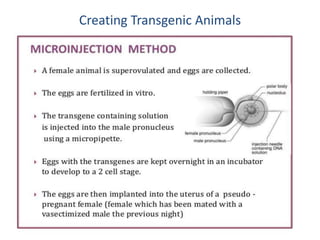
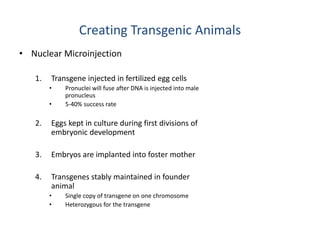
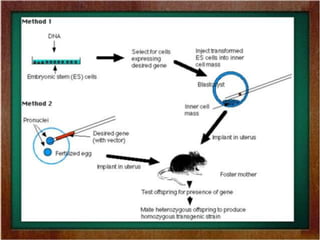
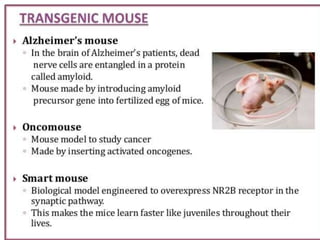
There are two main methods for creating transgenic animals: nuclear microinjection and using embryonic stem cells. Nuclear microinjection involves injecting a transgene into a fertilized egg before the pronuclei fuse, allowing for around a 5-40% success rate. Embryonic stem cells are derived from the blastocyst and can be engineered with a transgene before being inserted into an early embryo, resulting in a genetic chimera with some transgenic tissues. Retroviruses can also be used to infect embryonic stem cells and integrate a transgene into the genome.