This document provides information about generators and their operation. Some key points:
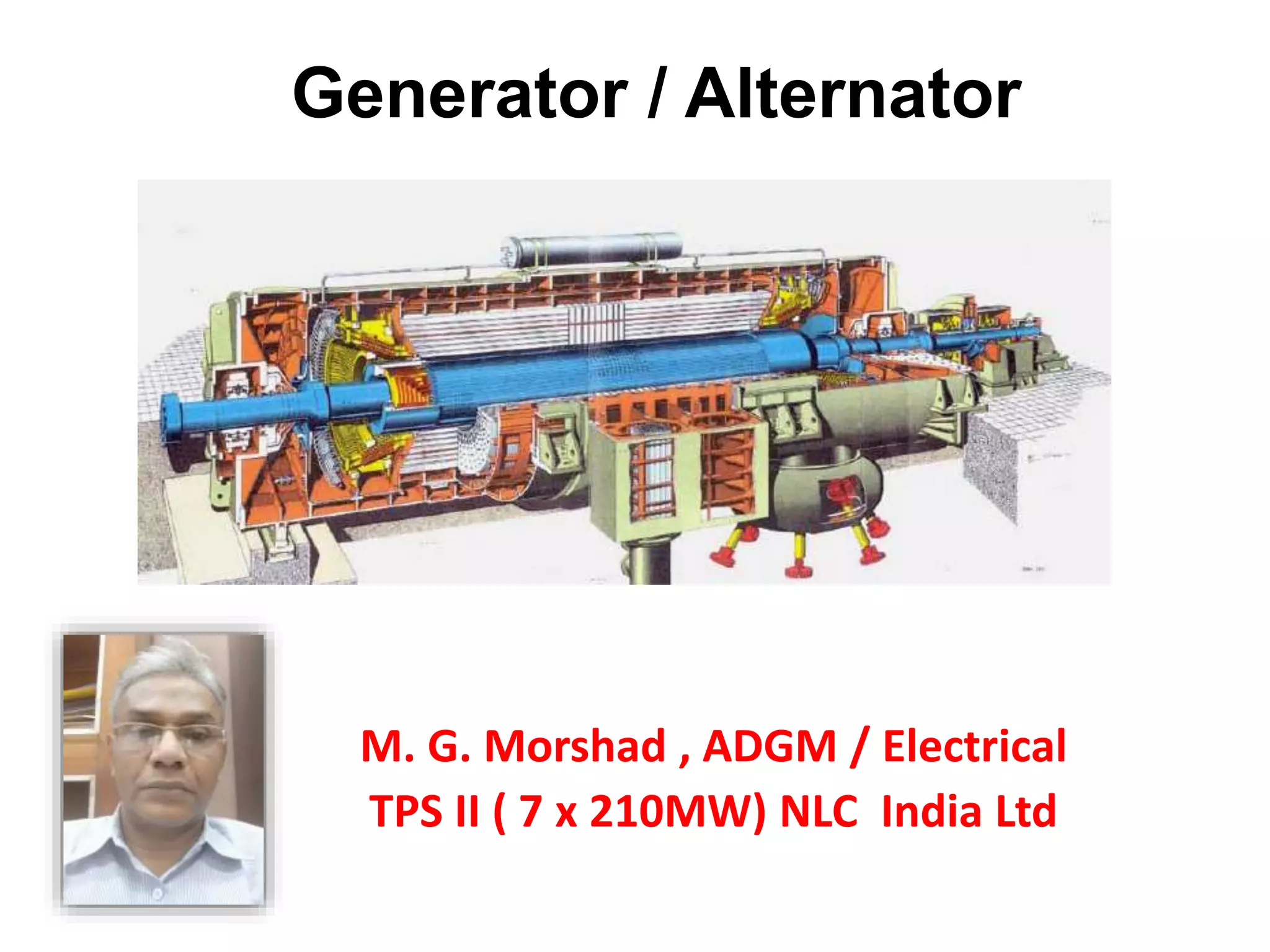
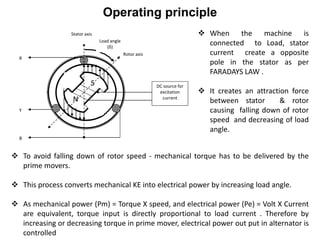
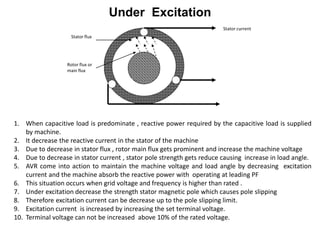
1. Generators are synchronous machines that convert mechanical energy from turbines into electrical energy. The rotor is an electromagnet controlled by excitation current to produce rotating magnetic fields.
