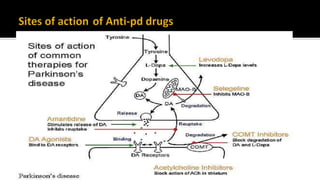
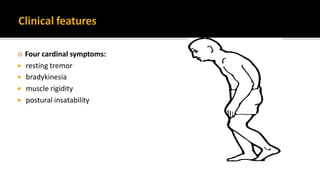
This document discusses Parkinson's disease (PD), including its diagnosis, progression, and treatment. PD is the second most common neurodegenerative disease characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons. The four cardinal symptoms are resting tremor, bradykinesia, muscle rigidity, and postural instability. Diagnosis involves confirming a parkinsonian syndrome and excluding other possible causes. Treatment focuses on reducing motor symptoms through pharmacological therapies like levodopa and dopamine agonists. As PD progresses, many patients experience motor fluctuations and dyskinesia that require adjustment of medications.








![ Because people with PD may develop impaired cognitive ability, a communication
deficit and/or depression, they should be provided with both oral and written
communication throughout the course of the disease. NICE Level D (GPP) [2006]
Offer people with Parkinson's disease an accessible point of contact with specialist
services. This could be provided by a Parkinson's disease nurse specialist. [2006]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-10-320.jpg)
![ Suspect Parkinson's disease in people presenting with tremor, stiffness, slowness,
balance problems and/or gait disorders. [NICE 2006]
If Parkinson's disease is suspected, refer people quickly and untreated to a specialist
with expertise in the differential diagnosis of this condition. [NICE 2006, amended
2017]
Diagnose Parkinson's disease clinically, based on the UK Parkinson's Disease Society
Brain Bank Clinical Diagnostic Criteria. [NICE 2006]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-11-320.jpg)

![ People diagnosed with Parkinson's disease should be seen at regular intervals of 6–
12 months to review their diagnosis and reconsidered if atypical clinical features
develop.[NICE 2006]
In patients with newly diagnosed PD, older age at onset and rigidity/hypokinesia as
an initial symptom should be used to predict more rapid rate of motor progression.
AAN Level B
The presence of associated comorbidities (stroke, auditory deficits, and visual
impairments), Postural Instability/Gait difficulty (PIGD), and male sex may be used
to predict faster rate of motor progression. AAN Level C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-13-320.jpg)
![ Consider SPECT for people with tremor if essential tremor cannot be clinically
differentiated from parkinsonism. [NICE 2006, amended 2017]
Do not use positron emission tomography (PET) in the differential diagnosis of
parkinsonian syndromes, except in the context of clinical trials. [NICE 2006,
amended 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-14-320.jpg)
![ Do not use structural MRI to diagnose Parkinson's disease. It may be considered in
the differential diagnosis of other parkinsonian syndromes. [NICE 2006, amended
2017]
Do not use acute levodopa and apomorphine challenge tests and objective smell
testing in the differential diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes. [NICE 2006,
amended 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-15-320.jpg)











