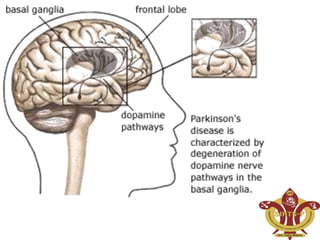
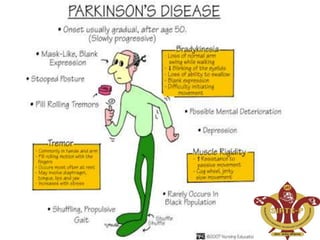
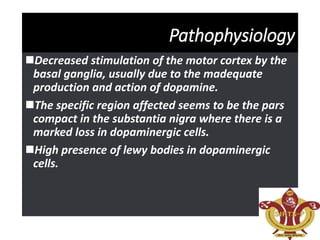
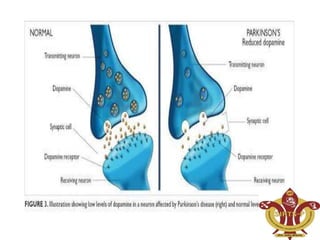
This document discusses Parkinson's disease (PD), a chronic neurodegenerative movement disorder caused by a lack of dopamine in the brain. It describes dopamine and its role in PD, the major symptoms of tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, postural instability, and fatigue. It then provides more details on tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability. The document also covers potential causes of PD including genetic and environmental factors, as well as the pathophysiology involving decreased stimulation of the motor cortex due to inadequate dopamine production and loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra.