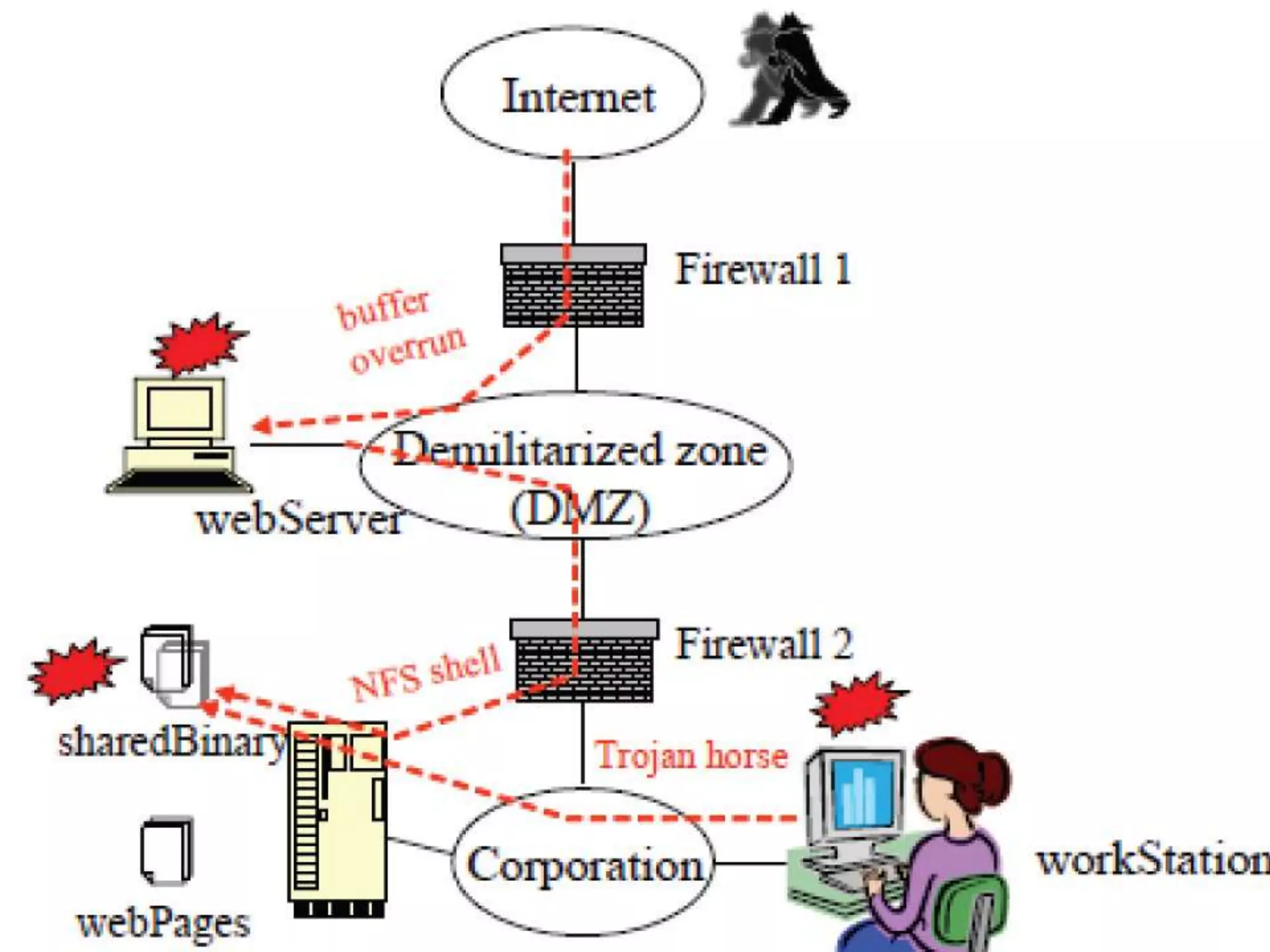
This document discusses situational awareness, both traditional and cyber, and presents a scenario of a cyber attack. It introduces the Instance Based Learning Theory (IBLT) model for evaluating a security analyst's cyber situational awareness when responding to network events during an island hopping attack. Key factors that influence the analyst's decisions are described. The IBLT model represents situations, decisions, and utilities to model how analysts make judgments based on prior experiences stored in memory.