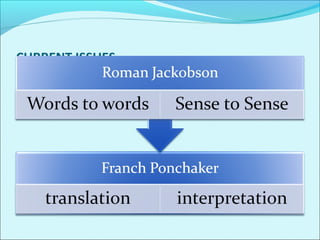
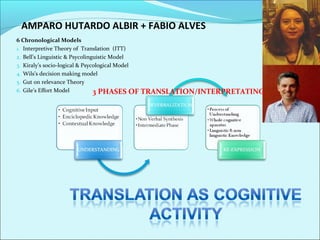
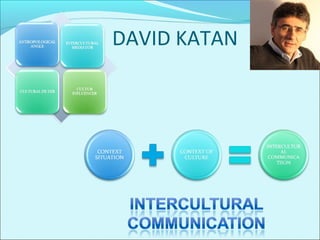
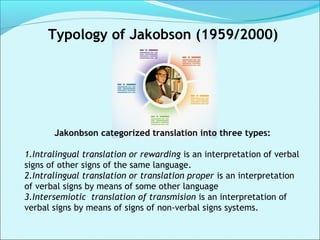
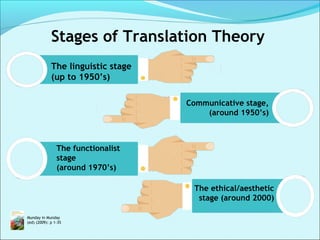
This document discusses the history and theories of translation. It summarizes several key theorists and models of translation. Jakobson categorized translation into three types: intralingual translation (within a language), interlingual translation (between languages), and intersemiotic translation (across sign systems). The document also outlines the stages in the development of translation theory from the linguistic stage to the current ethical/aesthetic stage. Finally, it discusses various approaches to translation based on prioritizing the source language or target language, such as word-for-word translation or communicative translation.