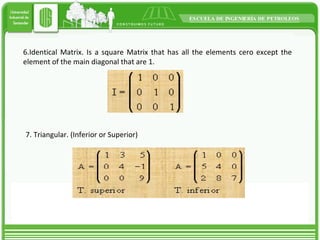
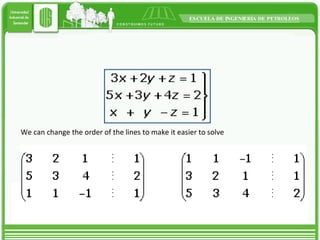
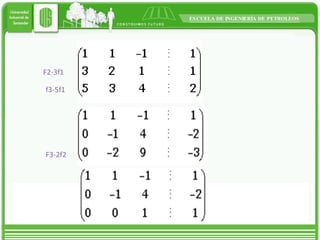
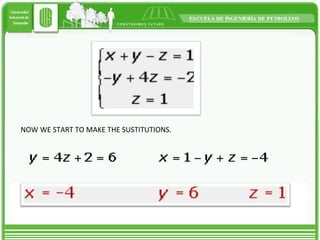
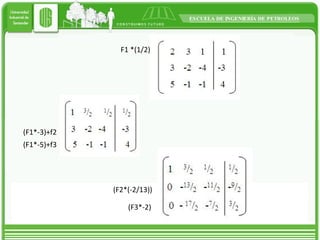
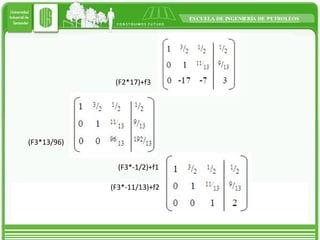
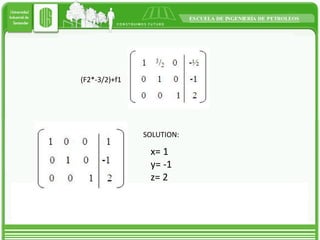
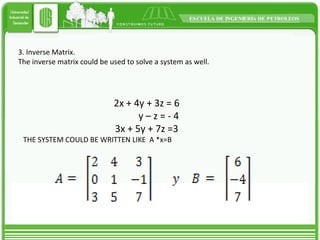
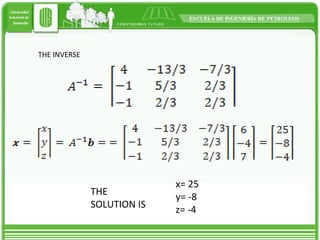
This document discusses different types of matrices and methods for solving linear equation systems. It describes rectangular, transposed, void, symmetric, diagonal, and identity matrices. It also explains the simple Gauss method which converts the matrix into upper triangular form and then back substitution to solve for unknown values. The Gauss-Jordan method converts the matrix into an identity matrix to more easily solve the system. Inverse matrices can also be used to solve systems by writing it as A*x=B and then calculating x as the inverse of A multiplied by B.