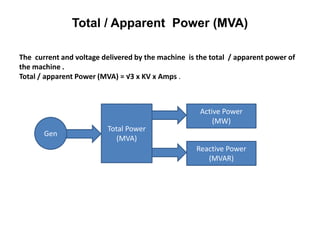
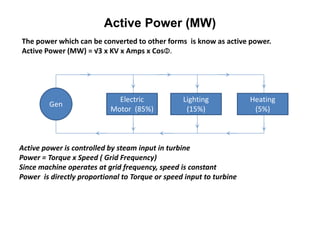
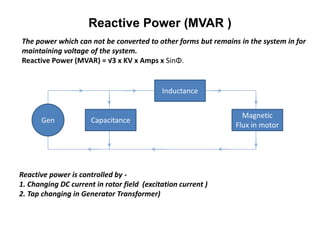
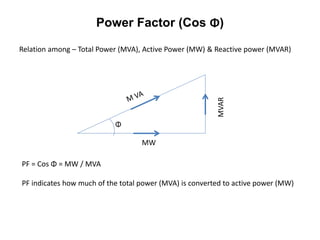
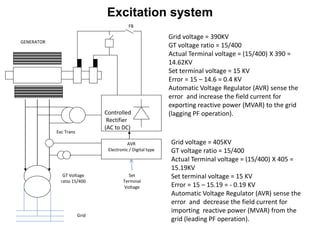
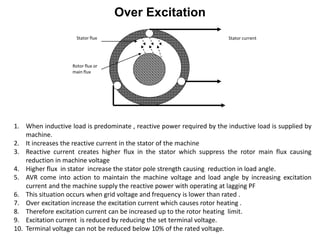
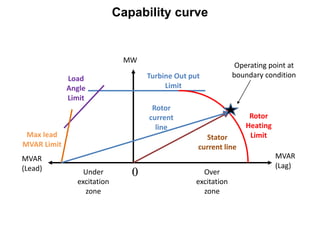
2. Generators can deliver active power and reactive power by operating at lagging or leading power factors. Active power is controlled by steam input to the turbine, while reactive power is controlled by excitation current.
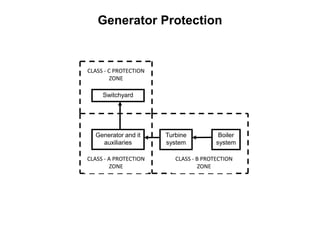
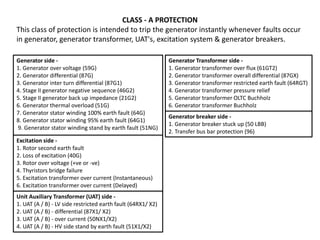
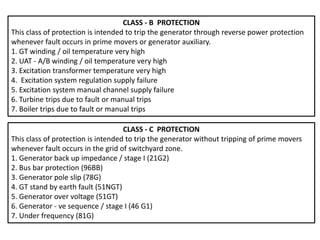
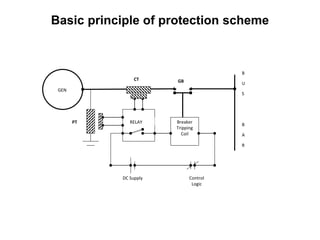
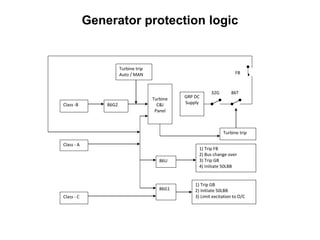
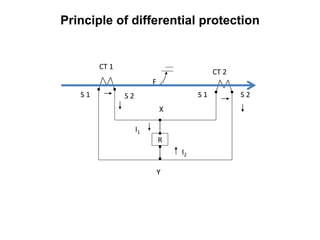
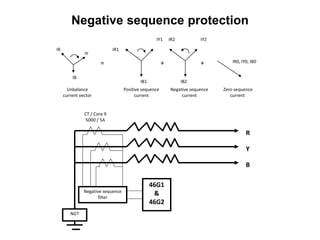
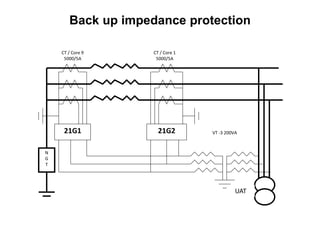
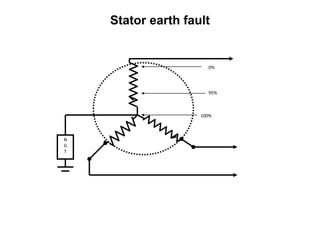
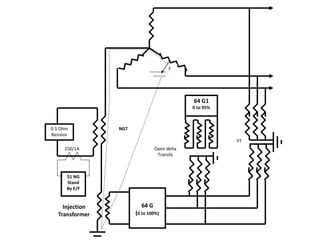
3. Generators have different protection systems to trip for faults in the generator itself (Class A) or for faults in connected equipment like turbines (Class B). Protection devices monitor parameters like voltage, current, temperature and differential currents.
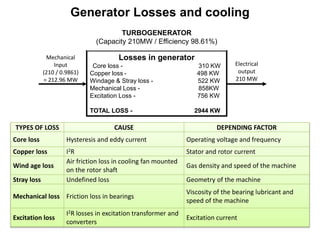
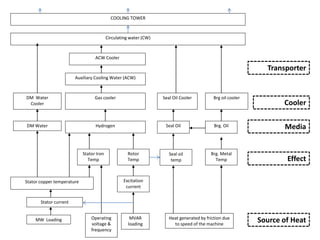
4. Cooling systems are