![ Antiparkinsonian medicines should not be withdrawn abruptly or allowed to fail
suddenly due to poor absorption to avoid the potential for acute akinesia. [NICE
2006]
The practice of withdrawing people from their antiparkinsonian drugs (so called
'drug holidays') to reduce motor complications should not be undertaken because
of the risk of neuroleptic malignant syndrome. [NICE 2006]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-27-320.jpg)
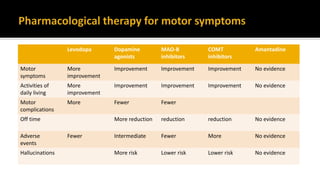
![ If symptoms are very mild, the patient may be choosen not to begin therapy.
Offer levodopa to people in the early stages of Parkinson's disease whose motor
symptoms impact on their quality of life. [NICE 2017]
Consider a choice of dopamine agonists, levodopa or monoamine oxidase B (MAO-
B) inhibitors for people in the early stages of Parkinson's disease whose motor
symptoms do not impact on their quality of life. . [NICE 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-28-320.jpg)
![ Offer a choice of dopamine agonists, MAO-B inhibitors or COMT inhibitors as an
adjunct to levodopa for people with Parkinson's disease who have developed
dyskinesia or motor fluctuations despite optimal levodopa therapy [NICE 2017]
If dyskinesia is not adequately managed by modifying existing therapy, consider
amantadine [NICE 2017] AAN Level C
Do not offer anticholinergics to people with Parkinson's disease who have
developed dyskinesia and/or motor fluctuations [NICE 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-29-320.jpg)
![ Do not offer ergot-derived dopamine agonists as first-line treatment for Parkinson's
disease . [NICE 2017]
Only consider an ergot-derived dopamine agonist as an adjunct to levodopa for :
who have developed dyskinesia or motor fluctuations despite optimal levodopa
therapy
whose symptoms are not adequately controlled with a non-ergot-derived
dopamine agonist.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-30-320.jpg)
![ The different types of impulse control disorders –
▪ compulsive gambling,
▪ hypersexuality,
▪ binge eating
▪ obsessive shopping
Recognise that impulse control disorders can develop in a person with Parkinson's
disease who is on any dopaminergic therapy at any stage in the disease course. [NICE
2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-32-320.jpg)
![ Impulse control disorders can also develop while taking dopaminergic therapies other
than dopamine agonists. [NICE 2017]
Recognise that the following are associated with an increased risk of developing
impulse control disorders:
Dopamine agonist therapy.
A history of previous impulsive behaviours.
A history of alcohol consumption and/or smoking. [NICE 2017]
Discuss potential impulse control disorders at review appointments, particularly when
modifying therapy, and record that the discussion has taken place. [NICE 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-33-320.jpg)
![ first gradually reduce any dopamine agonist and monitor [NICE 2017]
Offer cognitive behavioural therapy targeted at impulse control disorders if
modifying dopaminergic therapy is not effective [NICE 2017]
Discuss the following with the person and their family members](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-34-320.jpg)
![ Good sleep hygiene should be advised in people with PD with any sleep disturbance
NICE Level D (GPP)
Consider modafinil if a detailed sleep history has excluded reversible
pharmacological and physical causes. [NICE 2017] Level D(GPP), (AAN 2010)
Care should be taken to identify and manage RLS and RBD in people with PD and
sleep disturbance. NICE Level D (GPP)
Consider clonazepam or melatonin to treat RBD if a medicines review has addressed
possible pharmacological causes [NICE 2017]
Methylphenidate may be considered for fatigue (AAN 2010)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-35-320.jpg)
![ Consider levodopa or oral dopamine agonists to treat nocturnal akinesia in people
with Parkinson's disease. [NICE 2017]
Consider rotigotine if levodopa and/or oral dopamine agonists are not effective in
treating nocturnal akinesia. [NICE 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-36-320.jpg)
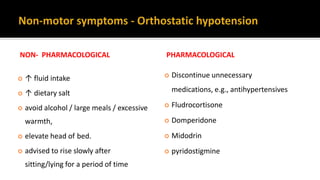
![ Review the person's existing medicines to address possible pharmacological causes:
▪ antihypertensives (including diuretics)
▪ Dopaminergics
▪ Anticholinergics
▪ Antidepressants [NICE 2017]
Consider midodrine for people with Parkinson's disease and orthostatic Hypotension
[NICE 2017]
If midodrine is contraindicated, not tolerated or not effective, consider
fludrocortisone [NICE 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-38-320.jpg)
![ Consider emotional fluctuations associated with “OFF” periods → Reduce “OFF”
time
When depression is accompanied by symptoms of anxiety, the first priority should
usually be to treat the depression. [NICE 2017]
For patients with persistent subthreshold depressive symptoms or mild to
moderate depression, consider CBT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-39-320.jpg)

![ Do not treat hallucinations and delusions if they are well tolerated by the person
with Parkinson's disease and their family members [NICE 2017]
Consider quetiapine to treat hallucinations and delusions in people with Parkinson's
disease who have no cognitive impairment, if not effective, offer clozapine
[NICE 2017]
Be aware that lower doses of quetiapine and clozapine are needed for people with
Parkinson's disease than in other indications
Do not offer olanzapine to treat hallucinations and delusions, other antipsychotic
medicines (such as phenothiazines and butyrophenones) can worsen the motor
features[NICE 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-41-320.jpg)

![ Donepezil should be considered for the treatment of dementia in PD. AAN Level B
Consider memantine for people with Parkinson's disease dementia, only if
cholinesterase inhibitors are not tolerated or are contraindicated. [NICE 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-43-320.jpg)
![ Eating chewing gum or a hard candy often decreases drooling by triggering
increased spontaneous swallowing movements.
Only consider pharmacological management for drooling of saliva in people with
Parkinson's disease if non-pharmacological management is ineffective.
Consider glycopyrronium bromide or topical atropine, if not effective consider
botulinum toxin A [NICE 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-44-320.jpg)
![ Vitamin E should not be used as a neuroprotective therapy for people with PD.
[NICE Level A 2006 amended 2017]
Co-enzyme Q10, dopamine agonists, monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) inhibitors
should not be used as a neuroprotective therapy for people with PD, except in the
context of clinical trials. [NICE Level B 2006 amended 2017]
45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-45-320.jpg)
![ Consider the Alexander Technique for people with Parkinson's disease who are
experiencing balance or motor function problems [NICE 2017]
no evidence that one type of physiotherapy was superior to others](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-46-320.jpg)







![ Offer people with advanced Parkinson's disease best medical therapy, which may
include intermittent apomorphine injection and/or continuous subcutaneous
apomorphine infusion. [NICE 2017]
Apomorphine (subcutaneous infusion or injections)-Apomorphine is the most
potent dopamine receptor agonist and it can provide symptom relief similar to
that of L-dopa. Apomorphine is rapidly absorbed, with onset of effect within 5-15
minutes of subcutaneous injection.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-54-320.jpg)
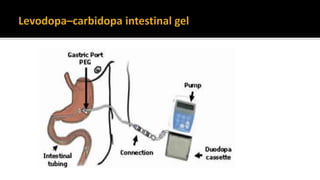
![ Levodopa–carbidopa intestinal gel is currently available through an NHS England
clinical commissioning policy. It is recommended that this policy is reviewed in light
of this guidance. [NICE 2017]
Adv - faster absorp-tion, and maintenance of more constant levels of levodopa.
L-Dopa emulsion can be applied by an external pump via a percutaneous tubing into
the jejunal cavity in order to provide a nearly constant continuous supply of L-Dopa
to the blood and thus to the CNS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-180121191544/85/parkinsons-disease-recent-updates-55-320.jpg)