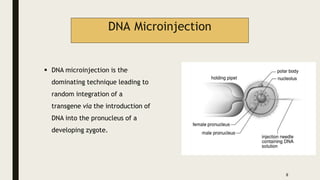
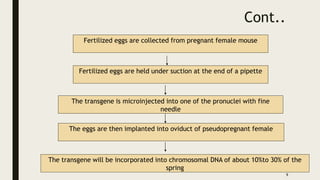
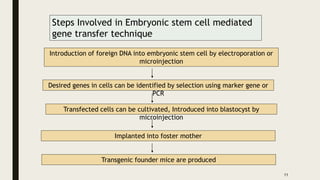
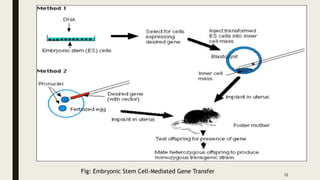
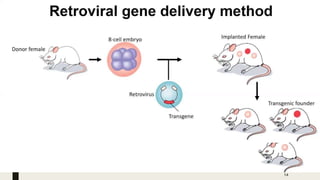
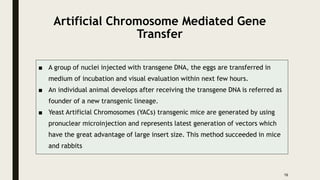
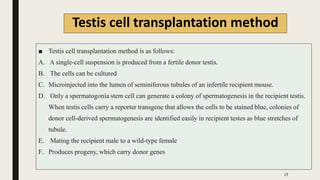
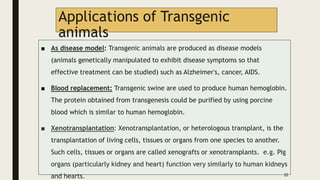
Transgenic animals are produced through several methods: (1) DNA microinjection involves injecting DNA into the pronucleus of a zygote, (2) Embryonic stem cell mediated gene transfer inserts DNA into embryonic stem cells which are then implanted into a host, (3) Retroviruses can introduce genes into germline stem cells. Transgenic animals are detected using techniques like PCR and dot blot hybridization. They are useful as disease models, for producing pharmaceutical proteins, and improving agricultural products. Examples include glowing mice carrying green fluorescent protein and faster growing salmon with added growth genes.