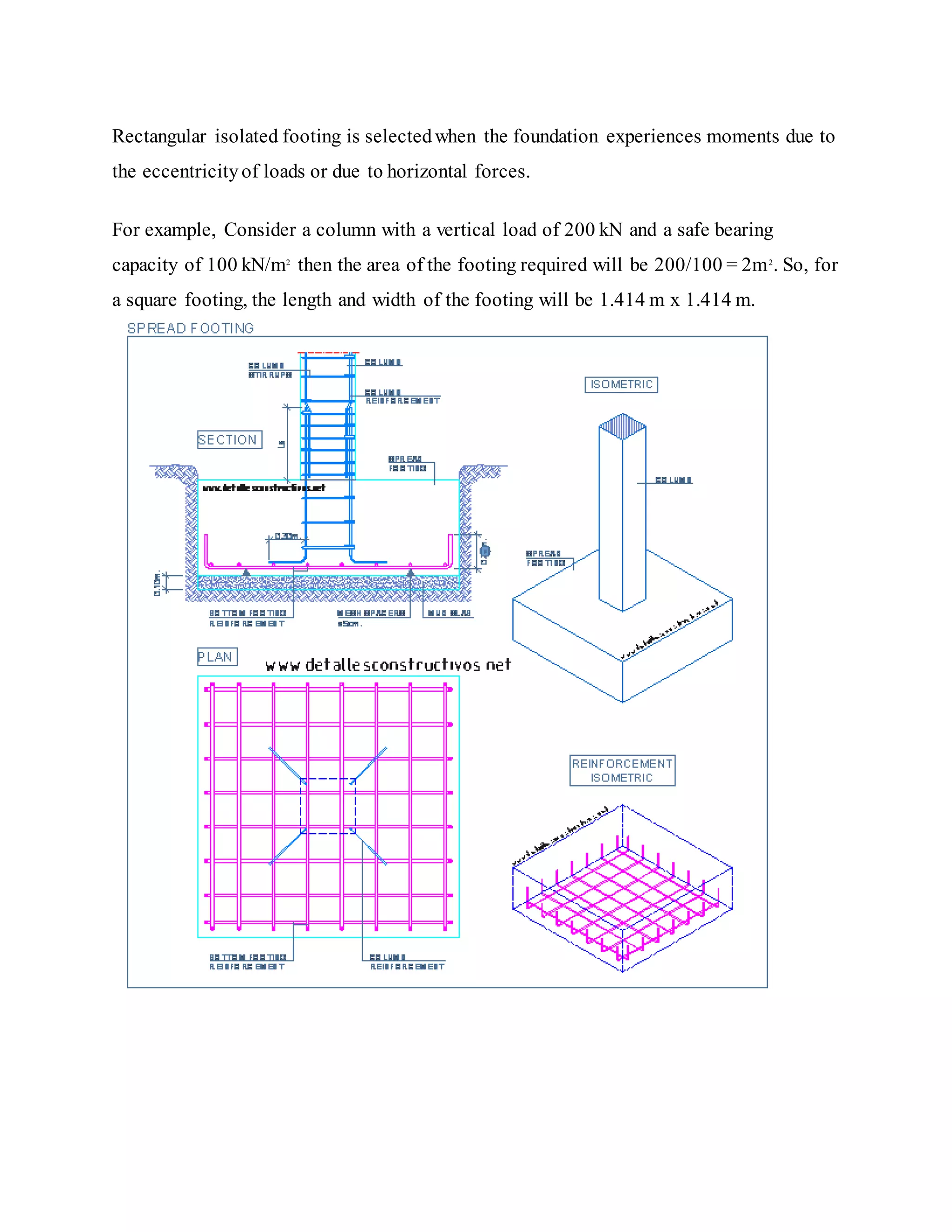
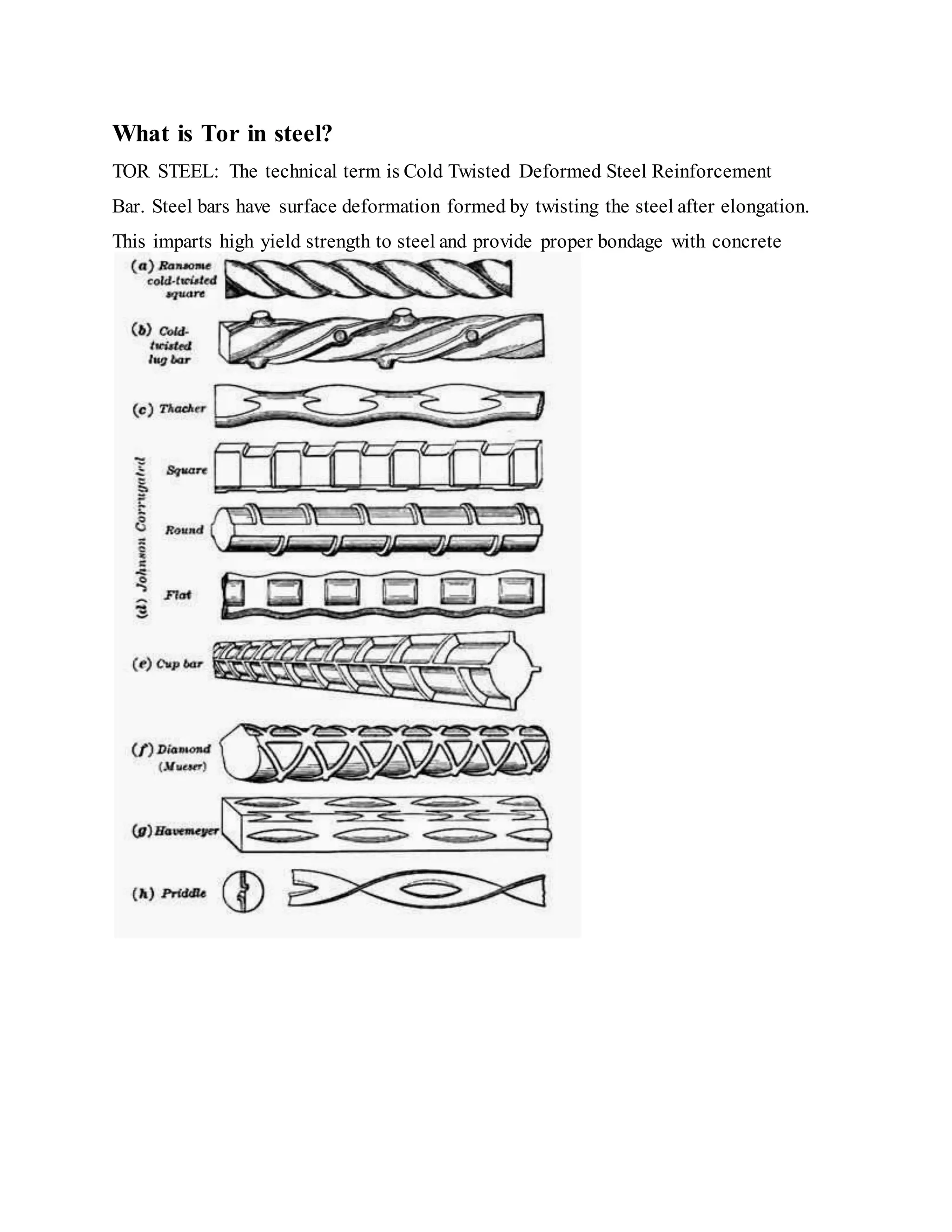
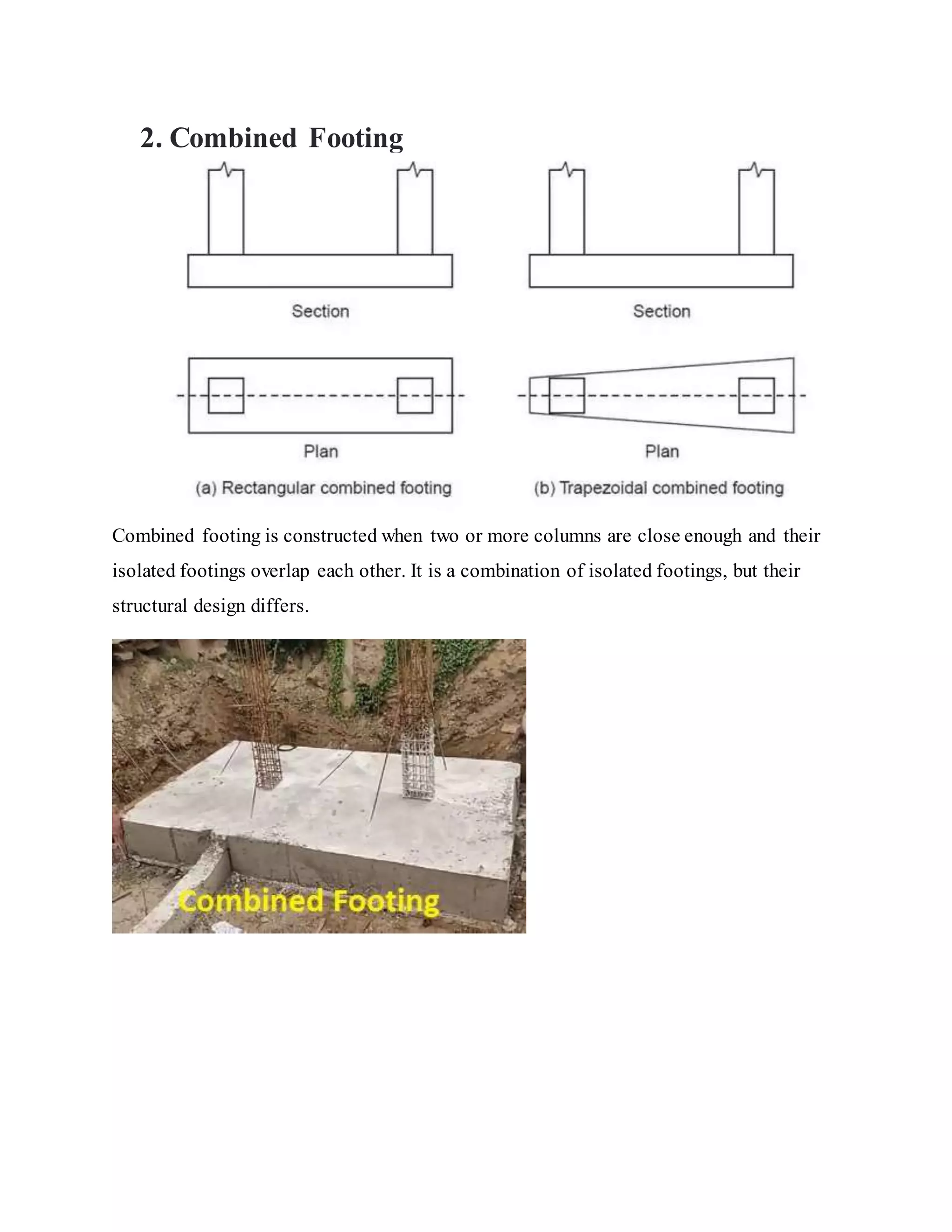
