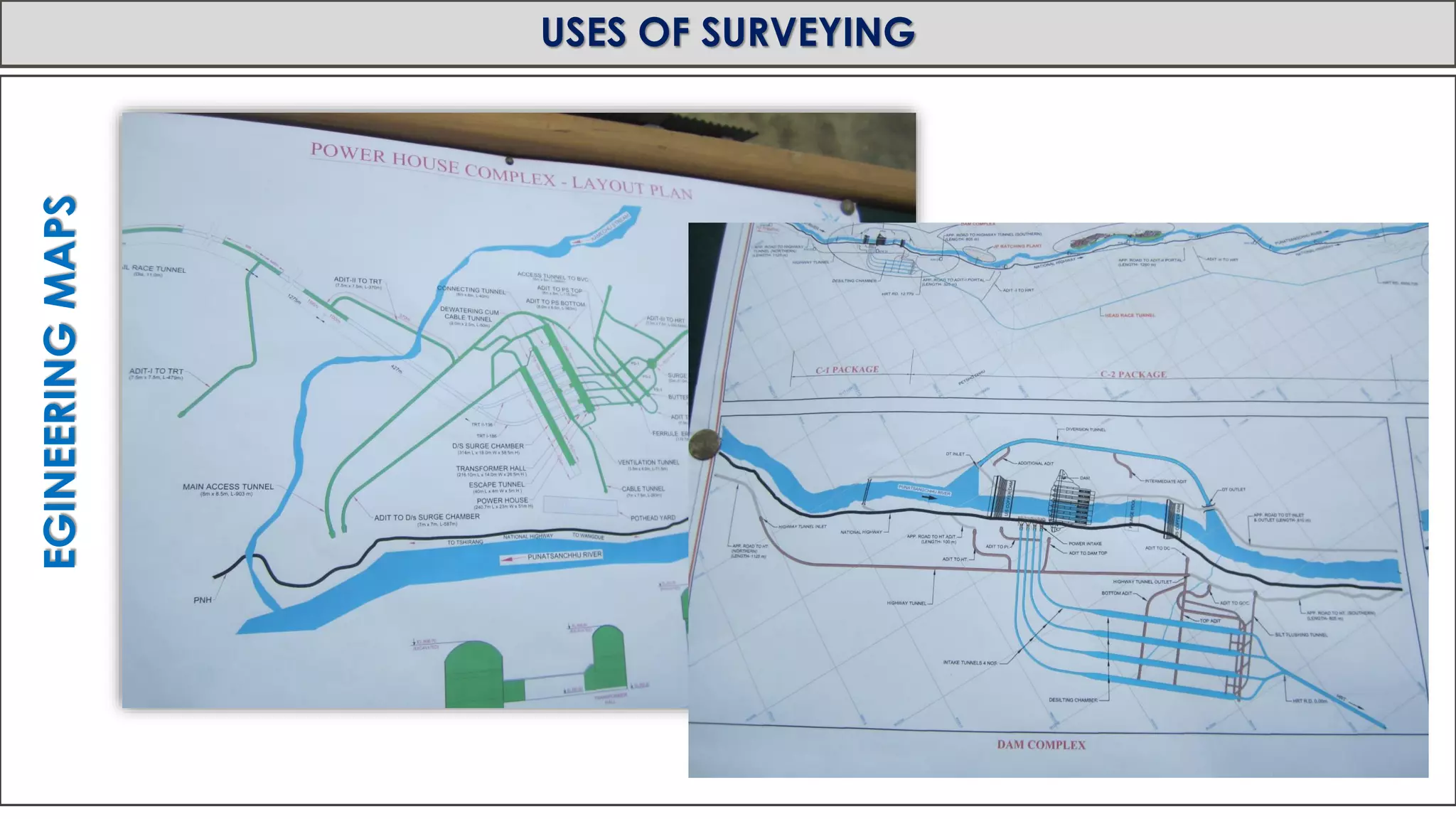
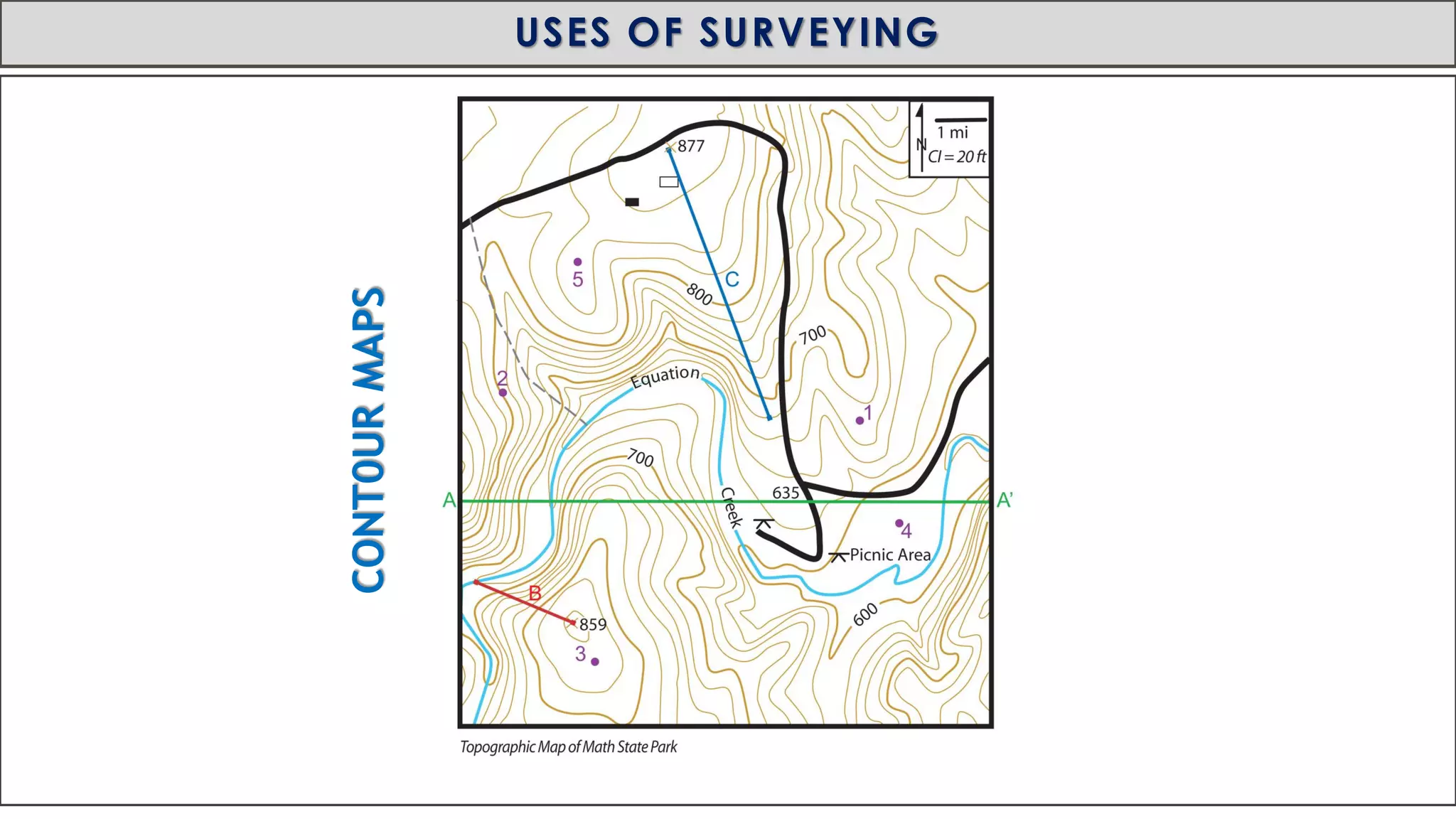
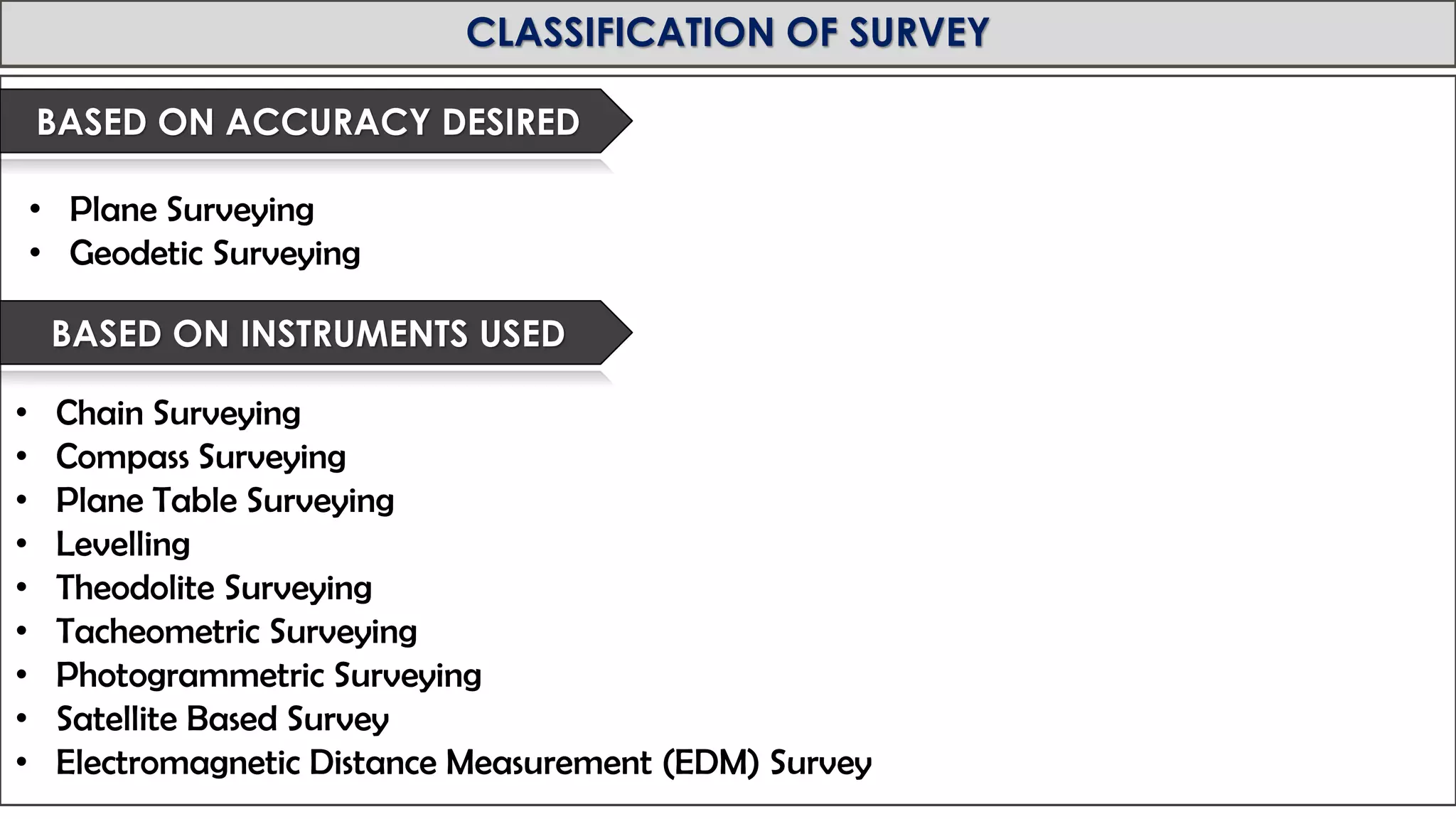
