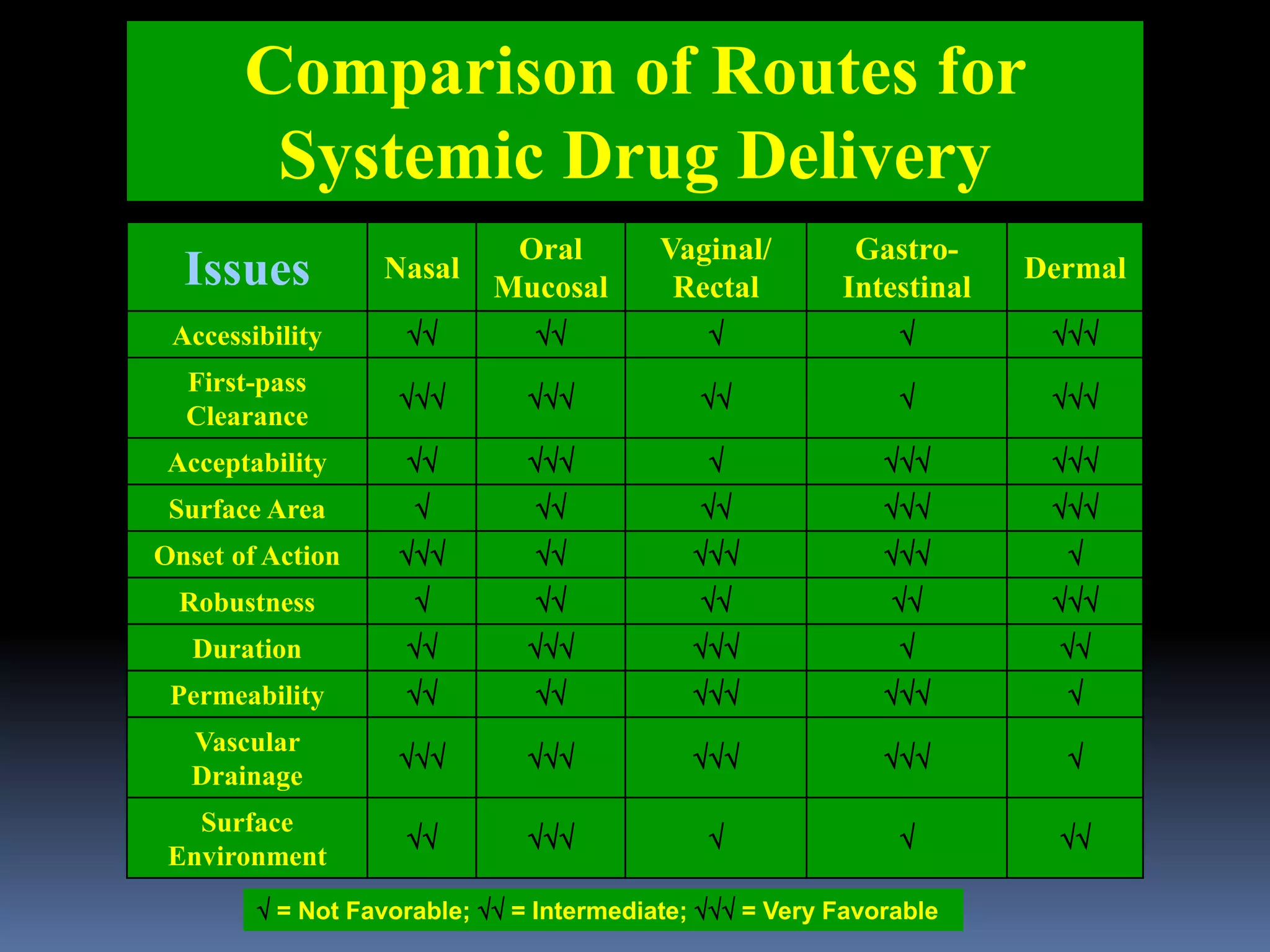
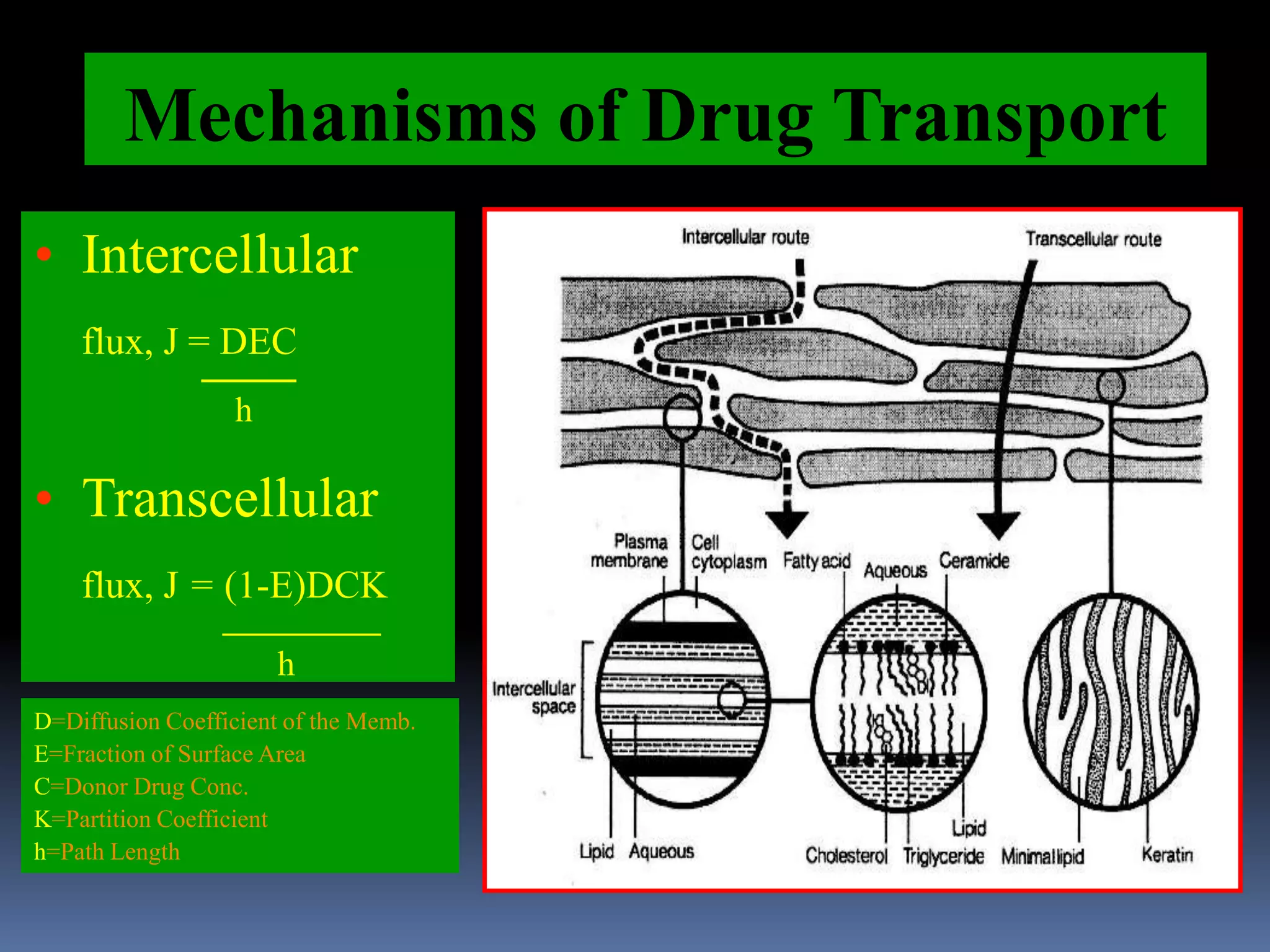
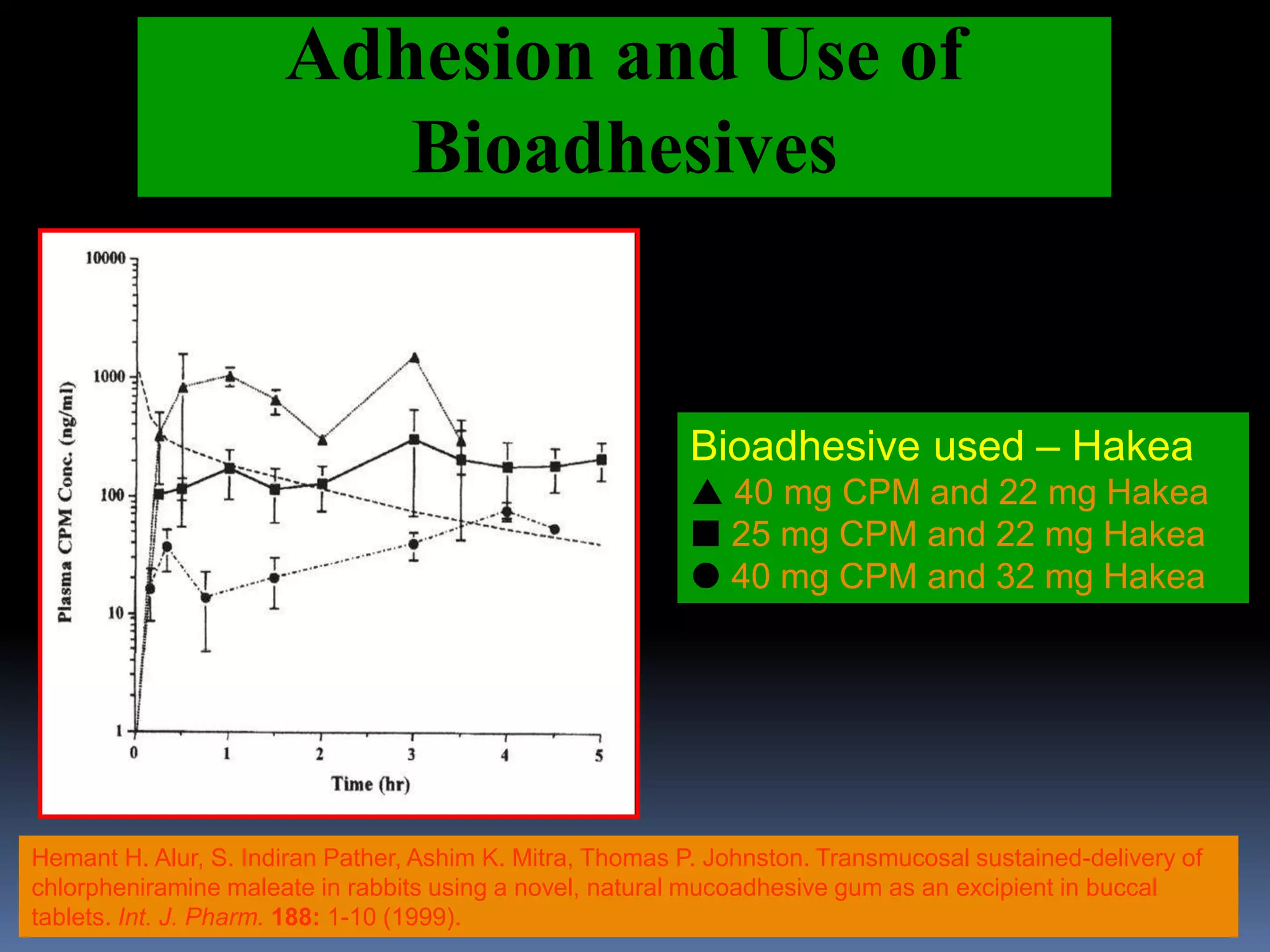