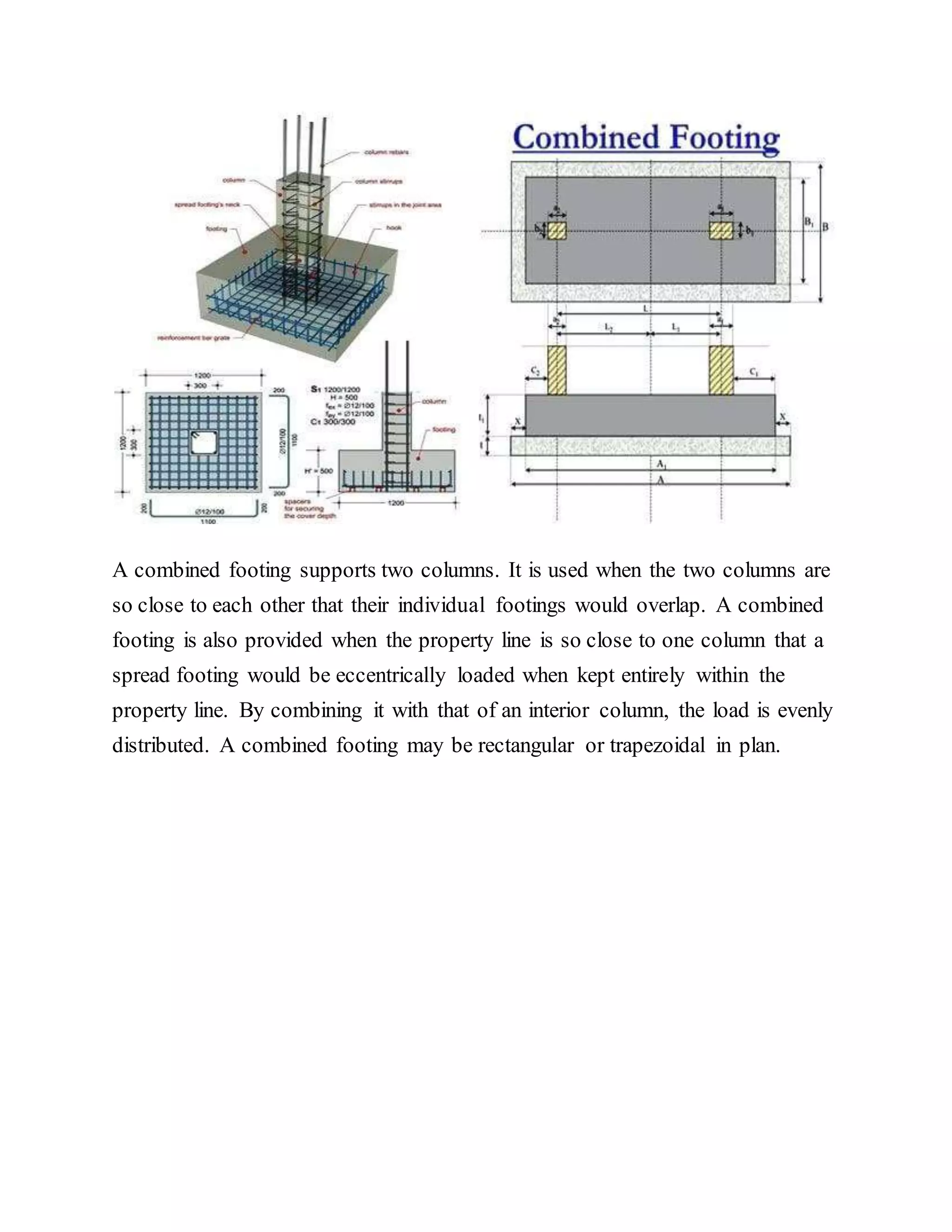
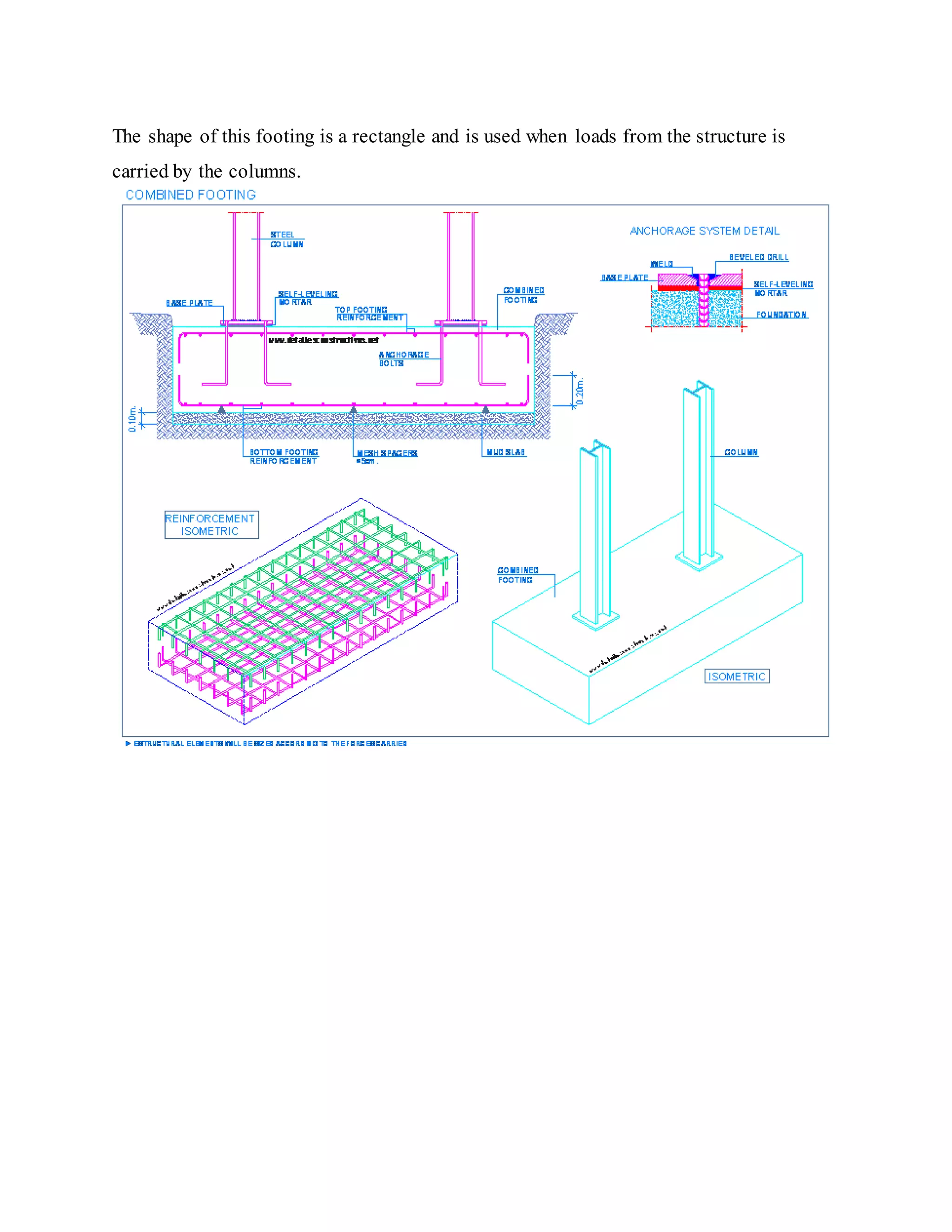
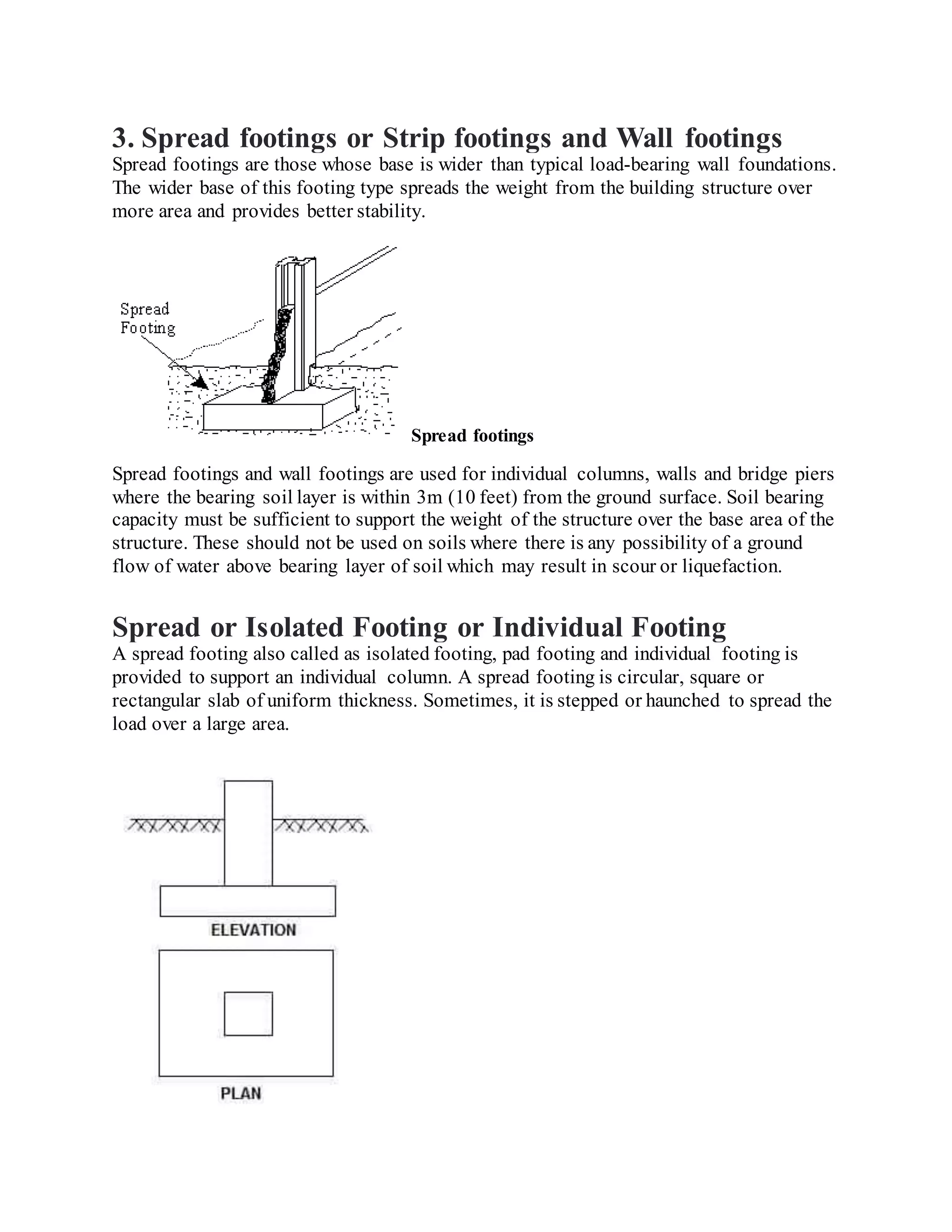