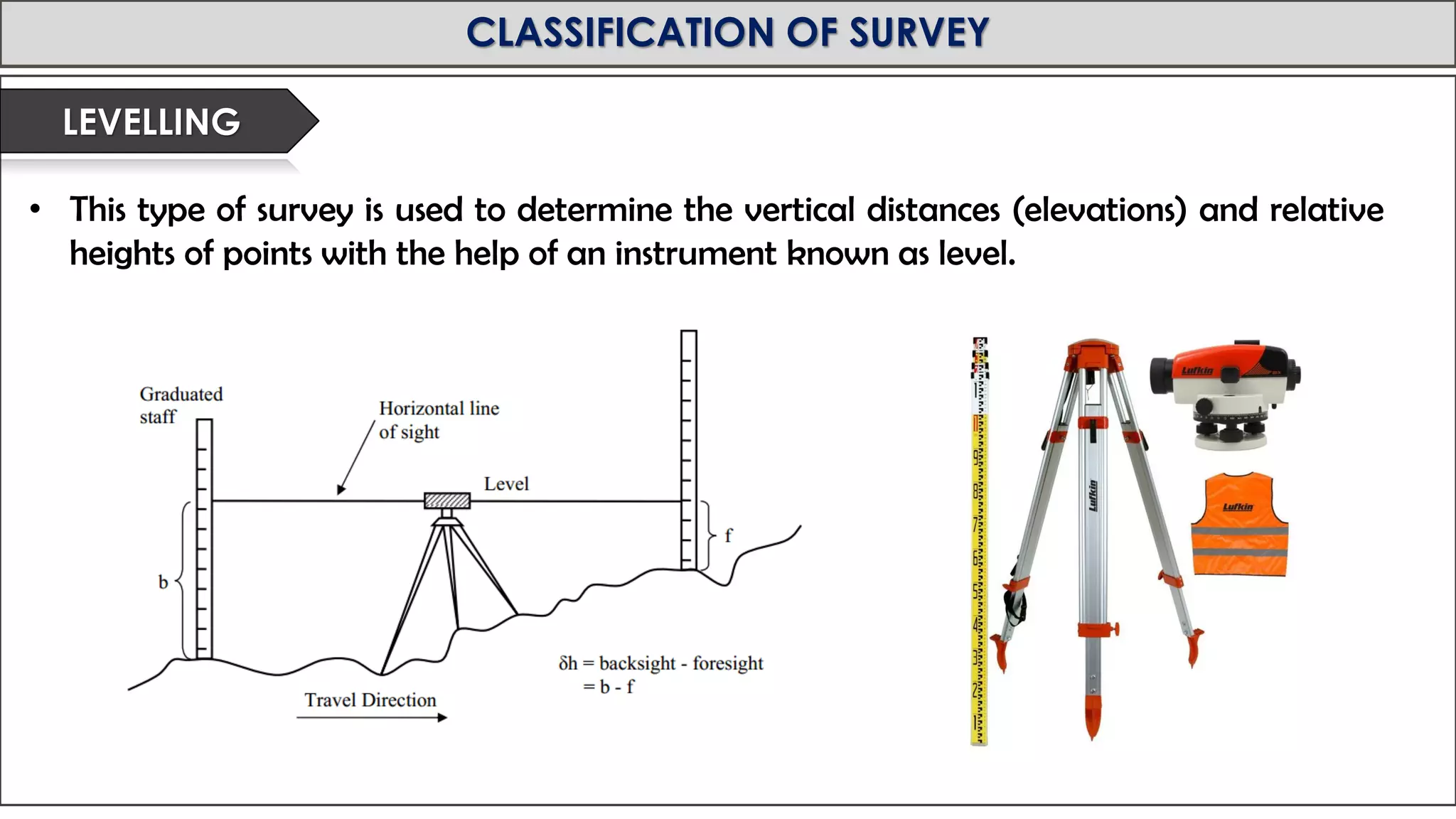
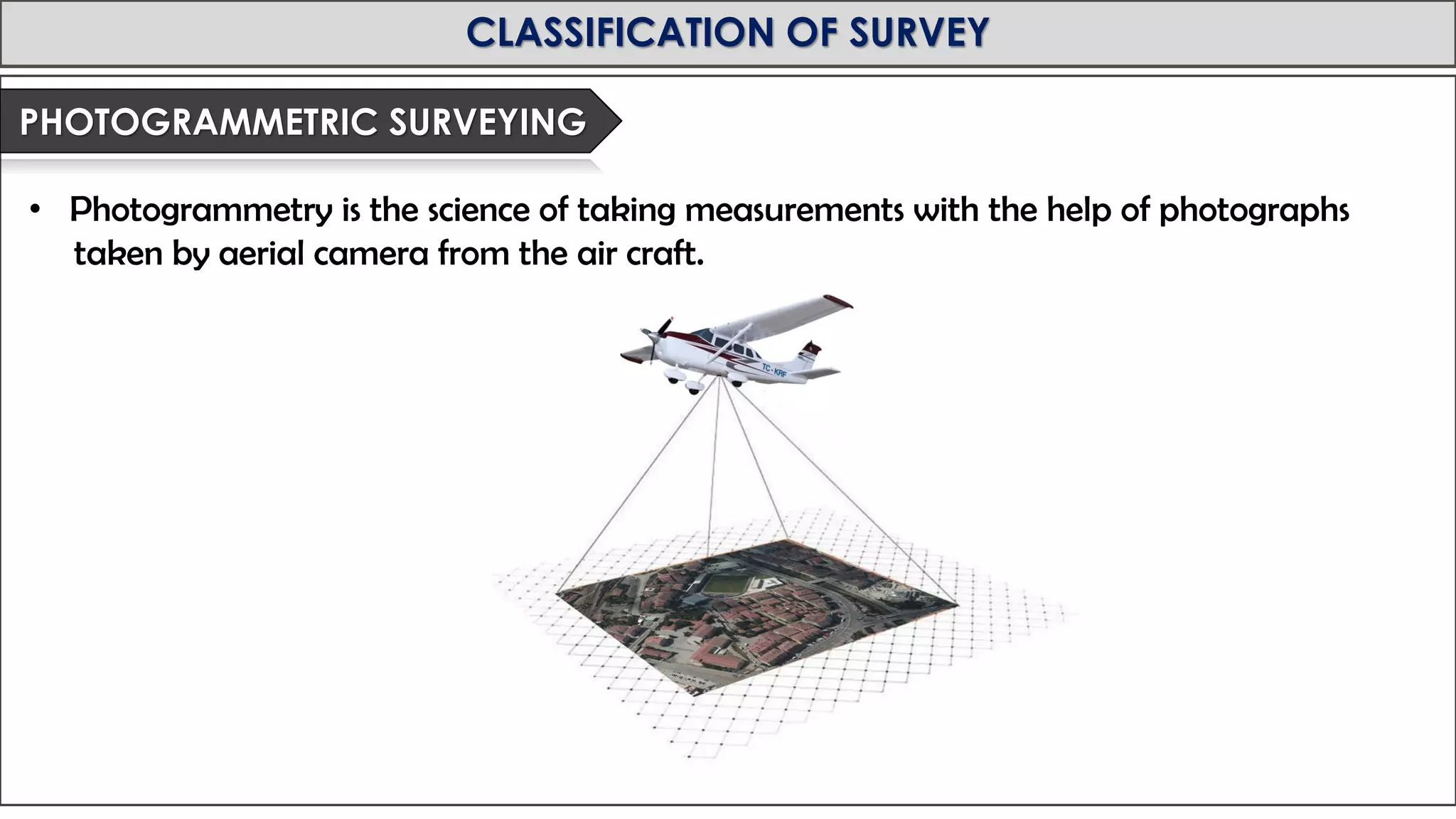
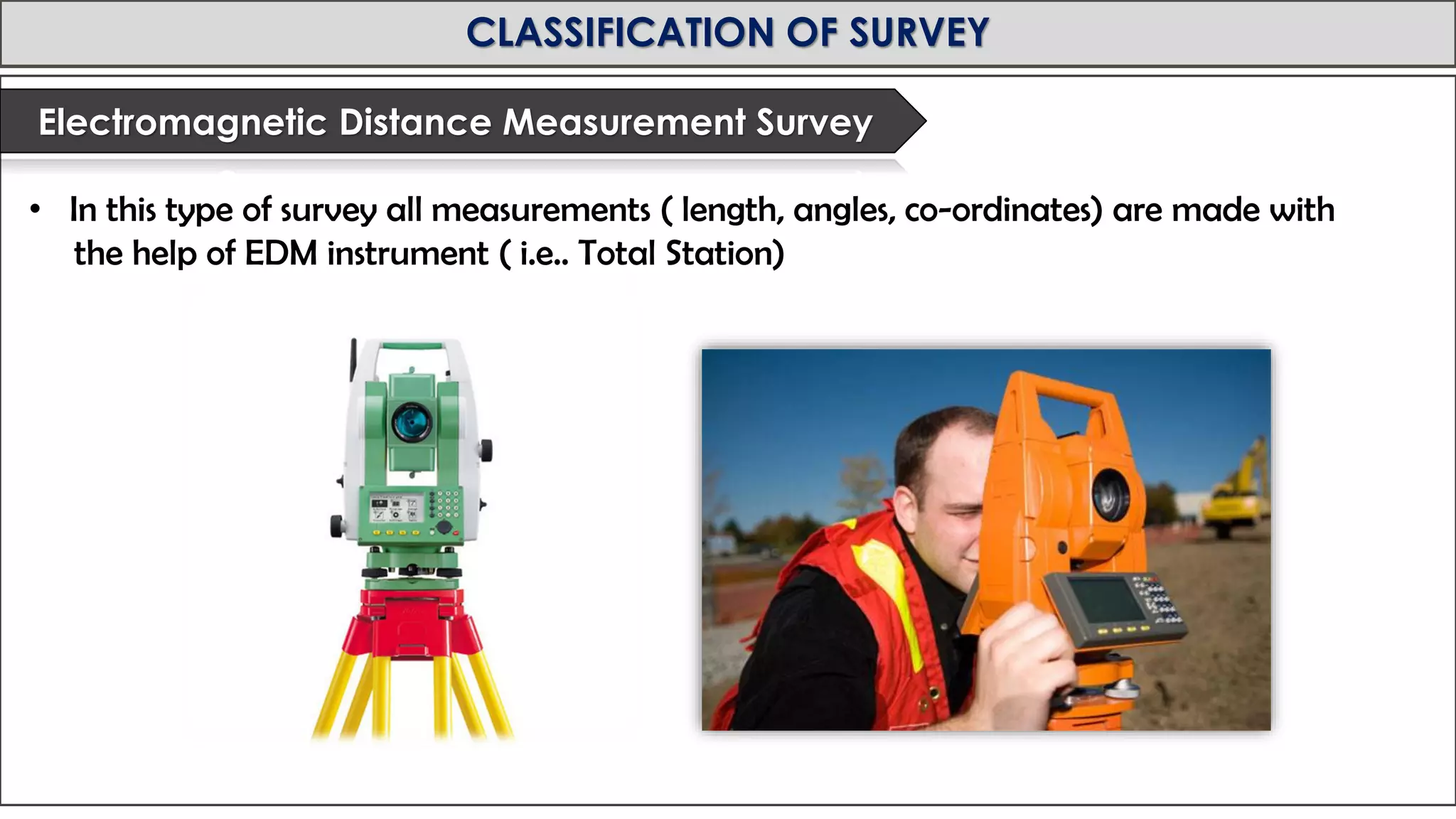
This document provides an overview of surveying from the Royal University of Bhutan. It defines surveying and its objectives, which include preparing maps and showing natural and man-made features. It also discusses the different types of surveying classified by accuracy, instruments used, methods, purpose, nature of field, and essential definitions. The primary divisions are plane surveying which ignores earth's curvature, and geodetic surveying which considers curvature over large areas.