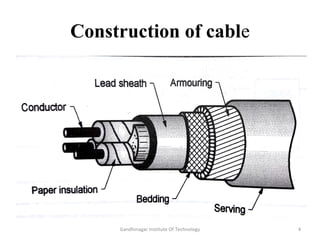
The document discusses the construction of underground cables. It describes the various parts of an underground cable including conductors, insulation, metallic sheath, bedding, armoring, and serving. It explains the purpose and materials used for each part. Common insulating materials like rubber, impregnated paper, PVC, and XLPE are also explained. Underground cables have advantages like better appearance, lower maintenance costs and reduced faults compared to overhead cables, but higher installation costs.