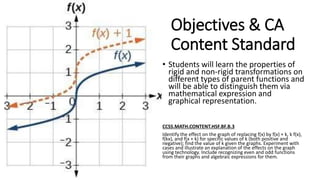
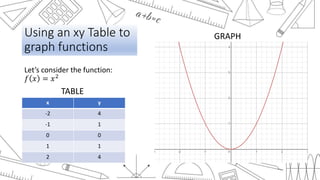
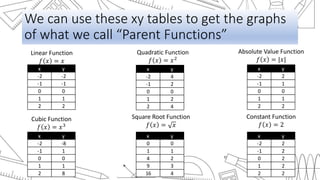
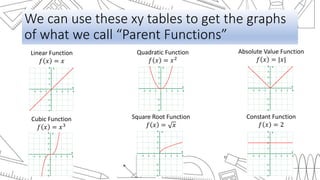
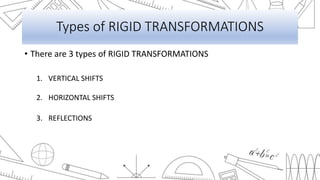
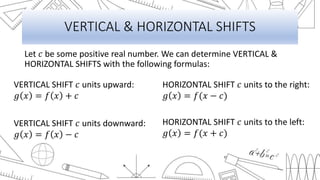
This document discusses transformations of functions. It begins by introducing common parent functions like linear, quadratic, absolute value, cubic and square root functions using xy-tables and graphs. It then demonstrates how adding or subtracting values like 1, 5, or 2 to a quadratic function f(x)=x^2 results in a rigid transformation that shifts the graph up, down, left or right but maintains the same basic shape. The document defines rigid transformations as those that only change the position of the graph and lists the three types as vertical shifts, horizontal shifts, and reflections, providing formulas for shifting graphs vertically and horizontally.