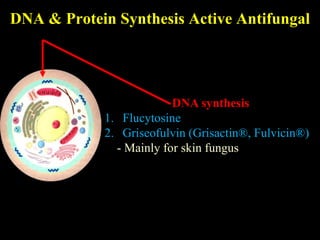
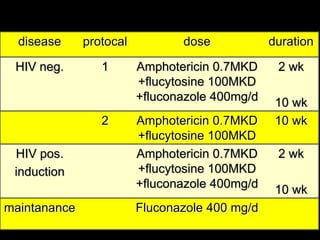
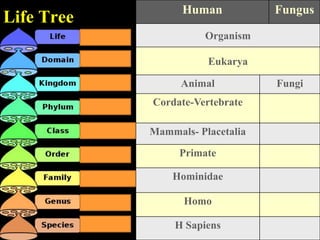
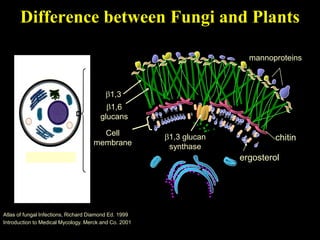
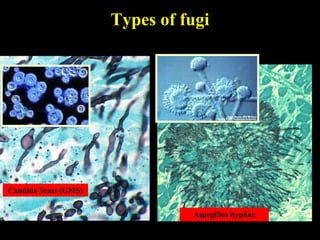
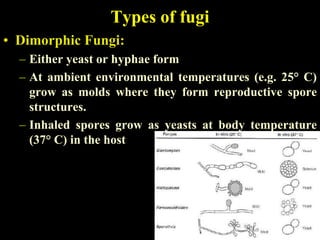
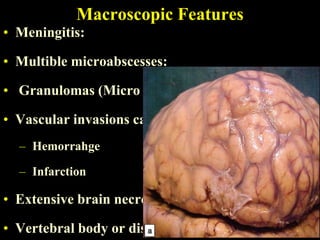
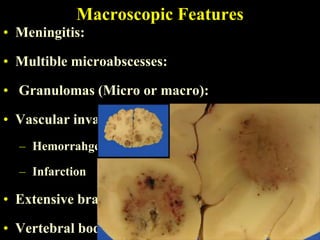
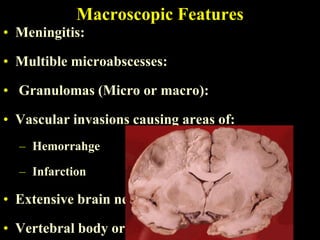
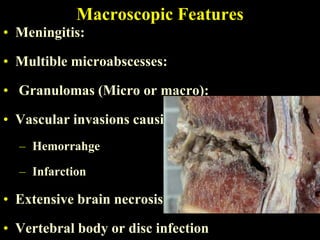
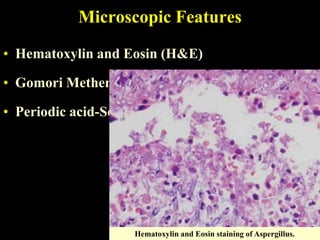
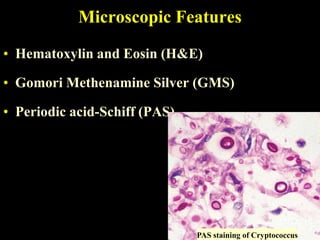
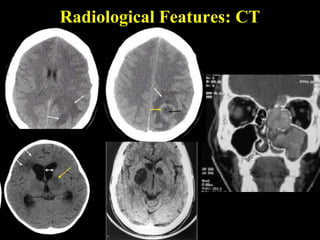
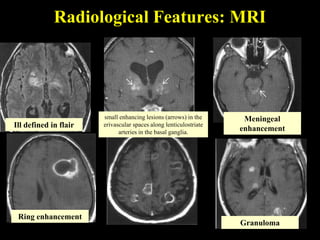
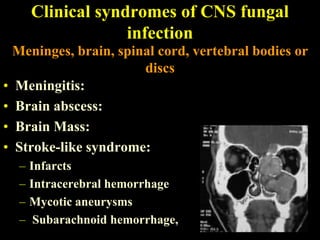
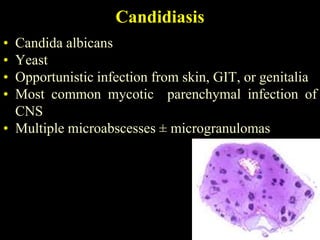
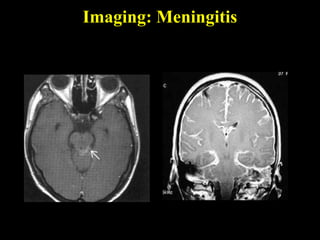
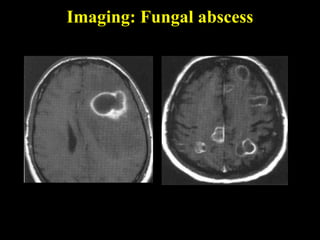
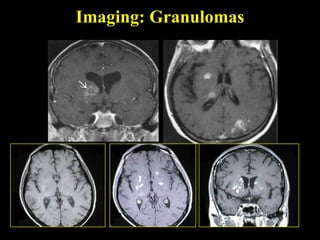
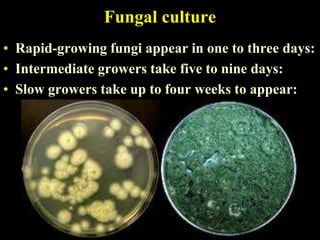
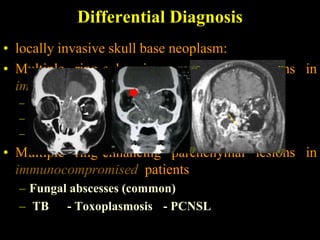
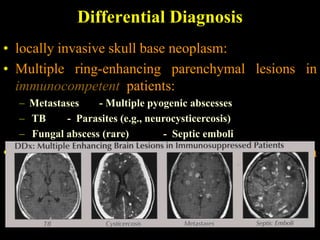
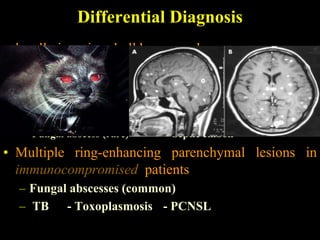
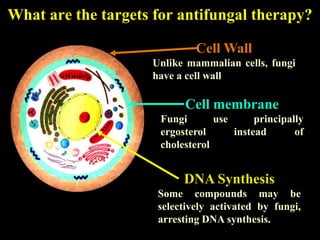
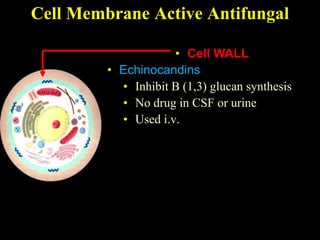
The document discusses central nervous system (CNS) fungal infections. It covers several topics including the common causative organisms, their characteristics, epidemiology, gross and histopathological features, radiological