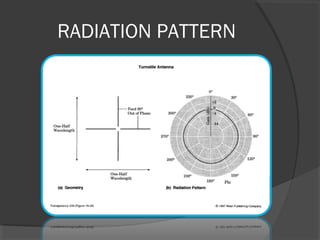
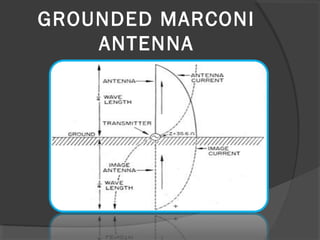
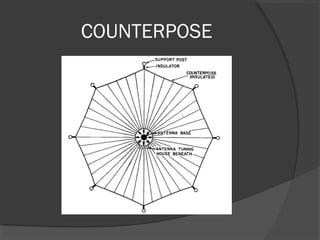
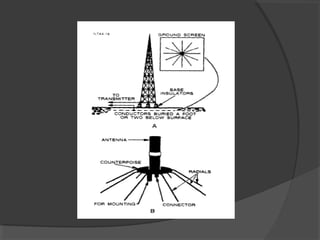
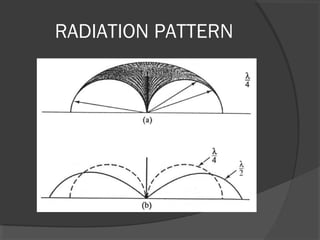
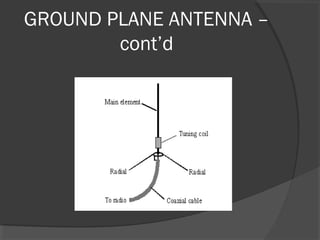
A turnstile antenna consists of two dipole antennas oriented at right angles and fed 90 degrees out of phase, producing an omnidirectional radiation pattern. It has 3dB lower gain than a single dipole but provides coverage in all directions without needing to rotate. Turnstile antennas are commonly used for FM radio reception. A Marconi antenna is a grounded monopole antenna used at frequencies below 2MHz that requires a grounding path. When near the ground, the earth acts as a reflector influencing the radiation pattern. A counterpoise is used to improve ground effects for antennas over poor conducting soil. A ground plane antenna is a variant of a dipole fed with coaxial cable using radials instead of a hollow inner