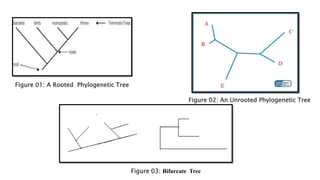
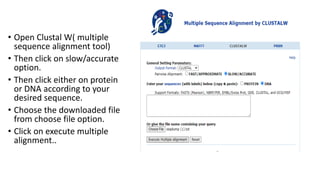
The document discusses Tree View, a software for visualizing phylogenetic trees, showing evolutionary relationships among species. It covers types of phylogenetic trees, including rooted, unrooted, and bifurcating trees, and outlines their applications in understanding human origins and disease origins. Additionally, it provides a step-by-step guide on generating a phylogenetic tree using related software tools.