features, clinical presentation, diagnosis and differential diagnosis, and treatment. The most common CNS fungal infections are caused by Candida, Cryptococcus, and Aspergillus species. Diagnosis involves imaging, laboratory tests of blood and cerebrospinal fluid, and biopsy when possible. Treatment involves antifungal medications, with amphotericin B and fluconazole being two of the main options discussed.

































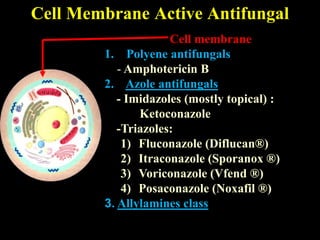

![Fluconazole (Diflucan®)
• Mechanism of action:
• Antifungal Activity: Broad spectrum for yeast only
• Rout of administration:
– Oral cap: 50 & 150 or syrup 50mg/5mL
– Intravenous: 50 ml (2mg/ml)
• Adverse effects:
– The most common adverse reaction is relatively minor gastrointestinal
upset
– Drug interaction:
• (Diflucan®) ↑ serum level of phenytoin, oral hypoglycemic
• (Diflucan®) serum level ↓ by cimetidin and Rifampin
• Dose:
– Loading dose for one day: Double maintenance dose (up to 400mg)
– Maintenance dose: 200-400mg/d on a single dose [Pediatric: 3-12 mg/kg/d
(max 400mg/d) ]
• Duration: until infection resolved](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fungalinfections2012-120326122005-phpapp02/85/Fungal-infections2012-63-320.jpg)