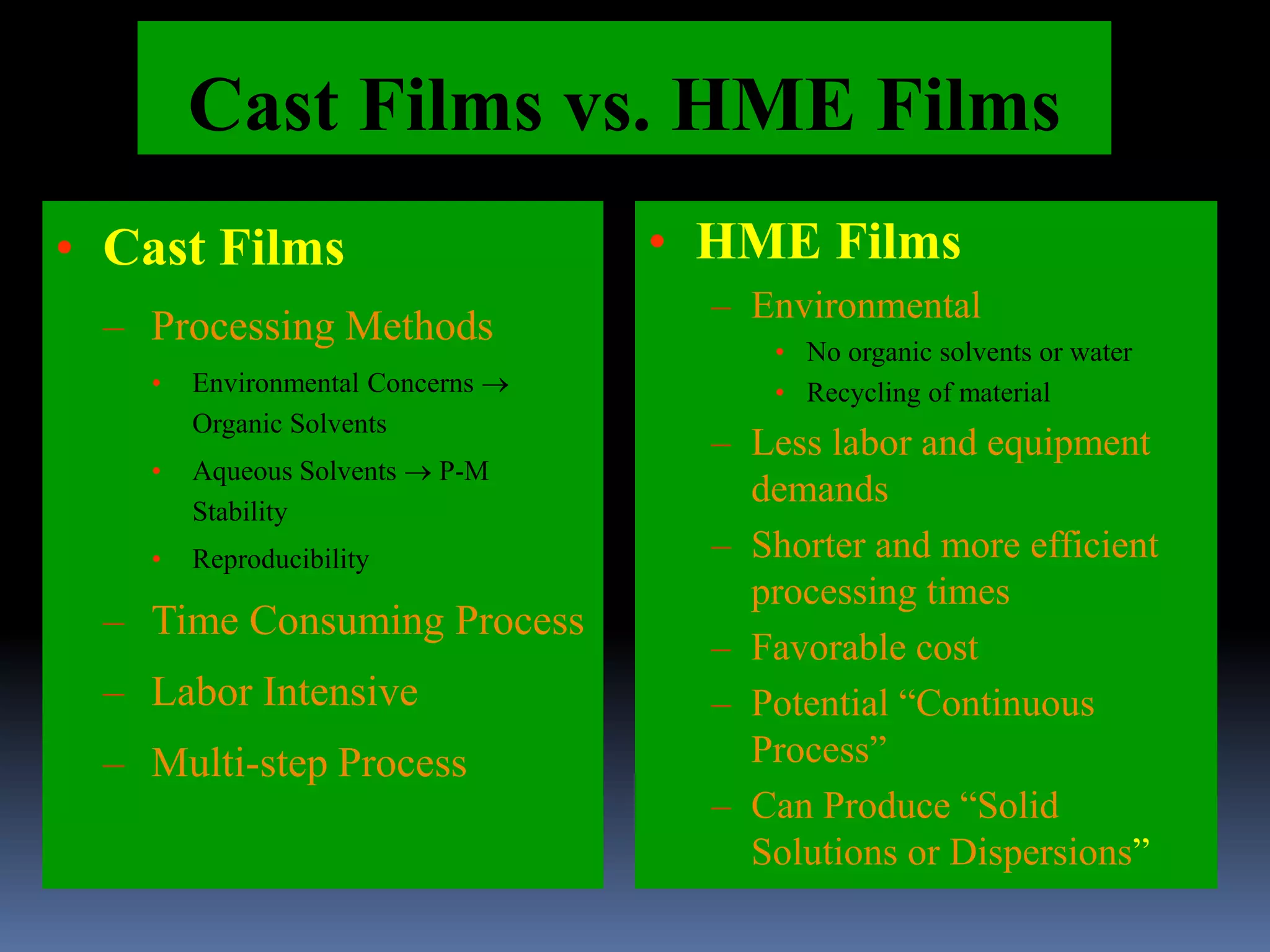
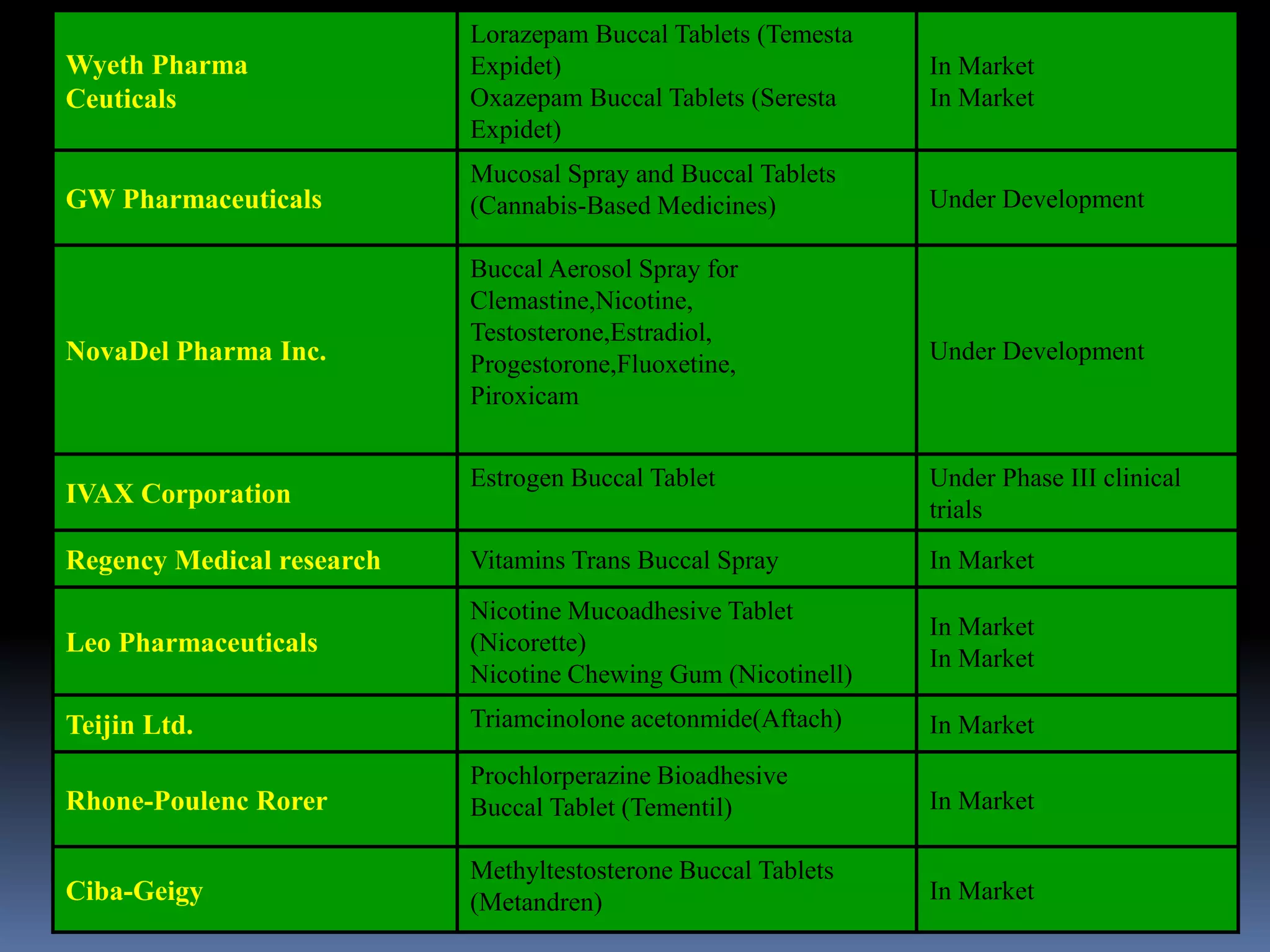
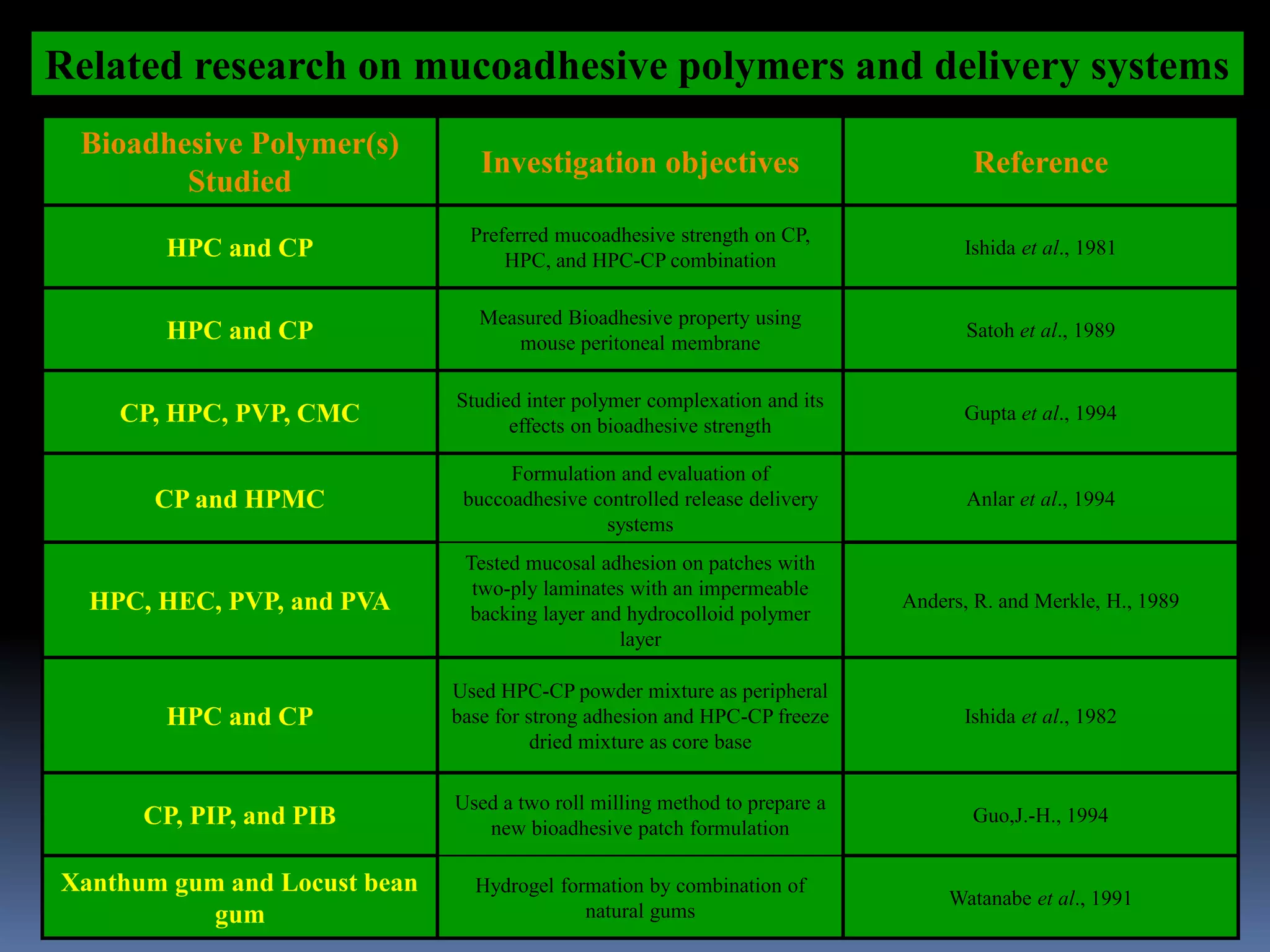
