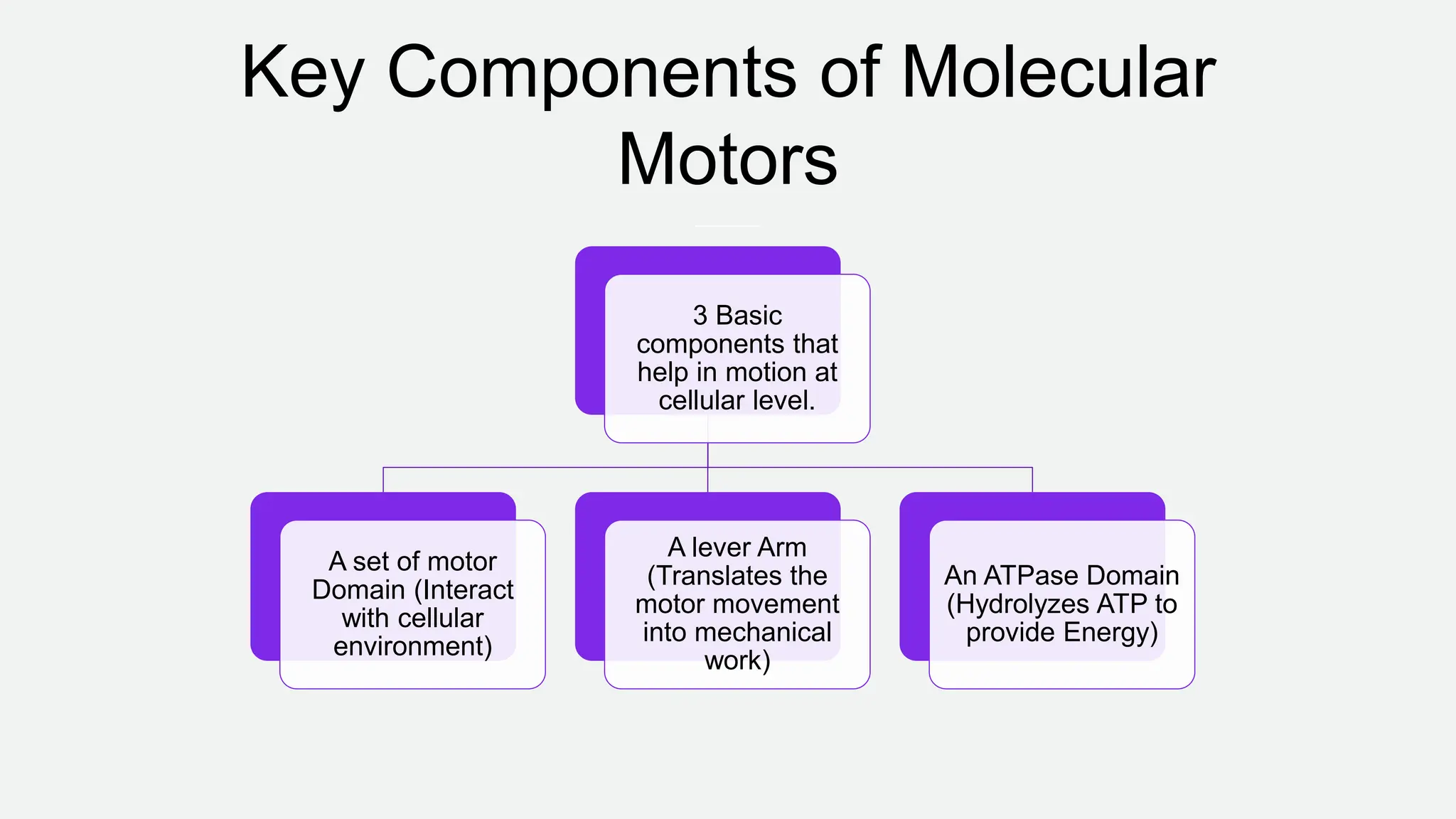
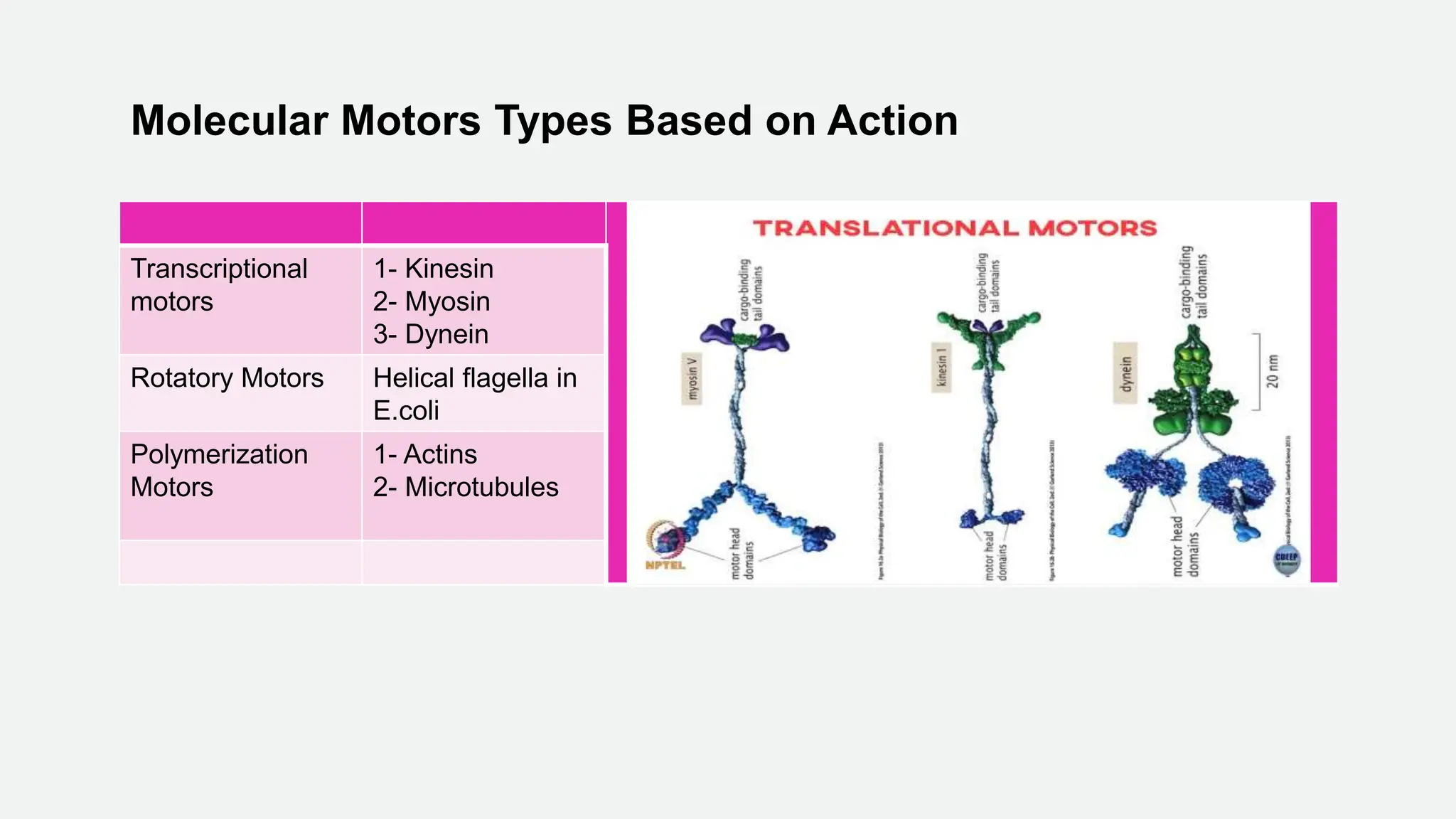
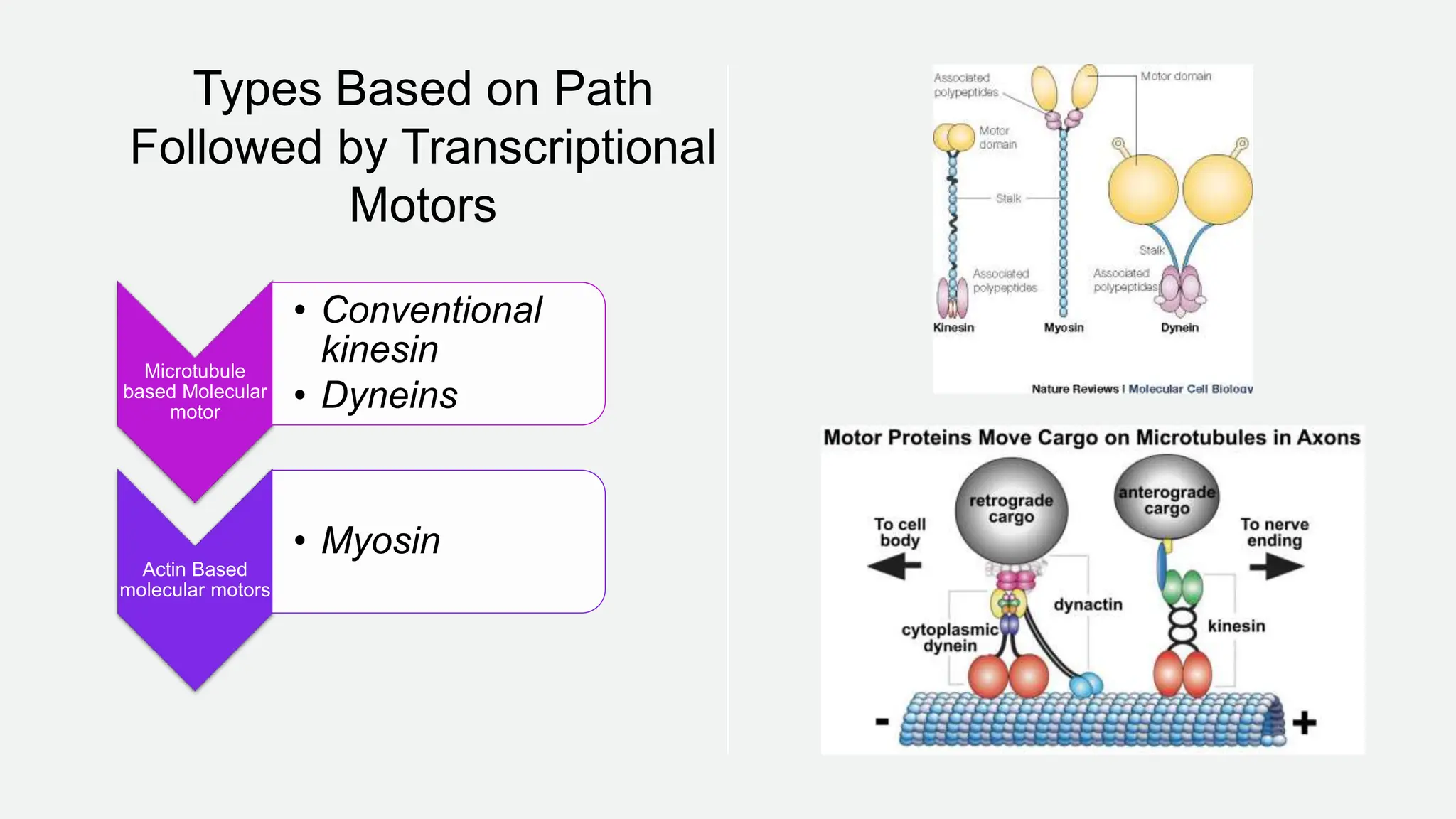
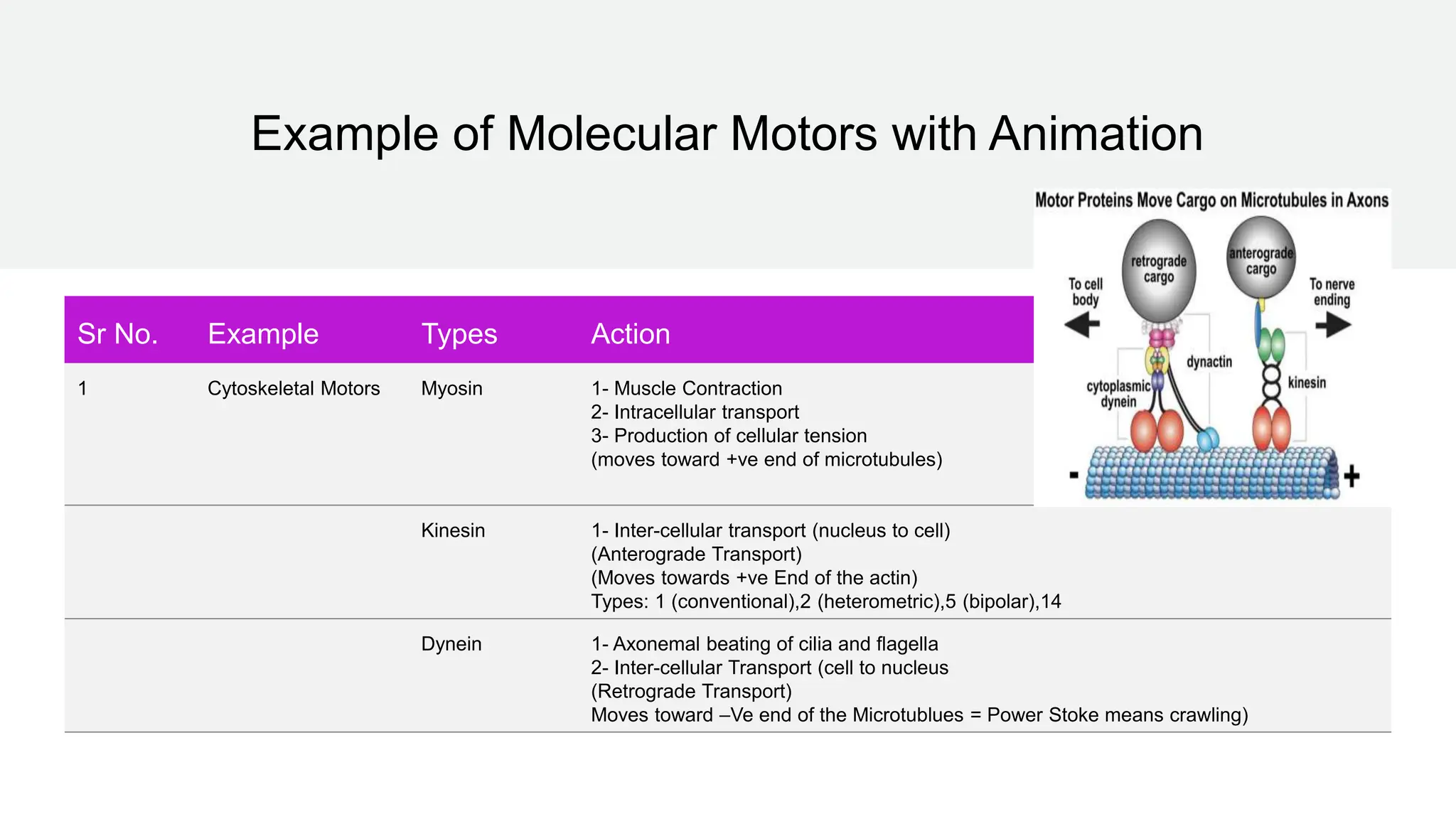
