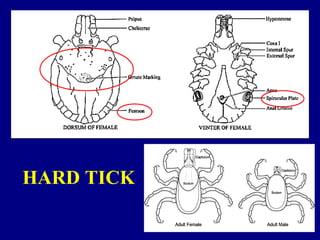
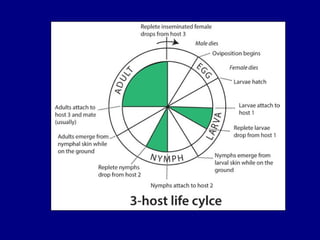
This document provides information about different types of mites and ticks. It begins by listing different orders and families of mites, including Acaridae which are commonly found associated with bees and wasps. It then provides more details on several mite species, including Acarus siro which lives on grains, and Tyrophagus species which live on foods like cheese and can carry pathogens. The document also mentions the mite Rhyzoglyphus robini which infests bulbs and floral plants. Finally, it discusses ticks, comparing features of hard and soft ticks like their life cycles and feeding behaviors.