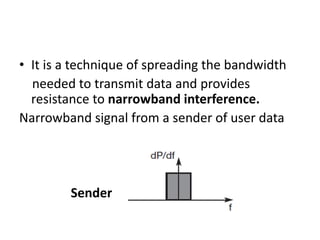
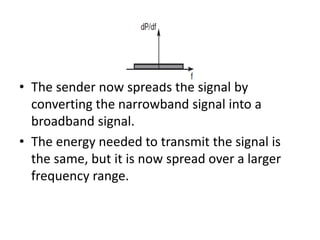
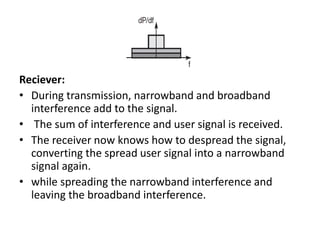
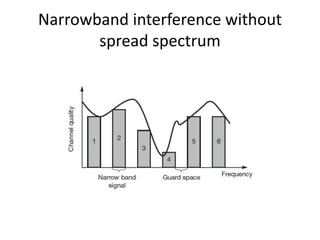
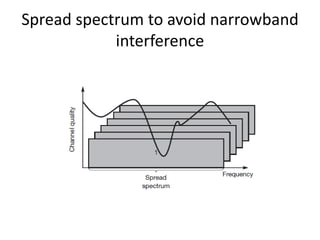
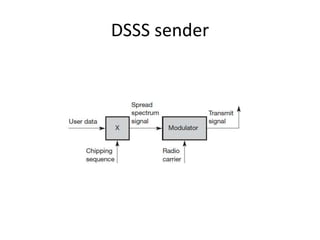
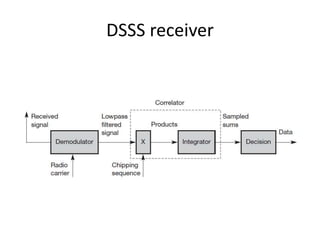
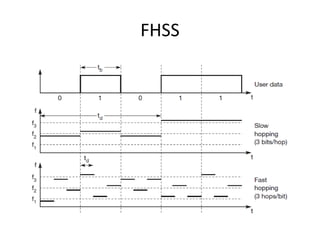
Spread spectrum is a technique that spreads user data signals across a larger frequency band to provide resistance to narrowband interference. It works by converting a narrowband signal into a broadband signal at the sender, then reconverting it back to narrowband at the receiver while spreading any interference. Two common spread spectrum techniques are direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS), which spreads signals using a chipping sequence, and frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS), which splits the bandwidth into smaller channels and hops between them.