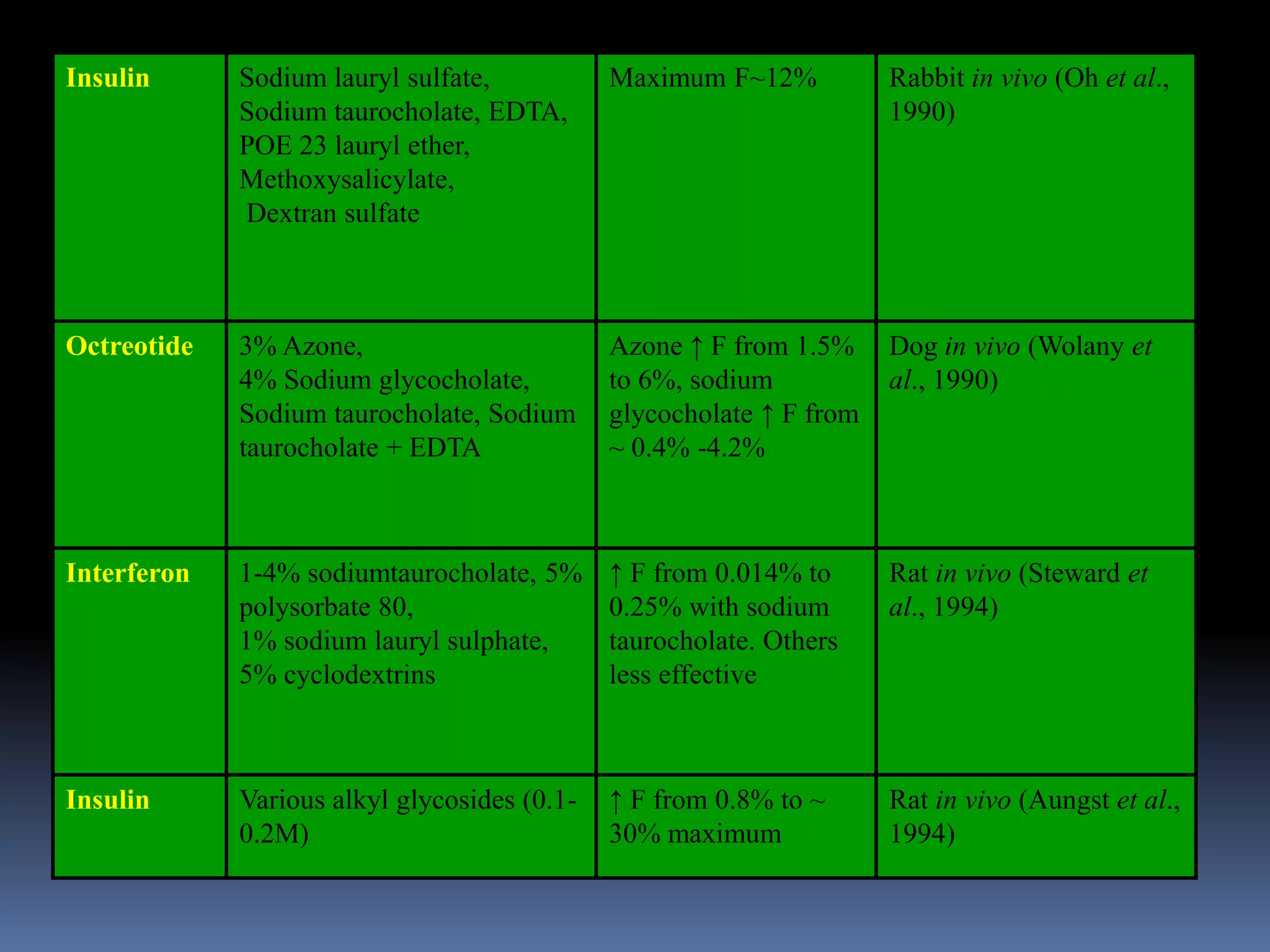
This document discusses trans mucosal drug delivery systems. It begins by comparing traditional drug delivery routes like oral and parenteral and their limitations. It then introduces trans mucosal delivery as an alternative that avoids first pass metabolism and provides controlled release. The document discusses the anatomy and characteristics of different mucosal sites. It also examines factors that influence trans mucosal delivery such as drug properties, biological factors, and formulation techniques. Finally, it reviews various trans mucosal delivery devices, methods for optimizing formulations, and quality control testing.