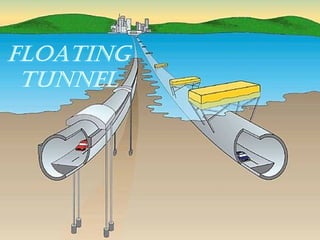
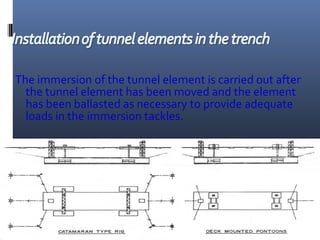
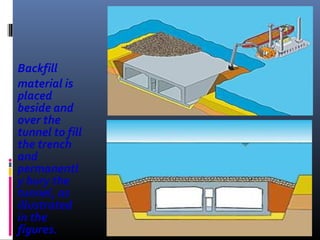
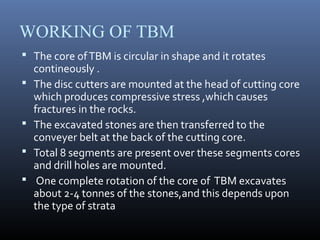
The document discusses different types of tunnels used for transportation, including those resting on the sea bed, floating in the sea, and tunnels dug below the sea bed. It focuses on submerged floating tunnels, which are tube-like structures that float underwater at a certain depth, fixed by cables. This allows tunnels to be constructed in extremely deep waters where conventional bridges or tunnels are not feasible. The document outlines the principles behind submerged floating tunnels and describes their construction process which involves building segments on dry dock and joining them together underwater. Examples of significant tunnels discussed include the Channel Tunnel between Britain and France, and the Seikan Tunnel in Japan. Tunnel boring machines are also described as the method used to excavate underwater and below sea bed tunnels