This document provides an overview of Parkinson's disease including its aetiology, incidence, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment. Some key points:
- It is the most common cause of parkinsonism and is often idiopathic but can be caused by environmental toxins, viral infections or rare genetic mutations.
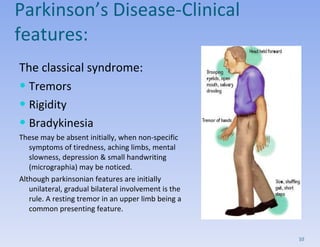
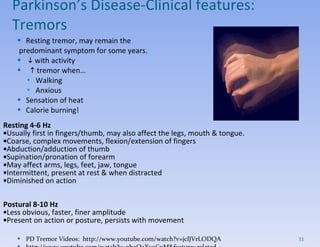
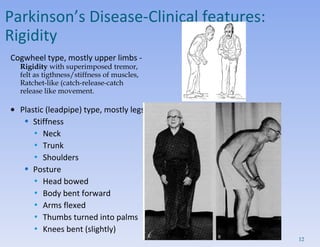
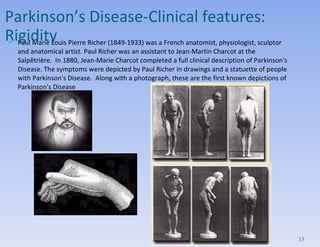
- Clinical features include tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia and impaired gait/posture. Diagnosis is clinical and imaging rules out other causes.
- Prognosis is variable but onset after age 70 is unlikely to shorten lifespan. Current treatment focuses on symptomatic relief using levodopa and other dopamine agonists and inhibitors.






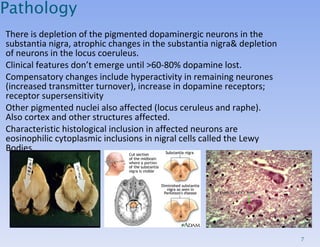






![Investigations: The diagnosis is made clinically, as there is no diagnostic test for Parkinson's disease. Imaging (CT or MRI) of the head may be needed if there are any features suggestive of pyramidal, cerebellar or autonomic involvement, or the diagnosis is otherwise in doubt (e.g to exclude stroke). [ 18 F]dopa PET and β-CIT SPECT images. [ 18 F]dopa PET uptake in the putamen is reduced in PD.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parkinson-100715002508-phpapp02/85/Parkinsons-Disease-18-320.jpg)























