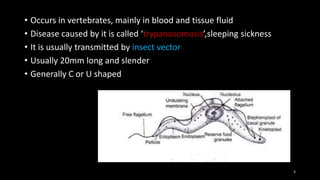
Trypanosoma is a genus of parasitic protozoa that can cause diseases like sleeping sickness in vertebrates. It is transmitted by insect vectors and exists in different morphological forms depending on its host. In vertebrates it is usually trypomastigote form, which is elongated with an undulating membrane and flagellum. In invertebrates it can be procyclic or epimastigote forms. Its life cycle involves multiplication in the blood of vertebrates followed by transmission back to the insect when it takes a different form. Symptoms in infected animals include fever, anemia, edema and emaciation. Diagnosis involves microscopic examination of blood and tissue or animal inoculation. Treatment options