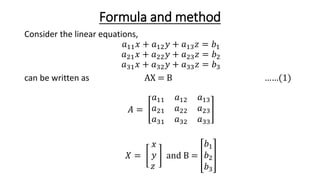
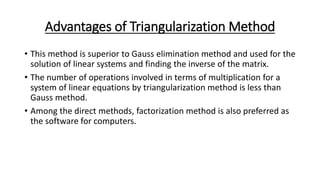
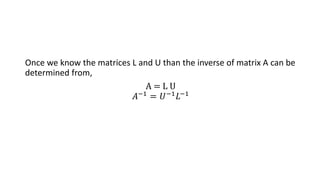This document describes the triangularization method for solving systems of linear equations. It involves decomposing the coefficient matrix A into the product of a lower triangular matrix L and an upper triangular matrix U. This decomposition is done by calculating the elements of L and U such that their product equals the original matrix A. The system of linear equations can then be solved through back substitution by first solving the system LUx=B as two separate systems involving L and U. The triangularization method is preferable to Gaussian elimination as it requires fewer operations and can also be used to find the inverse of a matrix. However, it fails if any diagonal elements of L or U are zero.