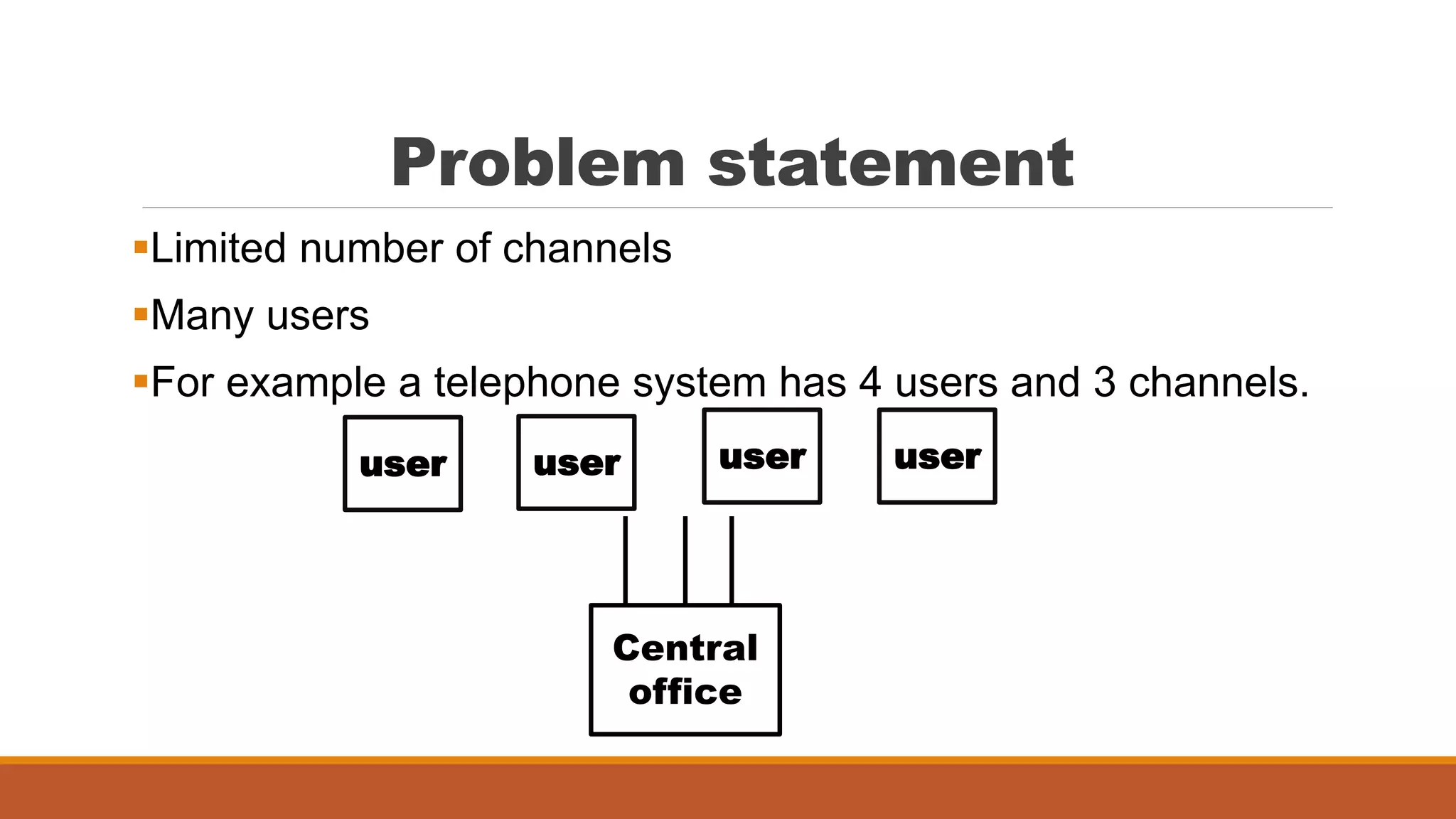
Trunking theory, developed by Erlang, is utilized to optimize the allocation of limited communication channels among many users, such as in telephone and cellular systems. It defines essential concepts like traffic intensity, set-up time, and types of trunked systems, specifically blocked calls cleared and blocked calls delayed. The document explains how to calculate traffic intensity to ensure adequate capacity and service quality for users at peak times.