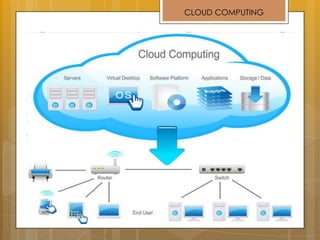
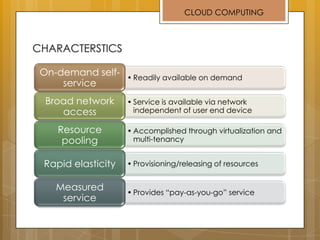
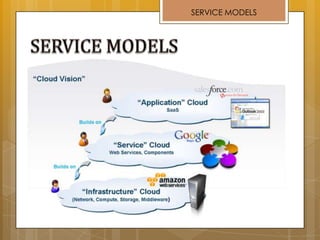
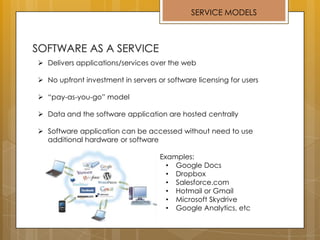
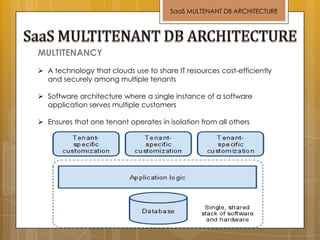
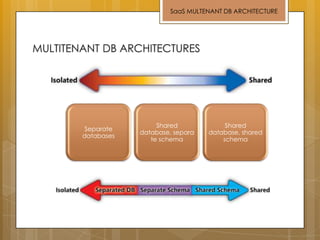
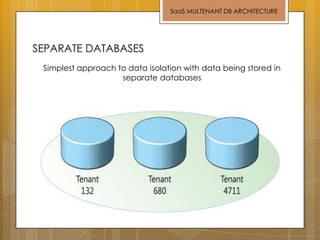
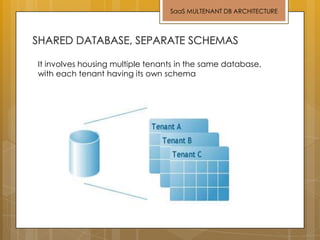
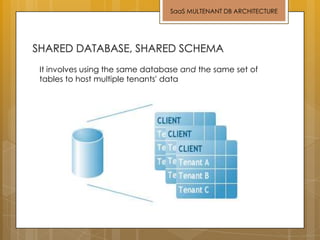
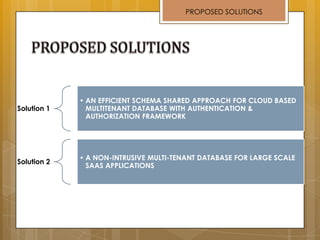
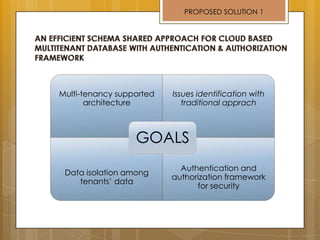
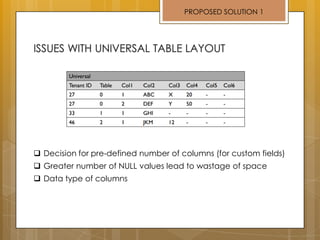
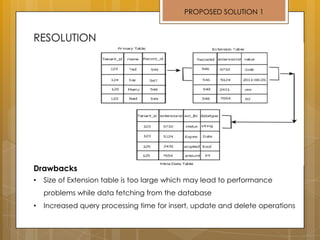
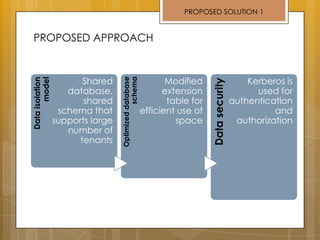
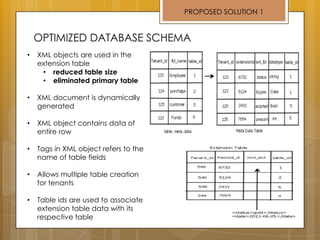
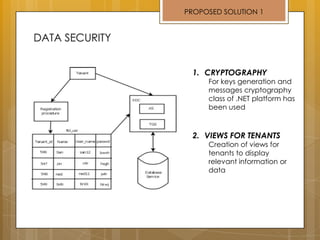
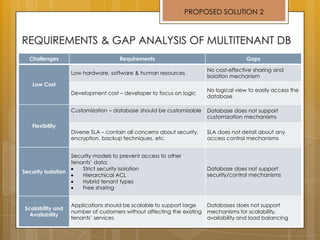
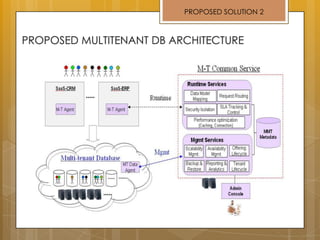
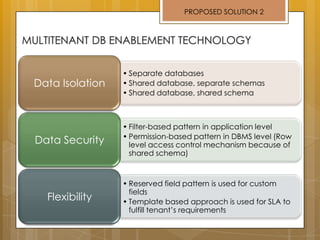
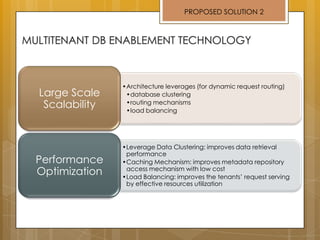
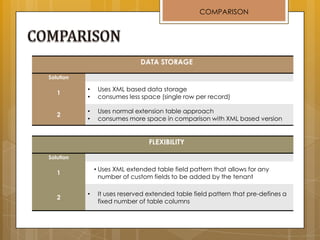
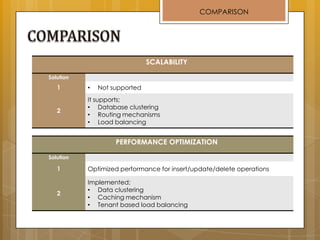
The document discusses cloud computing and service models including SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. It then describes challenges with multitenant databases and proposes two solutions. The first proposes an efficient shared schema approach with authentication and authorization. The second proposes a non-intrusive database for large-scale SaaS with data isolation, security, and scalability. It compares the solutions and recommends backup strategies, encrypted data storage, and unique ID generation.