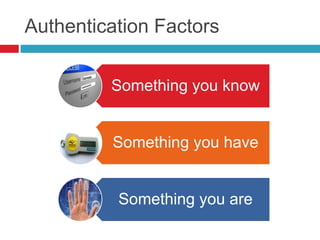
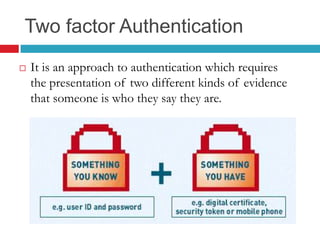
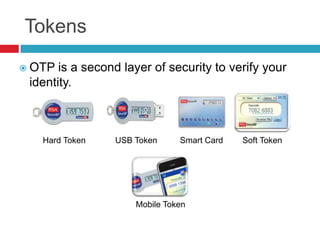
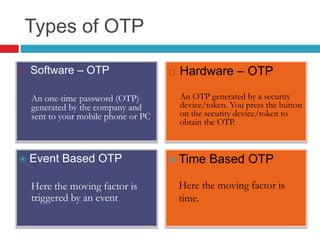
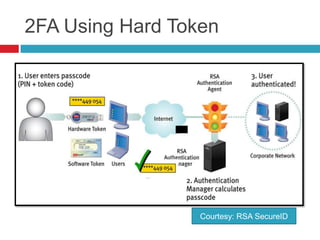
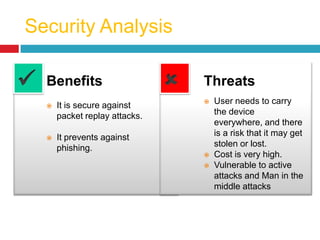
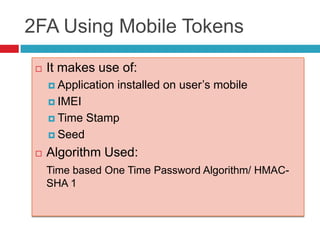
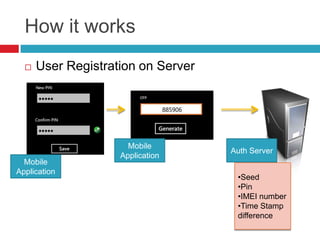
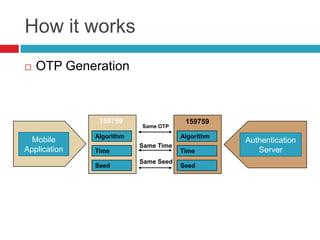
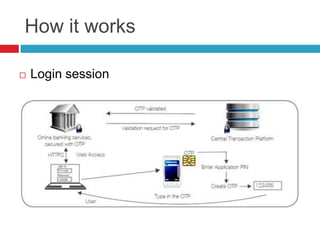
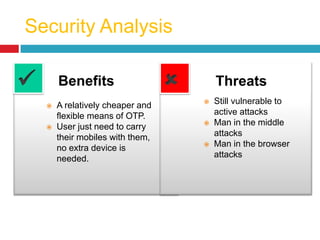
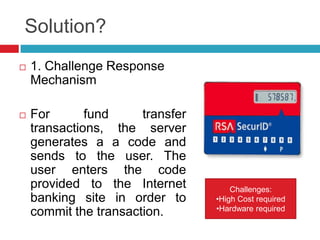
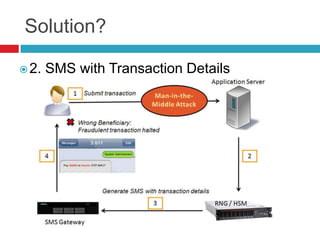
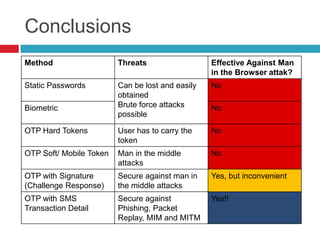
This document discusses two-factor authentication (2FA) as a method to strengthen user authentication beyond just a username and password. It describes how 2FA uses two different factors, something you know and something you have/are, to verify identity. Specifically, it evaluates using one-time passwords (OTPs) with hard tokens, mobile tokens, and SMS. While hardware tokens are very secure, they are also expensive and inconvenient. Mobile tokens are cheaper but still vulnerable to attacks. The best approach recommends sending the OTP via mobile token while sending transaction details via SMS to separate the factors and prevent SIM swap attacks. The document provides recommendations like using HTTPS and hashing to further improve security with 2FA.