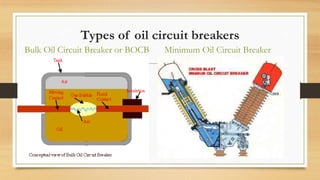
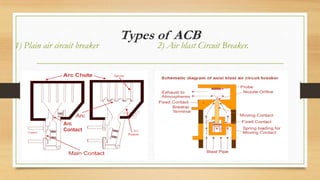
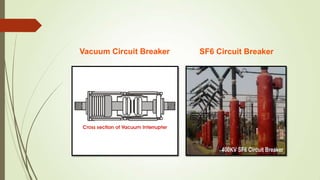
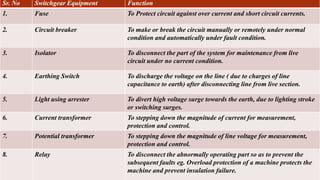
Switchgear and protection systems play a vital role in modern power systems. Switchgear includes all switching devices associated with power system protection, control, metering and regulation. The main switching device is the circuit breaker. Circuit breakers can interrupt faults such as single line-to-ground faults, line-to-line faults, double line-to-ground faults, open circuit faults, and three phase faults. Circuit breakers use arc interruption to break current flow during opening of contacts. Common types of circuit breakers include oil, air, SF6, and vacuum circuit breakers. Switchgear equipment like fuses, circuit breakers, isolators, earthing switches, and current/potential transformers serve protection, control