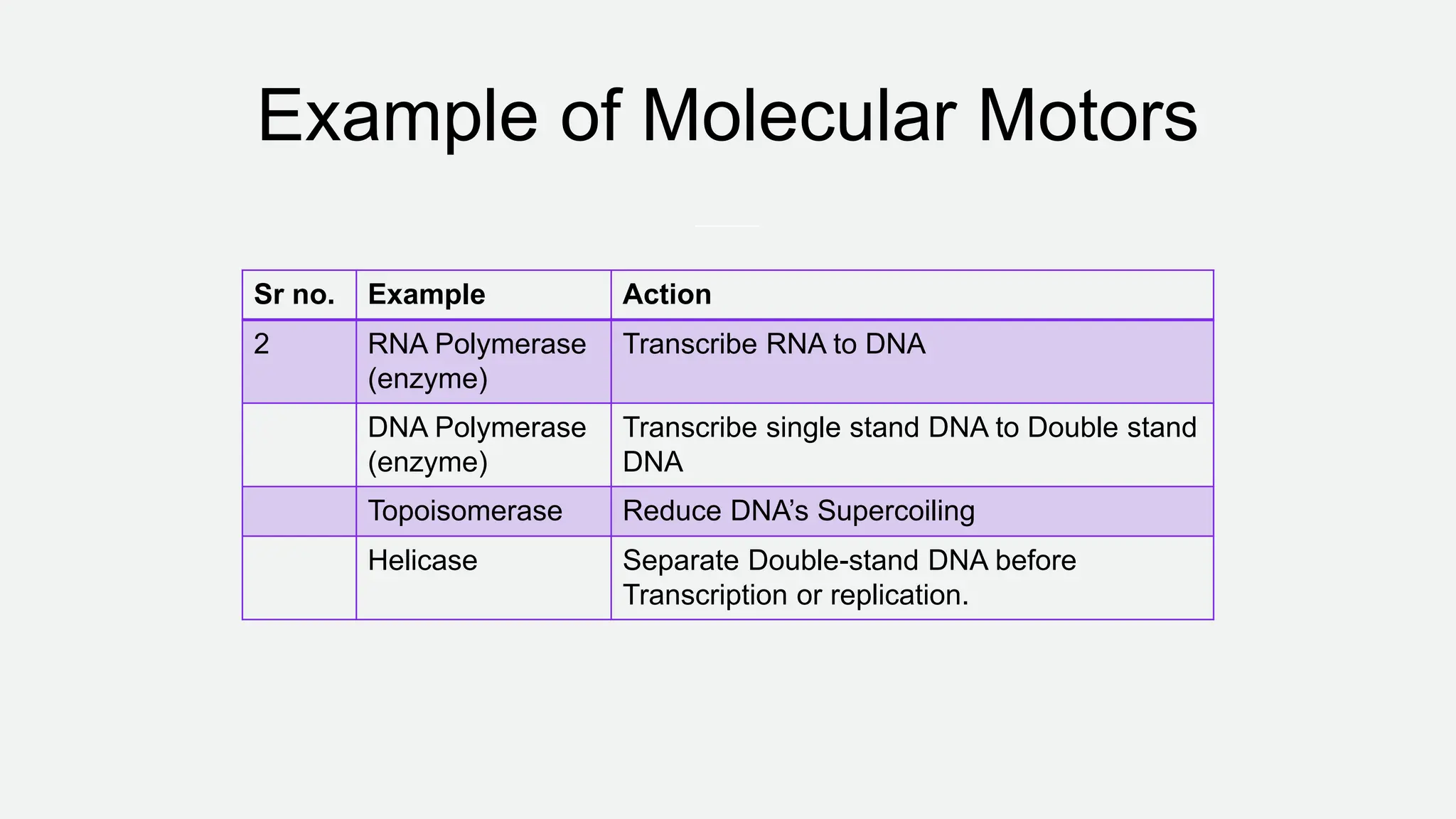
Molecular motors are natural or artificial machines that convert chemical energy to mechanical work, essential for movement in living organisms. They consist of a motor domain, a lever arm, and an ATPase domain, with examples including kinesin, myosin, and dynein for transport along microtubules and actin filaments. Techniques to study these motors include single molecule fluorescence microscopy and atomic force microscopy, while their activity is regulated by phosphorylation and binding of regulatory proteins.