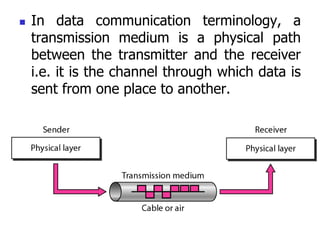
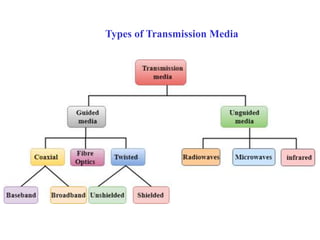
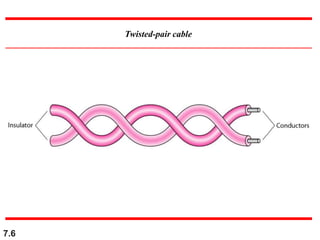
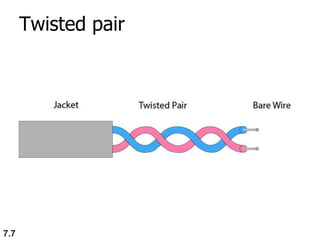
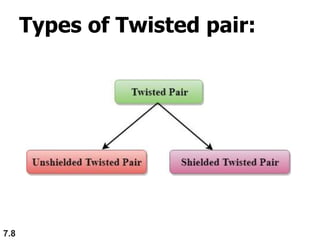
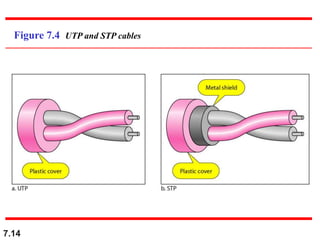
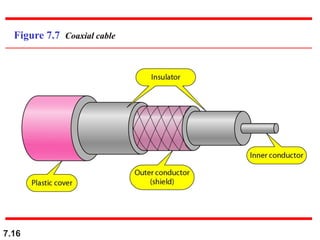
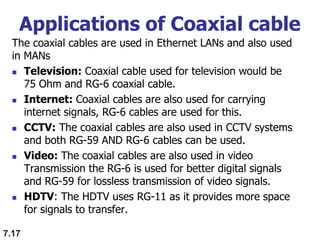
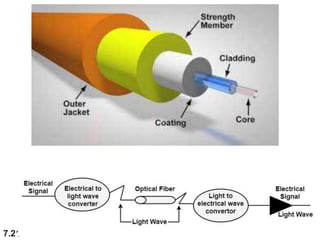
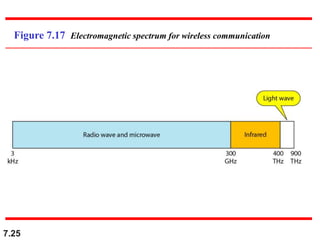
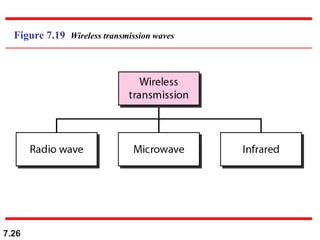
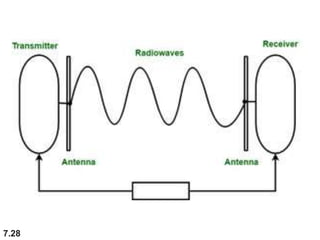
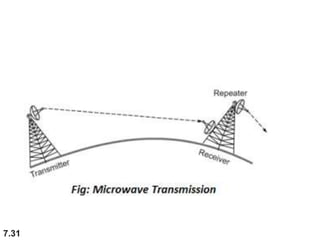
The document discusses various types of transmission media used in data communication, including guided media (like twisted-pair, coaxial, and fiber-optic cables) and unguided media (such as wireless transmission). It outlines the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of each type, highlighting the features such as cost, ease of installation, and applications for different cable types. Additionally, the document explains the functioning of wireless transmission, including radio waves, microwaves, and infrared signals.