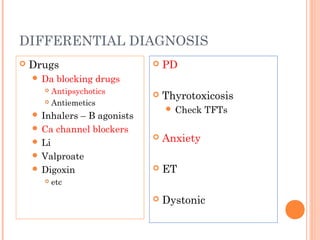
This document discusses tremors and Parkinson's disease. It provides information on different types of tremors, including essential tremor and drug-induced tremors. It also discusses Parkinson's disease and how it is diagnosed using a DAT scan. Two case studies are presented, one with drug-induced parkinsonism and another with essential tremor. The treatment options for different conditions are outlined.



















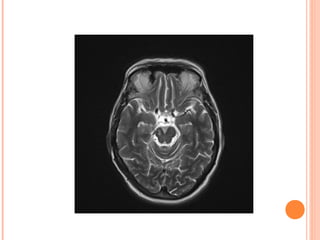
![[123I]FP-CIT SPECT (DAT
SCAN)
Normal Abnormal
caudate
putamen](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tremorsforgpmarch2015-copy-170308220355/85/Tremors-2017-23-320.jpg)