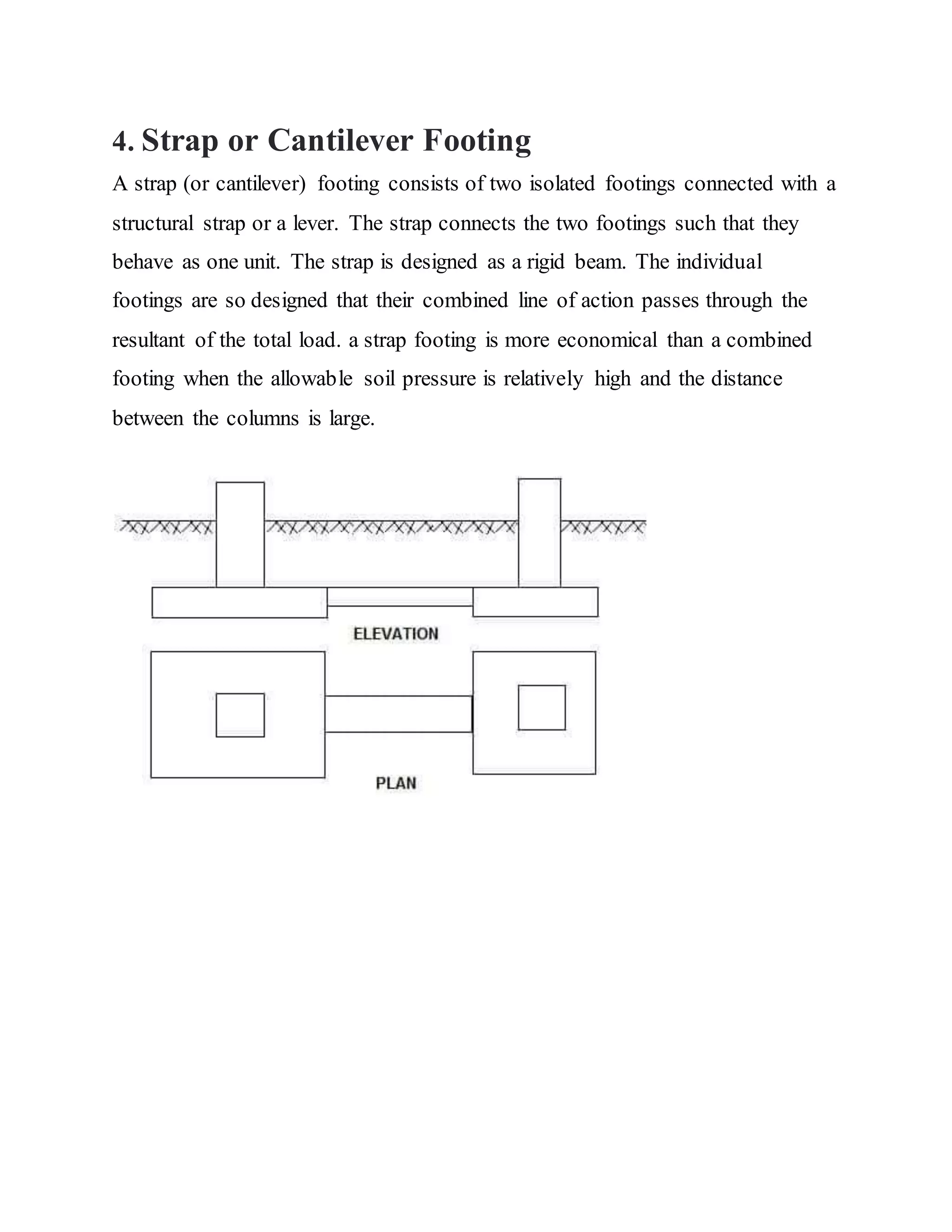
Building foundations are broadly classified as shallow and deep foundations. Types of shallow foundations include individual footings, combined footings, strip foundations, and raft or mat foundations. Deep foundations include pile foundations and drilled shafts or caissons. Combined footings are used when column footings are close together, while raft foundations are used for high structural loads. Drilled shafts can transfer larger loads than piles and are used when hard soil is 10-100m deep.